THE USING OF RANK-KHILSH TUBE FOR HEATING
Kolosovskii S.V., Dolzhikova E.V, Piatishkin
G.G.
Lately at the deficit of natural gas as the source of heating and hot
water-supply heat-generators of different construction are used. Very often by
the name (heat-generator of cavitation type, heat-generator hydraulic,
hydrodynamic heater, vortical system of heating, heat-generator of stream type,
cavitational-rotor heat-generator and etc.) it is difficult to suppose their
works about principle.
Most such devices use the effect of vertical tube. The incoming stream
of liquid or gas due to the orientation in space acquires rotatory motion and
at expansion divides into two streams. The first is sent into a circular crack,
continuing initial forward motion, and second - returns, moving to meet to the
first in the central area of tube, and goes out through a diaphragm.
It is possible to assume that molecules of environments, having larger
kinetic energy, will stronger carry with the revolved stream and centrifugal
force to deviate on periphery of tube, forming an area with higher temperature.
The «slow» molecules of environment accumulate in a center, providing creation
of stream with lower temperature. Varying the width of crack, it is possible to
regulate charges and temperatures of cold and hot streams.
In the mode of heating the exit of cold stream from a vortical tube is
blocked, with hope about constancy of output temperature of hot stream.
It is possible to take to dignities of vehicles of vortical type:
- the simplicity of construction - they have not a single locomotive
part;
- the combination in itself two devices: refrigerator and heater;
- the possibility of implementation of vortical tube of any power and
any size - from a few meters to a few millimeters.
In this work authors bring an analysis of results of experimental
researches of vortical heat-generator at heating the working area by it.
Overall sizes of plant – 1600 x 650 x
Voltage of electric network - 380 W, power of electric motor - 45 kilowatt.
The density of heat-carrying agent made 1 kg/l, pressure of 7 - 8 atm.
Mass of warmed-up heat-carrying agent is
The temperature of surrounding air was 291 K.
A vortical tube in plant works with the closed cold output.
2 experiments were made with the different initial temperatures of
liquid. Time of carrying out every test - 2,5 hour. Measurements of temperatures
of liquid were made with an interval in 30 minutes.
The temperatures of heated heat-carrying agent in the vortical tube - tn and liquids in the boiler - tb
are shown in the picture 1.
Consumable energy was calculated in times of carrying the test:
Qgen = Q1 + Q2 + Q3, watt-seconds,
where: Q1 is an amount of heat, used on heating of water;
Q2 is an amount of heat, used on heating of metal of construction;
Q3 - heat loss of the system in
an environment.
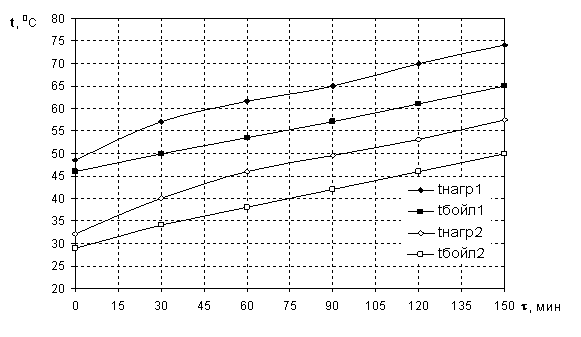
Fig. 1 - Values of temperatures of heat-carrying agent during an
experiment.
Heat, used on heating the water, which is found on a formula:
Q1 = m*(t2 -t1)*c1,
where: m – the mass of heat-carrying agent, kg;
c1 - a specific heat capacity of heat-carrying agent, joule/(kg*K);
dt = t2 - t1 is a temperature of
heat-carrying agent at the beginning and end of tests, K.
Heat, used on heating of setting and pipelines:
Q2 = (m1+ m2+m3)*(t2 -t1)*c2,
where: m1,m2,m3 are the masses of electro-pump, heat-carrying agent and
pipelines;
c2 - a specific heat capacity of steal, joule/(kg*K).
Heat loss into the environment are found with a formula:
Q3 = A*dt *F*v,
where F is the area of the uninsulated surface
of the system, m2;
A - is a coefficient of heat emission out of the
surface of setting an environment, watt/(m2*K);
v - is time of
carrying out the test, sec.
Efficiency of setting is expected in the total:
n = (Qgen/ Q cons)*100% =
92%.
The explored heater allows to heat a liquid directly
at its motion, that provides an ecological cleanness, eliminates the change of
high-quality composition of a liquid, the appearance of crust and other unfavourable phenomena in the heated liquid.
This plant for making the heat, works out of electric
power. It appeared more effective, than ordinary, working on the use of natural
gas. In spite of relative cheapness of natural gas by comparison to
electricity, the charges, connected with its serve and exploitation of gas
equipment, in a number of cases result in unprofitableness
of its use. Therefore in this case economically useful became the use of
individual source of hot water-supply, built on the base of vortical tube
appeared expedient.