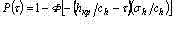
Biography Electronic library Refs.s on the topic Report on a search Individual task
Reliability of functioning of technological systems in a significant measure is defined by reliability of the cutting tool. The increase of the cutting tool reliability is a major reserve of growth of efficiency of the modern manufacture. The successful decision of this task requires creation of the complex system guarantee of the quality parameters. Alongside with search of the new technical decisions on perfection of the tool it is required development of the rules of its rational exploitation. In the present work it is developed the technique guarantee of the cutting tool reliability in the different conditions of the exploitation. This technique is realised for the modular cutters and the face mills with mechanical fastening of the cemented carbide alloy plates intended for the draft processing by cutting. One of major tasks of the reliability theory is the research of failures technical systems. The most adverse kind of failure is the destruction of the tool resulting in off-schedule equipment downtimes and the raised charge of a tool material. In this connection the task of forecasting and decrease of probability of the tool destruction in various conditions of operation is rather urgent. In represented work the technique of a quantitative estimation of probability of the cutting tool destruction on parity of levels of its durability and working loading is developed and checked experimentally. This technique allows to predict the basic parameters of the tool reliability in various conditions of operation and to improve a choice of rational conditions of cutting tool operation for raising reliability of technological systems.
The theoretical and experimental researches of reliability of the modular cutting tool with mechanical fastening of the cemented carbide alloy plates received on the basis of the complex approach to the analysis of stochastic laws of its functioning, optimisation of the basic parameters of reliability and their operational maintenance.
The theoretical investigations of the cutting tool reliability are used for decision of the following tasks:
- creation the probability model of the cutting tool failure with accounting the strength and loading;
- creation the structure model of the cutting tool reliability as the system of the construction elements;
- creation the parametrical model of function reliability of the cutting tool at the different exploitation conditions.
The experimental investigations of the cutting tool reliability are used for the substantiation of the cutting tool failure kinds and of the reliability parameter distribution law
The input dates for formation of probabilistic models of failures are established ground of analysis of stochastic processes of a cutting tool edge deterioration and destruction. The main assumptions at mining probabilistic model of the tool failures in connection with achievement of marginal wearing the set of implementations of wearing on a flank surface is characterized by a normal distribution law at any moment of time τi with parameters: h(τi) - mean values of wearing in the moment τi and standard deviation σh . The time history of average values of wearing is described by a function h(τ), which one with adequate accuracy within the limits of a zone of the natural wear can be adopted linear by constant speed of deterioration ñh: h(τ) = h + ñh τ. The value of yardstick of bluntness hêð is received pursuant to the referential - normative documentation. In this case stability up to achievement of marginal wearing of a cutting blade is subject to a normal distribution law. The probability of non-failure in a given instant ? can be determined as follows:
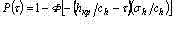
where Ô(z) - normalized function Laplass; parameters of the law: the mean term of stability ÒÈ = hêð*ñh and standard deviation σÒ = σh/ñh. The main assumptions at mining probabilistic models of the tool failures in connection with destruction: load which is operational on a cutting tool edge characterized by cutting force Ðz(τ) and its strength characterized by marginal force Ðèí are fixed random variables with known distribution laws at any moment of time τi. For a normal distribution law of strength and load with parameters - average values of forces in an instant τi Ðèí: and Ðz(τi) and standard deviation ?Ð and linear time history of average values of of cutting force, distribution law of actual stability before destruction also normal. The probability of non-failure in a given instant t can be determined as follows:
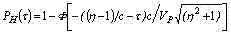
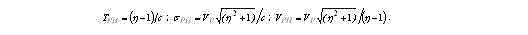
The actual mean term of stability before destruction is interdependent to stability up to wearing as follows:
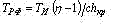
For the law Veybull of distribution of strength and load with average values of forces in an instant τi Ðèí: and Ðz (τi) with parameter of the form bï and also non-linear time history of average values of force of cutting the distribution law of actual stability before destruction represents known distribution of extreme values. In this case probability of non-failure is peer:
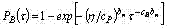
Parameter of the form of the obtained distribution of extreme values - bý = ñ3bn. Parameter of a scale describing actual mean term of stability before destruction ÒР= (η/ñÐ)-1/Ñ3. The actual mean term of stability before destruction is connected to stability up to wearing as follows:
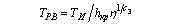
The mean term of stability before destructions observed in exploitation outgoing from a density function fÒðô(τ) of actual stability before destruction ÒÐÔ as for normal and law Veybull of distribution of strength and load is peer:
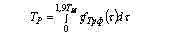
The designed probabilistic models of failures allow ground of analysis of legitimacies of a random change in time of process parameters of deterioration and destruction of the cutting tool edge to create a technique of calculation of the main parameters reliability of a modular cutting tool and also to establish intercoupling of reliability parameters with processing conditions.
In a case when a primary kind of the cutting tool failures is the achievement of marginal wearing the normative mean term of stability ÒÍ = ÒÈ is determined on known relations introduced in the referential - normative literature. Thus the dispersion of stability is unsignificant and factor of its variation VÍ does not exceed 0,33. If there is the cutting tool failures bound with its destruction the mean term of stability Ò in matching with normative ÒÍ is reduced and the coefficient of variation VÒ is increased :
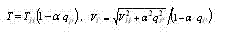
Âwhere qÐ - probability of destruction of the tool, qÈ - probability of deterioration, and (qÐ + qÈ) = 1; a - factor which is taking into account a ratio of the mean term of stability up to destruction ÒÐ with normative ÒÍ: . In the present activity as the main parameter of the cutting tool reliability along with the mean term of stability the gamma - interest period of stability - time in cut is esteemed during which one the tool does not reach failure with given probability γ expressed in percentage. For the most widespread law Veybull at the analysis of stability of a cutting tool gamma - interest period of stability or the stability with given probability Tγ is determined as follows:

where a and b is parameters of a scale and form of a distribution law:
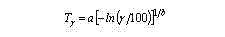
It is ground designed before probabilistic models of the cutting tool failures the probability of destruction of a cutting blade to an instant τ = 1,9ÒÍ – termination of the tool term of stability with allowance for its dispersions is established at two versions of distribution laws of strength and load - normal qÐÍ and Veybull qÐÂ:
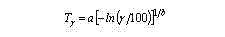
where 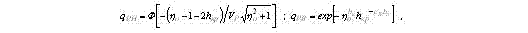 - margin of safety instituted depending on relative parameters of cutting modes, describing an alteration of cutting speed, feed and cutting depth in matching with values of these parameters adopted for base: : vo = v/vá, so = s/sá, to = t/t; xð, yð, n - parameters describing a degree of influencing of depth, feed and speed on the cutting force.
The change of cutting modes results to simultaneous change of all indicated characteristics including normative mean term of stability ÒÍ. In spent researches the constancy ÒÍ, together with factor with, is provided with updating of a cutting speed pursuant to selected values of a cutting depth and feed:
- margin of safety instituted depending on relative parameters of cutting modes, describing an alteration of cutting speed, feed and cutting depth in matching with values of these parameters adopted for base: : vo = v/vá, so = s/sá, to = t/t; xð, yð, n - parameters describing a degree of influencing of depth, feed and speed on the cutting force.
The change of cutting modes results to simultaneous change of all indicated characteristics including normative mean term of stability ÒÍ. In spent researches the constancy ÒÍ, together with factor with, is provided with updating of a cutting speed pursuant to selected values of a cutting depth and feed:
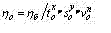
where - xv, yv – parameters describing a degree of influencing of depth and feed on a cutting speed instituted on the operation conditions. In this case margin of safety depending on a cutting depth and feed is peer:
The introduced relations allow to establishing influencing parameters of processing on gamma - percentage stability of the tool with allowance for probabilities of its destruction. The factor describing a ratio of given gamma - percentage stability of a cutting tool with normative can be counted under the formula:
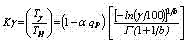
Introduced for γ = 70 % the two-parameter graph of a factor Êγ from relative parameters of a cutting depth to and feed so allows on known treatment schedules to forecast a gamma - percentage level of stability of a cutting tool and also to establish a mode level of cutting for maintenance of mean stability with any given probability level γ.
Thus the designed technique with allowance for of parameters of stochastic processes of deterioration and destruction of a cutting edge tool allows to execute forecasting of the mean term of stability and its dispersion in the different operation conditions, to establish nature and parameters of a stability distribution law and also to select treatment schedules ensuring demanded reliability level.
The time history of cutting force is established with allowance for wearing of cutting blade of the tool. The regularity of change of cutting force depending . The experimental relation of cutting force to wearing on a flank surface h - Ðz1(h) is obtained for following conditions: the chisel Ò5Ê10, cutting speed v = 200ì/min, feed s = 0,1ìì/rv., cutting depth t = 4ìì. The relation of cutting force to wearing can be adopted linear Ðz2(h) :
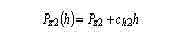
where Ðz2 = 1000Í, ñh2 = 1100Í/mm.The change of cutting force is more exact depending on wearing is described by a non-linear exponential function (chart 3):
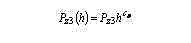
where Ðz3(h) = 2000Í, ñ3 = 0,75. With allowance for linear dependences of wearing from time are established of regularity of a time history of cutting force:

where ñ2 and ñÐ factors, equal: ñ2 = ñh2ch, ñÐ = ch CÂ, ñh= hêð/ ÒÈ.
At designing of the tool and solution of a problem of selection of new design or technological version influencing properties of a wear resistance and strength on reliability parameters in the given operation conditions estimates. At exploitation of the tool and solution of a problem of selection of rational treatment schedules influencing cutting modes on parameters of reliability of the tool estimates at a given level of properties of the tool. In a fig. 3 the charts of probability of non-failure Ð(τ) and density function of probability f(τ) for modular chisels with mechanical attachment of many-sided not sharpened back laminas are submitted. The experimental researches are executed for following conditions: Worked stock - steel 45, tool stuff - Ò5Ê10, cutting depth t = 6ìì, cutting speed v = of 114ì/mines, feed s = 0,47ìì/about. Conforming to these modes normative stability of the tool ÒÈ = 30 min Coefficients of variation VÈ = 0,3; VÐ = 0,3.A margin of safety ηá = 3. Speed of load change ñ = 1,1 hêð/ ÒÈ. The experimental parameters ÐÝ(τ), fÝ(τ) well enough coincide with idealized ÐÒ(τ), fÒ(τ) counted it is ground of normative parameters ÐÍ(τ), fÍ(τ) with allowance for destructions. Parameters for cutting modes distinguished from normative here are submitted: Ð1(τ), f1(τ) - on 10 % is lower normative; Ð2(τ), f2(τ) - on 10 % above normative.
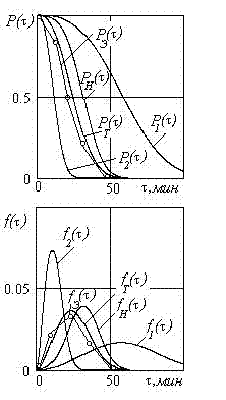
Fig 3. The charts of probability of non-failure Ð(τ) and density function of probability f(τ) for modular chisels
The developed stochastic model of he cutting tool functioning reliability establishes interrelation of the basic parameters of reliability with parameters of the tool and conditions of its operation. The created model allows to predict:- various kinds of failures of the cutting tool - destruction and wear process, and also probability of their occurrence depending on properties of the tool and working on it loading;
- basic parameters of non-failure operation and durability of the cutting tool - average period of stability and average of the periods of stability with the account of probability of destruction and wear process and also dispersion of these parameters depending on conditions of operation;
- parameters most widespread for of the cutting tool Veibull law of distribution of parameters of non-failure operation and durability - period of stability and number of the periods of stability in various conditions of operation;
- basic parameters of non-failure operation and durability with the given guaranteed level of probability - gamma-percentage period of stability and gamma-percentage number of the periods of stability for the established laws of distribution of these parameters.
Thus on the basis of carried out theoretical and experimental researches of reliability the recommendations are developed at the choice of conditions of operation of the cutting tool ensuring any required guaranteed level of its reliability. Defining for the given conditions of manufacture the optimum level of parameters of reliability is possible to reach a peak efficiency of use of the cutting tool at the minimal expenses for its operation.
Ivchenko T. (1999). The complex Approach to Estimation and Optimization of the cutting Tool Quality Indexes. Enttwicklungsmethoden und Entwicklungsprozesse im Mashinenbau: Tagungsband. Otto-von-Guericke-Universitat Magdeburg, pp 63-70.
Àâòîðåôåðàò Ýëåêòðîííàÿ áèáëèîòåêà Ññûëêè ïî òåìå Îò÷¸ò î ïîèñêå Èíäèâèäóàëüíîå çàäàíèå