 |
| DonNTU>
Master's portal
DonNTU>
Master's portal
ABSTRACT
Theme of master's work:
"Electromagnetic compatibility in the lihgting electric networks"
Leader of work: prof. Dmitrieva Elena
The purpose of this work is to evaluate the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) in the illumination of electric networks with different types of lamps.
Tasks:
-
Definitions of the different types of lamps characteristics.
Estimation of different types of lamps the impact to electricity quality in lighting networks.
Development of recommendations for the EMS in the lighting network.
Actuality is determined by the work that is more spread of fluorescent and compact fluorescent lamps (CFL), in contrast to incandescent lamps for their use can lead to serious distortion of sinusoidal voltage. So it is necessary to develop methods for of the estimation impact of CFL to the network and their influence.
Proposed scientific novelty consists in the impact influence of different types of lamps in the human sight by pulsation dose.
Planned practical result is to develop the impact influence of CFL methods to the lighting networks.
The deviation and vibration of voltage are related to EMC that come from the mains. Pulse illumination is created by the lamp, which causes additional fatigue. It occurs because of the supply voltage lamps is variable. By the change of the voltage the beat can be changed. For these reasons, indicators pulsations, vibrations are attributed to the performance of EMC.
Pulsation usually is estimated by the pulse coefficients (e. g. [1,2]) in percentage
 (1)
(1) where Åmax,min è Åñ – the maximum, minimum and average values of luminance for the period pulsation.
In [3] normalized allowable values of Êï coefficients of pulses in the range of 10 to 20% - depending on the type of visual work (from high to very low accuracy).
In [4] the drawbacks of the pulse coefficients are determined: it doesn’t take into account shape and frequency of pulsation. That is why we suggest universal indicator: dose and illumination Ψï. The dose is measured in (%)2, that is not desirable. That is why in [5] the coefficient of dose pulsation was established in per cents.
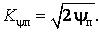 (2)
(2) The structure chart of diagram model for pulsation estimating [5] is shown in Fig. 1.1.

In general, the dose of pulsations in the r.u. is determined be expression [9]
and in the particular case of harmonic pulsations
Allowable values of dose pulsations for different classes of visual works PSï'
However, even with the implementation of inequality (7) reducing pulsations may be appropriate under the terms of labor productivity and human health.
Research productivity in different environments has been a large number of pulsations of scientists, such as: Krol TS.E., Chernilovskaya FM, Masekene KS, Samsonova, VG, etc.[10-14] Ivanov VP, Murasheva M.A, Raytselsky L.A.
At the present time CFL are becoming more and more use useful, because they lead to lower consumption of active power and durability. However, all these positive properties of CFL are not always compensate for their high cost, especially the bulbs of high quality. Therefore, the feasibility of CFL needs to assess their effectiveness, taking into account the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - a complex, by all indicators.
To justify the use of CFL in each case it is necessary to comply with the technical and economic calculations, which take into account all factors, both positive and negative. Passport data CFL to assess the economic efficiency only partially - by comparing the difference of greater value to the economy due to lower consumption of energy and more active life. Methods for estimating the EMC allow a comprehensive analysis of the impact of the deterioration of EMC. Let us consider the relevant components of the economic efficiency associated with the load conductors and active power losses. For certainty, the analysis are made on a conventional example of uniform distribution of phases of 300 lamps KLL3 power to 21 W each, which are the parameters of lighting replaces 300 LN capacity of 100 watts. When feeding LN current in neutral is equal to zero, and therefore the cross section is selected from the current phase of 100 lamps. In the case of
and under the table. 1.3.7 of [18] requires the cable cross-section of 6 mm2. When feeding KLL3-section is necessary to choose the current zero-wire, which for a single lamp is 0,216 A, for 100 bulbs - 21.6 A. In this case it is sufficient to have the cable cross-section of 2.5 mm2. As expected, the capital cost of the network significantly more LN. Loss of active power from LN is created in three phases, and from the CFL - and in neutral. The sum of squares of the three phase currents in the LN is A2. For the CFL should be taken into account not only the current one phase equal to 0,133 and from one lamp, ie, 13.3 A of 100 bulbs, but also current in neutral. In this case, the sum of the squares of the current
That is in 6.23 times lower than in LN. However, the resistance of a wire in the LN-fold in less than in the CFL, so the loss of active power during the transition to the CFL will be lower only once. Thus, despite the additional loss of power from nesinusoidalnosti and current vice versa, the loss in the CFL is much less than in LN.
In contrast to the CFL, LN nesinusoidalnosti do not create tension.
Hence the use of CFL provides a social benefit, since they reduce the dose of the lamp voltage fluctuations and ripple, improving eyesight. Scientific leader in the [24] proposed to evaluate the effect of UAH. - By taking into account the insurance premium in case of loss of vision.
The proposed method of estimating nesimmetrii and nesinusoidalnosti voltage curves for the loss of voltage (21) is an accurate and to ensure the accuracy of estimating the EMC on these indicators. Modern CFL pose little or no pulsation light, therefore the dose of pulsation, they are out of competition with other types of lamps. Techno-economic feasibility of a CFL must be justified not only for the consumption of active power, life and cost of the lamps, but also on indicators of EMC - as improving or worsening conditions of EMC. Completed studies have shown the need to complement existing documents: in section 3.32 of [25], in paragraph 4.4 and Annex E of [3] indicate the preference for the use of energy-efficient gas-discharge lamps with a low-pulsation. Since the pulsation endanger the health of people, especially students, should be required to indicate on the packaging of the lamp or the rate of pulsation for any visual works can be used lamps.