RUS | UKR ||
DonNTU >
Master's portal

Lobkova Julia
Faculty: Fiziko-metallurgical
Speciality: Metal science
Theme of master's work:
The research of the influence of the preliminary deformation-thermal treatment on the structure and the properties of the instrumental steel for cored instrument
Scientific advisers:
prof., d.e.s. Alimov Valerij
grad.st. Georgiadu Maria
Materials on the theme of master's work:
About author | Library | References |
Contact information | | Individual section
Abstract on the topic of final work
Instrumental steel are the most vast and important group. They are intended for making of instruments of four types:a) cuttings, b) instrumentation, c) stamps of cold deformation, gramme; d) stamps of hot deformation.
High values of hardness and thermostability, to viscidity and durability at the minimum expense of alloying components, and also high stability of these properties, necessary for reliable, faultless work of instrument are traditional requirements, produced to instrumental materials.
A thermal rough-down is conducted with the purpose of receipt optimum structure and properties in the initial state. At the production of wares, and also a plastinchataya structure turns out during the leadthrough of heat treatment (picture 1, a)

Picture 1 – Microstructures of pearlite (Х 1000): а - plastinchatyy; б,в - plastinchatyy, partly growing into grainy; г - grainy.
A grainy structure (picture 1, g) is an optimum initial structure before tempering.
Sferoidiziruyuschim annealing is name heating became on 10-30 oC higher than point of As1 with subsequent slow the 20-50 oC/h cooling to 650 oC:
Тн = т.Ас1 + (20-30 оС)
The slow cooling must provide sferoidizaciyu and coagulation of appearing cementite (in alloyed stalyakh – carbides).
Sferoidiziruyuschiy annealing is done for the carbon and alloyed instrumental steel; hot-rolled round, square, hexahedral and other types from a construction high-quality carbon and alloyed steel, sharikopodshipnikovye steel, an automat steel, high-speed steel, other.
Heat treatment was executed in a laboratory stove.
The standards of different brands of steel were selected.Тhe study of the initial state rotined that distributing of hardness on a section was uneven. For restoring of metal to a ravnovesnoe state normalization and perekristallizacionnyy annealing conducted. After it the sferoidiziruyuschiy annealing was done.
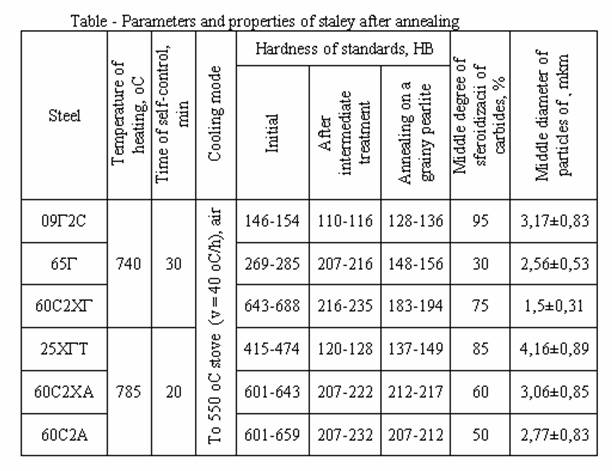
The study of hardness of standards rotined that took place softening. By the microscope of Neophot-21 the microstructure of standards was studied (picture 2). The degree of sferoidizacii differed for every brand of steel. By the computer program Imagetool the middle diameter of sferoidizirovannykh particles was expected (table 1).

Picture 2 – Microstructures of anneal standards (х1000): а – 09Г2С, б – 65Г, в – 60С2ХГ, г – 25ХГТ, д – 60С2ХА, е – 60С2.
Sferoidizaciya of carbides on standards passed partly. Except for globular particles the small areas of plastinchatogo pearlite are visible also.
Thus, the degree of sferoidizacii of carbidic particles depends on chemical composition, initial structure, time of self-control and cooling mode. The degree of sferoidizacii at the compared modes increases at the increase of amount of carbon and alloying elements in steel
LITERATURE
• Брегер И.Д. Справочник инструментальщика: для мастеров и квалифицированных рабочих. – Минск: Б.И., 1961. – 475 с.
• http://pro-nozh.narod.ru/Otzhig.html
•
Кремнев Л. С. Перспективы развития быстрорежущих сталей и сплавов// МиТОМ. 1983. № 5. с. 2- 5
•
Гуляев. Металловедение, М.: Металлургия, 1978 - с. 285-293, с. 412-417
Геллер Ю. А. Инструментальные стали. - М.: Металлургия, 1983. – 527 с.
• Кремнев Л. С., Еремин А. И., Басаргин О. В. Влияние отпуска в процессе закалки на свойства быстрорежущих сталей//МиТОМ. 1989. № 5.с.24-29
•
Чикина В. Г., Хасин Г. А., Попова Т. Н. Производство и исследование быстрорежущих и штамповых сталей. – М, 1970. – 154 с.
•
Черный Ю. Ф., Спусканюк В. З., Сынков В. Г., Богданов В. А.. Бездольный Ю. И. Влияние гидропрессования на надежность режущего инструмента // Вестник машиностроения. 1979. № 4. с. 58 – 60.
DonNTU >
Master's portal ||
About author | Library | References |
Contact information | | Individual section



