
Paul Krivchenya
Faculty: Electrotechnical (ETF)
Departament: Electrical station
Speciality: " Electrical stations " (ES)
Improving the protection relay with ground fault in the networks own needs TPP
Scientific
superviser:
Dr.Sc. (in Engineering) Professor
Sivokobylenko Vitaliy
Autobiography
Introduction
Single-phase ground fault is the most common type of injury in electrical networks of the middle class voltage (up to 85-90% of the total number of violations of normal operation of networks depending on their destination and a design). They give rise to surges, damage to insulation and in most cases they develop in the phase to phase short-circuit or multi-seat breakdown of insulation from the group a faulty electrical equipment, accompanied by large-scale damage of equipments
To date, there are
large number of both directed and undirected
protection against phase-to-earth [1], but they are not reliable enough
and in
many cases triggered falsely. Therefore, in this paper is to build
protection
for the more selective and more sensitive than a defense based on the
relay
type ssh-1 and RTS-51.
Of the multiple
studies in the system's own needs TPP can be concluded
that due to varying distance load is connected to 6 kV buses, as well
as
various cable laying feeder earth fault currents in all feeders are
very
different from each other. However, they are usually very low values,
and the
total ground fault current rarely reaches the
From the
statistics obtained at Zuevskaya TPS, which are installed on
the engine fault on the ground working to disconnect the damaged
connection, it
is known that the closure of the land on the feeder with a small
capacitive
current on their own land, except for a damaged connection disconnected
feeder
with the highest current circuit on the ground, indicating that
non-selectivity
of protection installed on the relay type RTZ-51.
With regard to the
direction of protection relay ssh-1, which react to
the direction of power, then [2] it is known that in many cases off the
damaged
connection with the phenomenon Ferro resonance data relay false trigger
due to
loss of focus.
Based on the
foregoing, the task of developing a more sensitive and
selective protection from phase-to-ground fault is considered to be
relevant.
Create a
mathematical model for writing programs in MathCAD to
calculate the transient network's own needs
To increase selectivity and sensitivity of the protection of single-phase earth fault in the system's own needs Zuevskaya TPP by the improvement of existing protection or development of fundamentally new.
Research objectives
To achieve its
goals in the need to perform the following tasks:
1. Analysis of the
established protections and justification for the
miropriyatiya to improve them.
2. The development
of more reliable protection.
3. Development of
a mathematical model of a network with isolated
neutral.
4. Implementing
Math. Models in mathematical editor MathCad.
5. Calculation of
the sensitivity of established and new protections.
6. Comparison of
established and developed protections.
Alleged practical value
The results of
this study can be used to increase the sensitivity and
selectivity of protection against phase-to-ground fault in any system
with
isolated neutral. Especially effective protection in a system with a
small
current circuit to earth.
Review of
existing methods for solving the problem
To ensure high
reliability and selectivity of the tasks and the
technical result achieved by the fact that the protection device of
earth fault
in a network with isolated neutral, which contains the zero sequence
current
transformers on the quantities of linear connections, to the output of
which
parallel connected voltage limiters and intermediate transformers with
bridge
rectifier, the outputs are connected to the inputs of RC-circuit and
connected
to a dc amplifier, the outputs of the past combined with the executive
relays,
diodes and the first dividing by the number of connections, the source
of the
residual voltage, which is connected to the output voltage relay with
time
delay, the source reverse voltage, and resistor, with Klema connection
between
the neutral network and the ground. This device also has a changeover
contact
relay executive at the amplifier input dc moving contacts are through
the
opener voltage relay with time delay connected to the plus pole of the
polarity
of the voltage blocking, locking the fixed contacts are connected to
the plus
pole of the reverse voltage sources directly, but NC still contact
through the
appropriate separation diodes - to the condensers of these RC-circuits,
in
addition imposed on the number of accessions current-limiting resistors
in
series with dividing diodes, amplifiers, dc instant action and normally
open
contacts in series in the chain of input signals of each of the
reacting bodies
of the device.
Common features
with the prototype are listed in a limited part of the
formula. These include: zero sequence current transformers by the
number of
linear connections, voltage limiters and intermediate bridge rectifier
transformers, RC-circuit, DC amplifiers, executive relays, diodes
dividing by
the number of connections, the source voltage zero-sequence voltage
relay with
time delay zastiryvayuschego source voltage, and resistor, also in
quantity of
accessions changeover contact relay executive at the input DC voltage
mobile
relay with time delay, lock the fixed contacts and break the fixed
contacts
through that scheme are included through appropriate розділювальні
Diodes -
Capacitors for these RC-circuits.
Important
distinguishing features of the claimed device earth fault
protection with well-known features provide obtaining a technical
result, such
as: increased and improved reliability and selectivity of protection
against
earth fault.
The drawing shows
a schematic diagram of security device earth fault
for two accessions.
The device has the
transformers 1 and 2 to the current zero-sequence
(TTNP), measuring bodies made in the form of RC-circuit and operational
amplifiers 3 and 4 DC intermediate relays 5 and 6 at the outlet, which
also
serve as the executive body, connected to the transformer current 1 and
2
through rectifiers 7 and 8, intermediate transformers 9 and 10, the
source of
11 residual voltage connected to its output relay 12 residual voltage
with time
delay, isolating diodes 13 and 14, 15 and 16 limit the voltage.
In addition, the
device has a high resistance resistor 17, which is
included among the neutral network (for example, the zero point of the
winding
of high voltage transformer substation own needs) and the land that
creates
additional active ground fault current equal in magnitude to 50-100% of
the
capacitive current of the metal closure in the network (but not less
than
3-4A); power supply 18, which is also the source of reverse voltage, as
well as
tipping contacts 19 and 20. Advanced imposed resistors 21 and 22, which
included series with the diodes 13 and 14, and normally open contacts
22 and 23
which are guided by amplifiers 24 and 25.
It works this way.
In normal mode,
with no reduction of insulation resistance of one phase
relative to the ground below normal, that is, to a state single-phase
circuit,
the relay 12 is not triggered. Relay contacts 5, 6 and 12 are in the
initial
state, the capacitors through the closed relay contacts 5, 6 and 12,
diodes 13
and 14 charged from the power supply voltage 18, which closes
transistor
amplifiers 3 and 4 of the DC relay 5 and 6 remain deenergized, contacts
22 and
23 are open.
In a single-phase
ground fault through resistance, whose values are
within range of protection, the relay 12 and time delay opens its
contact
trigger elements 24 and 25, snap contacts 22 and 23, thus providing the
same
conditions recharge capacitor "C" despite the introduction of the
scheme of current-limiting resistors 21 and 22, capacitors RC-chains
are
beginning to be recharged from TTNP 1 and 2 through the intermediate
transformers 9 and 10, rectifiers 7 and 8, and the faster, more zero
current
line. Upon reaching the capacitor required level of building the relay
5 (with
confirmation of line 1), a signal to switch off the corresponding
circuit
breaker, and exchanged contact 19 provides switching power 18 reverse
voltage
so that the capacitors on the RC-circuits of all other accessions
resumes
reverse voltage, and firing the executive relay other accessions did
not occur.
After switching
off the damaged line, the circuit returns to its
original state. Needed for selective operation of this unit is the
difference
between the amplitude values of zero sequence currents in the damaged
and
undamaged accessions, provides grounding network via high-resistance
resistor
17. Thus the invention provides a stable setting alarm relay executive
in
blocks of all accessions, and also has a high enough
pomehooshibkoustoychivosti, selectivity and reliability.
The use of this
device improves the reliability of electricity
consumers and improve the safe operation of personnel during the
operation of
electrical distribution networks.
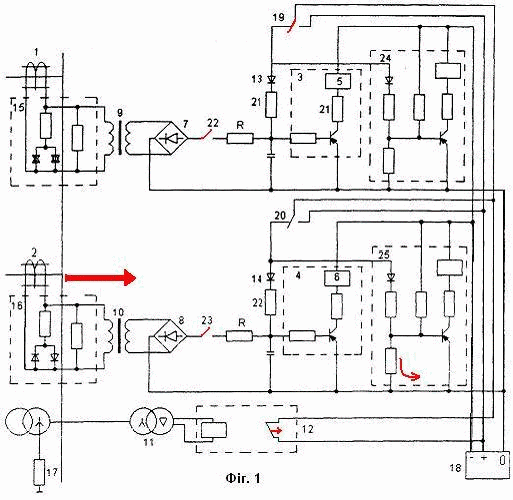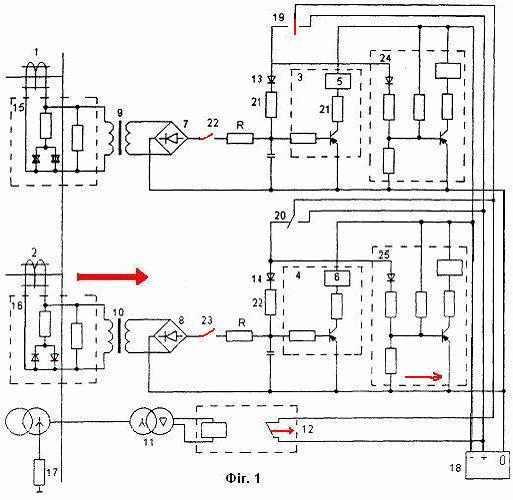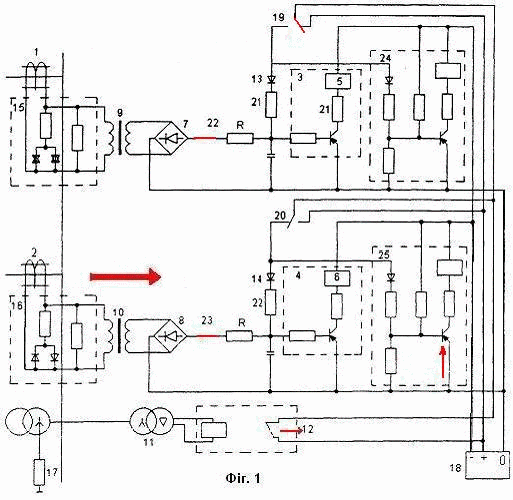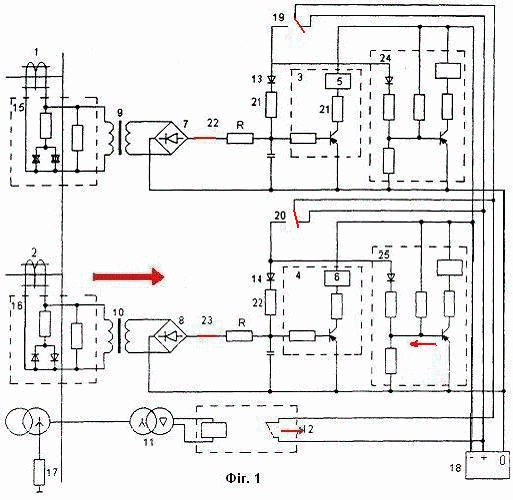
Figure 1 - The model of the
proposed protection. (Animation:
7 frames 9 reps)
A large number of papers [3,4,5] on
this subject offer connecting phase, with the greatest value of the
voltage
relative to earth with the earth through the first resistance,
simultaneously
linking phase with the lowest value of the voltage relative to the
ground with
the ground through a second resistance, measure the leakage current to
earth,
phase voltage and determine the insulation resistance of the network
from the
ground and compare it to an acceptable value and if it is less than the
allowable, then form a signal to turn off the damaged part of the
network,
record the value of insulation resistance at certain times, for it
determines
the future value of insulation resistance, compared to with a valid
value, and
if it is less than allowable, then form an information signal the
approach of a
possible accident, and each newly recorded value of insulation
resistance is
used in the subsequent calculation of future values of insulation
resistance
and determine the residual life of insulation.
However, this method of protection
from ground
fault
considerably difficult to
implement and requires replacement of basic equipment such as relays.
Besides
the description of these inventions are not considered false positives
if you
disable the other accessions.
The method used in the master's work
The method is to increase the
selectivity and sensitivity
of anti-single-phase ground fault by installed equipment, with a
defense of
more selective and sensitive than those discussed above.
The principle of protection is
based on the magnetization
of zero sequence current transformers [6], consisting of two identical
cores in
each of which is wound with two windings, so you can do the detuning of
the
current imbalance and increase the sensitivity factor on the damaged
accession
by strengthening the core of the magnetic flux produced by current in
primary
winding is connected to the flow created by the residual voltage
winding bias.
The drawback of the prototype
device is the possibility
of false positives when disconnecting circuit damaged accession because
of
overcharging occurring between a tank.
The purpose of the invention is to
increase the
selectivity and sensitivity towards the protection of single-phase
earth fault.
Conclusion
1. The causes of non-selective
earth fault protection in
networks of their own needs TPP with isolated neutral and selected
areas to
improve security in which the basis adopted by the overcurrent
protection with
directional bias of the core current transformer zero-sequence with an
additional winding connected to a voltage transformer.
2. Testing of protection on the
computer and physical
model confirmed the correctness of the principles of protection devices
are
phase-to-earth.
When writing this abstract the master’s qualification work is not completed. Date of final completion of work: December, 1, 2010. Full text of the work and materials on a work theme can be received from the author or his scientific supervisor after that date.
Literature
1. Назаров В.В. Защита
электрических сетей от
однофазных замыканий на землю – Киев
«Либідь», 1992, 124 с.
2. Сивокобыленко В.Ф., Лебедев
В.К., Ковязин А.В.,
Сердюков Р.П., Кряжок С.А., Гребенкин А.И, Зубенко В.В., Рябчук И.Э.
Повышение
надежности работы карьерных сетей при однофазных замыканиях на землю.
– Наукові
праці Донецького національного університету №9(158), 2009. ISSN 2074-2630.
3. Заявка: 2006111302/09,
06.04.2006 Булычев А.В. Гуляев В.А. Дежнев В.А - Способ защиты
трёхфазной сети
с изолированной нейтралью от однофазных замыканий на землю.
4. Заявка: 95117700/09,
28.09.1995 Булычев А.В., Ванин В.К. - Способ защиты трёхфазной сети с
изолированной нейтралью от однофазных замыканий на землю.
5.
Заявка: 2006140511/09, 16.11.2006 Буланов Р.Н., Гуров А.А., Мишутинский
В.Е. –
Устройство селективной защиты от однофазынх и многофазных замыканий на
землю
электрической кабельной сети с изолированной нейтралью.
6. Авторское свидетельство №74018 по заявке от 7 апреля 1947г.
7. Правила устройства
электроустановок. – М.: Энергоатомиздат,
1985.– 640 с
http://www.electromonter.info/download/
8. Петренко Л.И. Электрические сети и системы – Киев: Вища школа, 1981 320с.