| Autobiography |
| Русcкий | Українська | English |
ABSTRACT
Qualification of Master
"Developing a decision support system in obstetrics and gynecology"
INTRODUCTION
1 HOT TOPICS
2 Relationship work with scientific programs, plans, themes
3 PURPOSE AND OBJECTIVES OF
4 SCIENTIFIC NOVELTY
5 practical significance of results
6 REVIEW OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT RELATED
6.1 Review of existing methods
6.1.1 Neural networks
6.1.2 Genetic algorithms
6.1.3 Systems with fuzzy logic
6.2 Overview of existing tools
7 SELECTION AND JUSTIFICATION Fuzzy logic to implement the system
CONCLUSION
Bibliography
INTRODUCTION
To date, the processes of global computerization reached so awe-inspiring scale that almost everywhere you can find a computer. That area of ultrasound diagnosis is no exception. In the course of medical ultrasound diagnosis is often a large amount of time spent on verifying the results with the available reference data. At this time included a comparison of the resulting image with the examples in the references, as well as a comparison and analysis of the measurements with the available statistical data from various sources. Moreover, most of the time it takes analysis of the measurements.
End, to develop a decision support system is to simplify the process of selecting the most appropriate diagnosis. That in turn could increase the objectivity of the medical diagnostician, to reduce the amount of time required for inspection of one patient and to simplify the work of a physician with reference books. All these plus the ability to increase productivity study ultrasound, and this is the main purpose of automation of most processes - increasing productivity.
1 HOT TOPICS
In conducting prenatal ultrasound diagnosis of the time required for examination of one patient, ranges from 40 to 70 minutes. Of this time, approximately 5-7 minutes spent on the preparation before and after diagnosis, 10-15 minutes to conduct the necessary measurements, 5 minutes to complete documentation, 20-30 min to determine the diagnosis, the search for the necessary background information in books and if necessary, meeting with other professionals.
Obvious that at the time of diagnosis affect the qualities of the doctor-diagnostician, as experience, depth of knowledge of the material on the topic of research, as well as the rate of orientation in the available material. In addition to the personal characteristics of the doctor-diagnostician affecting the diagnosis, there are also such factors as accessibility and speed of search of background information.
Virtually all of these problems can be solved by using a decision support system, within which is an interactive guide. Thus, the accumulation of experience is provided by various experts, objective evaluation of research and high-speed search of background information.
2 Communications work with scientific programs, plans, themes
Qualifying master work was carried out during 2009-2010. In accordance with the scientific direction of the Department of Automated Systems ", Donetsk National Technical University.
3 PURPOSE AND OBJECTIVES OF RESEARCH
Due to the fact that the prenatal ultrasound diagnosis is associated obbem great knowledge and natural that one person can not always be taken into account any options may be the correct diagnosis, and the same low level of formalization of existing knowledge. We can distinguish the main purpose of this: Develop a system to support decision-making with specific knowledge of prenatal diagnosis, and the ability to quickly search for background information. To achieve this goal it is necessary to solve the following main tasks:
- Formalization and enforcement of existing knowledge in a convenient form of work;
- Develop a database structure for storing knowledge about the possible diagnoses;
- Develop a database structure for storing the results of the research;
- Develop principles and mathematical model of decision support systems;
- Experimentally verify the effectiveness of the program.
Object of research: the process of diagnosis of existing surveys.
Subject of research: methods and algorithms for decision making.
4 Scientific NOVELTY
Scientific innovation is to use the principles of fuzzy logic to solve this problem. This is achieved by relative output results and the possibility of determining the deviation from a perfectly correct result. Moreover, since fuzzy logic does not limit the list of displayed results can provide the user the choice between the most likely diagnosis.
Five practical significance of results
For any physician-diagnostician, the system will probably always objectively and more accurately diagnose. In addition, it will reduce the time to receive the patient from 40-70 minutes to 30-50 minutes due to the fact that it would significantly reduce the time to find corroborating information about the suspected diagnosis and the choice of the most probable diagnoses.
Also achieved the possibility of attendance statistics office, as well as reporting on the study, and separately for each patient, bringing them to print.
6 REVIEW OF RESEARCH AND DEVELOPMENT ON TOPIC
Consider the existing methods and tools used to solve this problem on a global level.
6.1 Overview of existing methods
6.1.1 Neural networks
Neural networks can be viewed as the modern computing tional systems, which convert the information in the image process owls occurring in the human brain. The processed information IME em numeric character, which allows the use of a neural network, example, as a model of the object with a completely unknown char teristics. Other typical applications of neural networks include recognition problems, classification, analysis and compression of images.
In its simplest form of neural network can be viewed as a way of modeling in engineering systems, principles of organization and functioning of the human brain. According to modern concepts, the cortex of the human brain is a set of interconnected elementary cells - neurons, whose number is estimated to number about 10 10 . Technical systems, which attempt to reproduce, albeit in a limited extent, a similar structure (hardware or software), received the name of neural networks.
This method is difficult to implement because practically difficult to track the correct operation of this method during debugging. As well as the impossibility of interpreting the intermediate data and the complexity of explaining the results of the network makes this method extremely inconvenient for use in this case.
6.1.2 Genetic Algorithms
Genetic algorithm is a method, reflect Officer natural evolution of methods for solving problems, and especially optimization problems. Genetic algorithms - a proce RY search, based on the mechanisms of natural selection and heritage ment. They used evolutionary principle of survival NAI more adapted species. They differ from traditional optimization methods, several basic elements. In particular Steph, genetic algorithms:
- not handle the parameters of the problem, and their encoded form;
- look for solutions on the basis not of a single point, and some of their populations;
- use only objective function, but not its derivatives or any other additional information;
- use probabilistic rather than deterministic right villa of choice.
Search (sub) optimal solution is performed in the course of evolution of the population - a consistent transformation of a finite set of solutions to another by means of genetic operators of reproduction, crossing and mutation. The presence of genetic algorithms entire "population" of solutions in conjunction with a probabilistic mechanism of mutation, suggest a lower probability of finding a local optimum, and greater efficiency in the Multiple landscape.
6.1.3 systems with fuzzy logic
For many applications related to the management of technological Kimi processes must construct a model of the process. Knowledge of the model allows to choose the appropriate regulator tor (control module). Often, however, the construction of the correct model is a difficult problem that requires some introduction of various simplifications. Application of the theory of fuzzy sets for the pack nance technological processes does not imply knowledge of fashion lei of these processes. It is only to formulate rules of conduct in the form of fuzzy conditional reasoning such as IF ... THEN.
Should be emphasized that the application of fuzzy sets covering vayut currently a wide range of tasks - from simple devices, household products, to more serious systems.
Figure 6.1 shows the block diagram of the classical control module based on fuzzy logic.
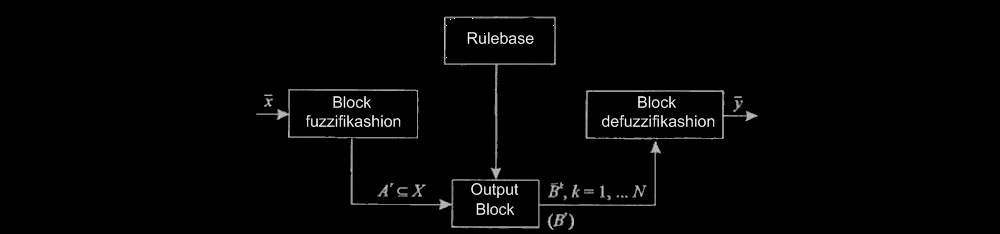
Figure 1 - Scheme of classical control module based on fuzzy logic
Base rules - a set of rules R (k), k = 1 .. n, this type:
 (6.1)
(6.1)
Where N - number of fuzzy rules, Aki - fuzzy sets.
![]() (6.2)
(6.2)
Bkj - fuzzy sets
![]() (6.3)
(6.3)
Symbols Xi, i = 1 .. n, and Yj, j = 1 .. m are denoted Correspondingly tively the space of input and output variables.
Fuzzifikatsii Block - the block, which converts its output fed to the exact value (numeric variables) in the relative values (linguistic variables, sewn into the block rules), taking into account the probability each of these variables.
Block the decision-making - the block in which the actual and adopted a list of all feasible solutions by computing the probability of each of them. Submitted to the input of this block relative values correspond to the rules, which are taken from the base of rules, and finally at the coincidence of the situation with the rule, we obtain one possible solution. And the probability of such an option is determined by multiplying the probabilities of relative values. If you have two contradictory results, we choose the one whose probability of above.
Block defuzzifikatsii - performs the function of reporting the results of the unit of decision-making in an accessible form for the object to a withdrawal to submit it to the object and thus to influence the management object.
6.2 Overview of existing tools
At this point in the software market including decision support systems have only one system that is as close as possible to support decision making in obstetrics and gynecology - a "CHIP - Prenatal monitoring of Down's syndrome, developed Ltd. Intelligent Software Systems "(Russia).
Designed for computer support processes survey of pregnant women during 15-18 weeks of pregnancy. Screening for a two-step (if necessary) the process of examination pregnant. At the first stage of a biochemical examination of blood. The result of this survey is to determine the risk of having a child with Down's syndrome or NTDs. In case of detection of high-risk working on a survey, a pregnant are encouraged to be clarifying further examination by a specialist in prenatal diagnosis or to undergo an ultrasound examination 2.
Package provides a set of two programs (the main and auxiliary) with different set of features.
Home program is installed in the center (GC), will ensure the fulfillment of the biochemical examination of blood and generating the necessary recommendations for further examination. Tools of the main program can perform all the service processes the first stage of prenatal screening, as well as the accumulation of factual data for statistical analysis of the completeness and adequacy of the initial data of biochemical studies. Support program is designed for use in medical centers forming the initial factual information about pregnancy (usually - women's clinics (LCD)). The need to use auxiliary programs is determined by the contingent and the presence of a certain number of points forming the initial information.
CHIP implements the following functional tasks.
- Facility and preservation of records of pregnant women.
- Facility data on the presence of specific diseases in pregnant women, as well as specific medical indications.
- Take account of the birth.
- Based on the analysis of blood.
- Take account of the implementation of action for prenatal diagnosis and ultrasound.
- Accumulation of data for the formation of the initial statistical analysis.
- Administration information base.
Required system parameters for the normal functioning of the software:
- Operating System: Microsoft Windows 98 / 2000 / XP / Vista
- Class Processor: Intel Pentium IV 2.0 GHz or higher
- RAM: 256 Mb
- Free space on your hard disk: 200 Mb
- Printer: Laser or inkjet A4
Among the shortcomings of this system include the following items:
- Not adapted to the environment Ukrainian laws and regulations.
- No application oriented separately for medical diagnostic ultrasound:
- Lack of checks on other types of pathologies, except for Down syndrome.
- Lack of opportunities for interactive viewing of characteristic images of one specific pathology.
- Absence of recommendations for additional measurements for the most accurate diagnosis.
- Is no possibility of replenishment of the knowledge base and rules diagnosed diagnoses and editing it.

Figure 2 - Deciding (animation frames (7), the infinite loop, the volume (50KB)
7 CHOICE AND JUSTIFICATION OF FUZZY LOGIC FOR THE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE SYSTEM
In the problem of the choice of possible diagnoses is not necessary to cover undocumented options, and hence there is no need to use neural networks. Especially given the complexity of the intermediate and resulting data that neural network is strictly not suitable for this task.
On the other hand the use of genetic algorithms is also not suitable. Because, firstly, it is difficult to make such a fitness function, which would include all possible input data, and even in this case, adding a new parameter for measurement. Secondly, the selected diagnosis may depend on only the coefficients of the variables in the fitness function. Thirdly, by and large is difficult to distinguish which chromosome will be the best: with one or several possible diagnoses. As a result, we have solved many difficult moments makes this method poorly suited for solving this problem. In addition, another big drawback of this technique is the fact that for genetic algorithms are needed rather large system resources, or a significant amount of time to process data.
As a result, the most appropriate method is to develop systems based on fuzzy logic. This method has the ability to find solutions according to their relevance in this situation, which is convenient for illustration doctor's recommendation. Also, given the fact that when you start the program is known in advance a list of possible diagnoses and conditions of their appearance, fashionable initially present knowledge as a system of rules in fuzzy logic.
CONCLUSION
As a result of research work have been collected and reviewed materials on issues related to the conduct of diagnostic ultrasound in obstetrics and gynecology, as well as studied the methods of implementation of decision support systems solutions.
Among the methods of organization of decision support systems were considered the main directions from the perspective of the strengths and weaknesses, and the most appropriate structure was selected using fuzzy sets and rules based on them. Because today the structure of logical reasoning, medical diagnosticians are very similar to that of systems with fuzzy logic, moreover, the system allows to abstract from the specific measurement values, and thus avoid repetition of similar rules for different periods of pregnancy. And this in turn will significantly reduce obbem knowledge base and as a consequence, the speed of application software will grow.
After consultation with the doctors diagnosis was also decided to introduce the user interface help. This guide is designed to make a final decision by the doctor-diagnostician after receiving the list of suspected diagnoses.
Planned to develop a software application that implements all the functions above, as well as further study of knowledge in the field of prenatal diagnosis in order to formalize them for future introduction in the knowledge base of application software. As well as conducting pilot studies and evaluating the performance objectives of the system.
Bibliography
1. http://www.incomsys.ru/board/4-1-0-5 - описание программы «Пренатальный Мониторинг Синдрома Дауна»2. http://terramedica.spb.ru/1_2002/kasheeva.htm - клинические испытания программы «Пренатальный Мониторинг Синдрома Дауна»
3. http://www.cs.cmu.edu/Groups/AI/html/repository.html - хранилище публикаций по искусственному интеллекту при университете Карнеги-Меллона;
4. http://www.comlab.ox.ac.uk/archive/comp/ai.html - включает каталоги отдельных лабораторий, занимающихся проблемами искусственного интеллекта;
5. Д. Руткоская, М. Пилинский, Л. Рутковский Нейронные сети, генетические алгоритмы и нечеткие системы // М.: «Горячая линия-Телеком», 2006, 303с.
6. Медведев М.В., Зыкин Б.И., Хохолин В.Л., Стручкова Н.Ю. Дифференциальная ультразвуковая диагностика в гинекологии. // М.: Видар, 1997.
7. Медведев М.В., Зыкин Б.И. Клинические лекции по ультразвуковой диагностике в перинатологии. // М., 1990.
8. Кулаков В.И., Кузнецова М.Н., Мартыш Н.С. Ультразвуковая диагностика в гинекологии детского и подросткового возраста. // М.: Медицина, 1994.
9. Г. К. Вороновский, К. В. Махотило, С. Н. Петрашев, С. А. Сергеев Генетические алгоритмы, искусственные нейронные сети и проблемы виртуальной реальности. // заказное. — Х.: ОСНОВА, 1997. — С. 112.
10. Заде Л. Понятие лингвистической переменной и его применение к принятию приближенных решений. // М.:Мир, 1976.
11. Аверкин А.Н., Батыршин И.З., Блишун А.Ф. Нечеткие множества в моделях управления и искусственного интеллекта. // М.:Наука, 1986.
12. Мелихов А.Н., Берштейн Л.С., Коровин С.Я. Ситуационные советующие системы с нечеткой логикой. // М.: Наука, 1990.
13. Шор Л.П. Согласование нечетких экспертных оценок и функция принадлежности в методе размытых множеств. Моделирование и исследование систем ав¬томатического управления // Владивосток, ДВНЦ АН СССР, 1978, с. 111-118.
| Autobiography |
| Русcкий | Українська | English |
