ABSTRACT
Contents
Introduction
Accidental interruptions of power supply happen because of electrical equipment damages, means of protection failure and because of the fault of the stuff, attending and operating the electrical equipment of the substation, in case the customers get electricity from the corresponding substation bus sections.
Reliability evaluation of power supply of the load nodes will be defined under the following conditions of work: static, dynamic and maintenance [1].
Under static conditions the elements damages as "circuit breakage" are taken into account. The failures of the secondary circuits of the relay protection and automatic equipment that lead to automatic switches opening and false or extra operation of the protection will be defined as the damages of such type. The parameter of the failure flow as "circuit breakage" is defined taking into account the number of accidental switches opening for the period of the research, the number of the switches of the similar type that are operated at the substation.
Under these operating conditions of substation the diagnosis of the state (with constant interval of time Q) of protective commutations is made and the failures of the automatic switching system that may lead to the failures because of the short circuit in the area of current protection are found out. The installations of relay protection, the integrity and the serviceability of the relay contacts, the serviceability of the opening coil are checked, the switch drive, arc chute, contact system, isolation are examined, the possibility of isolation overlap under condition of external and internal overvoltage is evaluated, the system of automatic putting into operation of the reserve on the sectional switch and the serviceability of the minimal voltage protection etc. are checked.
The parameter of "failure" flow of the switching system of the "i" protective switching device is defined taking into account the number of damages, that are found out in the system of switches opening for the time of examination "t" and the number of switches of the same class.
The protective switching device is considered to be the device which allows protecting (switching) the customer from abnormal conditions of its work (the short circuit, overvoltage etc.).
The collecting buses and isolators are also subjected to diagnostics: the attachment of pedestal insulators, their state (cracks, dust on the surface), contact system, measuring instruments are examined, all visible and invisible damages are found out and eliminated. The diagnostics of the collecting buses and isolators state allows increasing of time intervals between the appearance of the short circuits at the substation buses or at the isolator elements through which the operating current comes.
Under dynamic conditions the failures as "short circuit" and switches opening system failures at short circuit in the area of current protection are taken into account.
The damages as "short circuit" can happen at the network elements through which the primary operating current and accidental current comes (lines that are coming from commutations, buses, isolators, the windings of power transformers).
The serviceability of the load node is considered to be customers' and their automatic means of protection ability to resist the disturbance that may lead to emergent switching. The serviceability of the load node is defined under dynamic conditions, that is, when the short circuits accidentally happen in the system.
Under maintenance conditions the mistakes of the attending stuff while different maintaining switching that can lead to the de-energizing of the load node are taken into account.
The number of cases of the emergent switching of substation bus sections for the time of research T because of the attending and operating stuff mistakes is stated. The obtained information allows defining the parameter of emergent switching flow of the bus sections because of the stuff's mistakes.
The aim of the research
To evaluate the power supply reliability, in case the customers get electricity from one of the substation bus sections under static, dynamic and maintenance conditions of work.
The results of the research
Power supply reliability evaluation under static and maintenance conditions doesn't cause any difficulties. Under dynamic conditions it is necessary to take into account two parameters: the parameter of the short circuit flow in the net element and failure of the protective switching device through steady leakage emergent current.
The frequency of coincidence in space and time of such events as short circuit in the element that is protected and the failure of switching devices, through which the steady leakage emergent current comes, can be defined with the help of the formula [2]

where  is the parameter of short circuit flow in "j" element of the net;
is the parameter of short circuit flow in "j" element of the net;
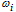 is the parameter of the protective switching device failure flow;
is the parameter of the protective switching device failure flow;
 is the time interval between diagnostics of the protective switching device disconnection system;
is the time interval between diagnostics of the protective switching device disconnection system;
 is the number of protective switching devices through which the steady leakage emergent current came and switched on their relay protections;
is the number of protective switching devices through which the steady leakage emergent current came and switched on their relay protections;
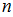 - is the number of J elements, which get electric power from I protective switching device.
- is the number of J elements, which get electric power from I protective switching device.
In case the voltage, transmitted to the load node (substation buses sections), disappears, the disconnection of the input switchgear unit by the protection of minimal voltage (zero phase sequence protection), the auxiliary contacts of the disconnected switch start the automatic putting into operation the reserve on the sectional switch and provide constant power supply of the substation buses.
The emergent disconnection of the load node happens, if two accidental events coincide in space and time: the emergent disconnection of the input switchgear unit by the protection of minimal voltage and the automatic putting into operation of the reserve on the sectional switch failure.
The parameter of the emergent load node disconnections flow will be defined in the following way because of the given above reason[7]:

where 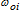 is the parameter of the emergent disconnections flow of I input switchgear unit because of the minimal voltage protection operation;
is the parameter of the emergent disconnections flow of I input switchgear unit because of the minimal voltage protection operation;
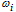 is the parameter of the failure flow of the system of the automatic putting into operation of the reserve on the I sectional switching device. ;
is the parameter of the failure flow of the system of the automatic putting into operation of the reserve on the I sectional switching device. ;
 is time interval between the diagnostics of the disconnection system of the automatic putting into operation of the reserve on the I sectional switching device.
is time interval between the diagnostics of the disconnection system of the automatic putting into operation of the reserve on the I sectional switching device.
The formulae are true under the following conditions: the time intervals between short circuit appearances in the net elements, time intervals between disconnections of input KRU by the protection of minimal voltage and time intervals between failures of protective switching devices don't contradict to exponential function of distribution of the possibilities with the corresponding parameters:  and the following proportion is true:
and the following proportion is true:

At the derivation of the previous two formulae the following assumptions were made: the protection device can go out of service, only when they are under expecting conditions; if by the moment of the damage appearance in the net, at which protective relaying should react, it was in service , then protective relayin's going out of order under alarm conditions is unlikely [3].
The failure of the protective switching device is such a failure that leads to the failure of the damaged net element disconnection during the short circuit at the area of relay protection, or during the disappearance of voltage at the line that powers switchgear unit the zero phase sequence protection fails.
In case when 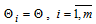 the first formula will be[6]:
the first formula will be[6]:
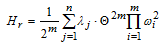
The parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections is:
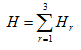
where 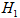 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under static conditions;
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under static conditions;
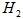 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under dynamic conditions;
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under dynamic conditions;
 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under maintenance conditions.
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under maintenance conditions.
The probability of constant power supply of the substation buses sections during the time t is:

If 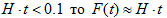 [5]
[5]
The average time between the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections is:
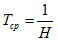
The average time of recovery of the power supply of the substation buses sections after the emergent disconnection is:
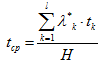
where 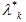 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnection of the substation buses sections because of the coincidence of the events corresponding to k minimal section in space and time;
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnection of the substation buses sections because of the coincidence of the events corresponding to k minimal section in space and time;
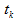 is the average time for recovery of power supply for substation buses section after the failures that took place according to K minimal section;
is the average time for recovery of power supply for substation buses section after the failures that took place according to K minimal section;
 is the number of minimal sections in the scheme of substitution.
is the number of minimal sections in the scheme of substitution.
Readiness factor of the substation scheme:
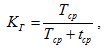
With the help of the provided formulae it is possible to evaluate reliability of the substation that supplies industrial enterprises with electrical power.

Picture 1 – Principal scheme of the main step-down substation
Let's mark next events:  - the appearance of short circuit in j element of the scheme;
- the appearance of short circuit in j element of the scheme; 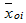 - the appearance of failures as "circuit breakage" in I switching device;
- the appearance of failures as "circuit breakage" in I switching device; - failure of I switching device because of current protection failure;
- failure of I switching device because of current protection failure;  - emergent disconnection of the input switch because of the zero phase sequence protection operation;
- emergent disconnection of the input switch because of the zero phase sequence protection operation;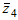 - failure of the switching device number 4 because of the failure of the zero phase sequence protection at voltage disappearance in the bus section I;
- failure of the switching device number 4 because of the failure of the zero phase sequence protection at voltage disappearance in the bus section I;  - disconnection of the bus section I because of the stuff mistakes. [4].
- disconnection of the bus section I because of the stuff mistakes. [4].
Using the principal scheme of the substation at picture 1, accepted markings of emergent events we build "the tree" that explains the reasons for the emergent disconnection of the bus section I at picture 2 and scheme of "the minimal sections" at picture 3.

Picture 2 –The tree that explains the reasons of emergent disconnection of the bus section I

Picture 3 – The scheme of the minimal sections
Schemes of the pictures 2 and 3 are obtained under the following assumptions: only binary coincidences of emergent events in time and space are taken into account; while damaging the windings of the power transformer 5, protection at switching device 6 will disconnect it safely; the failures of the switch disconnection system and means of protection are found out as the results of diagnostics that is provided with the time interval ; the appearance of two short circuits simultaneously in the different system elements is an unlikely event and is not taken into account in calculations.
Using the obtained scheme of "minimal sections" and initial data of the example, the parameter of the emergent failure flow of the buses section I: is found out I:
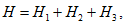
It is determined that 47,3% of emergent disconnections of substation buses sections happen because of the stuff mistakes at attending the electrical equipment, the rest 52,7% is the fault of the unreliable electrical equipment and protection means.
Conclusion
For the providing of the constant power supply special attention should be paid for the choice and training of the stuff that deals with the attending and maintenance of the electrical equipment of the substations. For obtaining of more trustworthy and objective evaluation of power supply reliability it is reasonable to examine not the group of the electrical equipment of the same type at several substations but the separate samples of the certain substation (switchgear unit, buses, isolators, transformers etc.), starting from the moment of putting it into service and up to the moment of its utilization.
The list of literature
- Руденко Ю. Н., Ушаков И. А. Надежность систем энергетики.— М.: Наука, 1986—320 с.
- Ковалев А. П., Якимишина В. В. О живучести объектов энергетики. Промышленная энергетика.—2006. №1.— С. 25-29.
- Фабрикант В. П. О применении теории надежности к оценке устройств релейной защиты —Электричество. —1965. №9. — С. 15-19.
- Китушин В.Г. Надежность энергетических систем. М: Высш.шк., 1984. — 256 с.
- Надежность систем энергетики. Терминология.М.: Наука, 1980.—Вып.95.—44с.
- Китушин В.Г. Определение характеристик отказов системы при цепочечном развитииаварий. — Изв. АНСССР. Энергетика и транспорт, 1977, №3. С. 20-30.
- Гук Ю.Б. Анализ надежности электроэнергетических установок — Л.: Энергоатомиздат.Ленинградское отделение, 1988.—224 с.


 is the parameter of short circuit flow in "j" element of the net;
is the parameter of short circuit flow in "j" element of the net;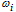 is the parameter of the protective switching device failure flow;
is the parameter of the protective switching device failure flow; is the time interval between diagnostics of the protective switching device disconnection system;
is the time interval between diagnostics of the protective switching device disconnection system; is the number of protective switching devices through which the steady leakage emergent current came and switched on their relay protections;
is the number of protective switching devices through which the steady leakage emergent current came and switched on their relay protections;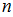 - is the number of J elements, which get electric power from I protective switching device.
- is the number of J elements, which get electric power from I protective switching device.
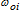 is the parameter of the emergent disconnections flow of I input switchgear unit because of the minimal voltage protection operation;
is the parameter of the emergent disconnections flow of I input switchgear unit because of the minimal voltage protection operation; and the following proportion is true:
and the following proportion is true:
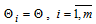 the first formula will be[6]:
the first formula will be[6]: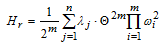
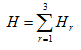
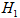 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under static conditions;
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under static conditions;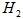 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under dynamic conditions;
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under dynamic conditions; is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under maintenance conditions.
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnections of the substation buses sections under maintenance conditions.
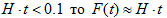 [5]
[5]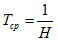
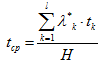
 is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnection of the substation buses sections because of the coincidence of the events corresponding to k minimal section in space and time;
is the parameter of the flow of the emergent disconnection of the substation buses sections because of the coincidence of the events corresponding to k minimal section in space and time; is the average time for recovery of power supply for substation buses section after the failures that took place according to K minimal section;
is the average time for recovery of power supply for substation buses section after the failures that took place according to K minimal section; is the number of minimal sections in the scheme of substitution.
is the number of minimal sections in the scheme of substitution.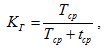

 - the appearance of short circuit in j element of the scheme;
- the appearance of short circuit in j element of the scheme; 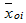 - the appearance of failures as "circuit breakage" in I switching device;
- the appearance of failures as "circuit breakage" in I switching device; - failure of I switching device because of current protection failure;
- failure of I switching device because of current protection failure;  - emergent disconnection of the input switch because of the zero phase sequence protection operation;
- emergent disconnection of the input switch because of the zero phase sequence protection operation;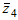 - failure of the switching device number 4 because of the failure of the zero phase sequence protection at voltage disappearance in the bus section I;
- failure of the switching device number 4 because of the failure of the zero phase sequence protection at voltage disappearance in the bus section I;  - disconnection of the bus section I because of the stuff mistakes. [4].
- disconnection of the bus section I because of the stuff mistakes. [4].