


Popchenko
Daria
Faculty of Ecology and Chemical Technology
Department of nature protection activity
Speciality "Mining Indusry Ecology"
FORMING OF ECOLOGICAL NETWORK IN THE DONETSK CITY BASED ON THE TECHNOGENIC RECOVERED ELEMENTS
Scientific adviser: candidate of engineerings sciences, professor Vladimir Artamonov
Faculty of Ecology and Chemical Technology
Department of nature protection activity
Speciality "Mining Indusry Ecology"
FORMING OF ECOLOGICAL NETWORK IN THE DONETSK CITY BASED ON THE TECHNOGENIC RECOVERED ELEMENTS
Scientific adviser: candidate of engineerings sciences, professor Vladimir Artamonov
| Resume |
Abstract
Content- The purpose, tasks and methods
- Relevance
- Scientific novelty and practical value
- The main provisions and normativ-legal base of creation of econet
- A review of the literature
- The concept of the rock dump. Influence of waste dumps on the environment
- The rationale for use of waste dumps mines as artificially recovered elements of ecological network
- Formation of technogenic recovered elements and their use as elements of econet
- Conclusions
- List of references
The purpose of the study is to justify the use of waste dumps as the elements of the ecological network, and to indicate how it is possible to implement.
Tasks:
- to note the main features of econet and analyze developments in this direction;
- to review and analyse the ecological situation of the region;
- to analyze the resources of Donetsk to create local econet;
- to determine the impact of waste dumps on the natural environment;
- spend the formation of technogenic recovered elements for the sake of environment protection.
The idea of the work consists in the fact that in place of the rock dump, thanks to its restoration, the green zone. The purpose of establishing such a zone is further included in the local ecological network. The creation of such a territory will contribute to the improvement of the environmental, economic and, first of all, the socio-cultural environment of the region.
Methods:
- analytical;
- generalize the well-known scientific-technical information;
- abstract-logical.
The total number of waste dumps of mines and concentrating factories in Ukraine exceeds 1100 units, and the territory occupied by them, is 6300 hectares of land, fertile and suitable for industrial and housing construction. Mass of the dump contains a large amount of flammable substances, which often leads to their spontaneous combustion, the evolution of harmful gases, deformation, explosions. From the burning blade medium in size during the year by approximately 15 thousand tons of carbon dioxide, 5 thousand tons of carbon monoxide and a large amount of dust.
In particular, in Donetsk, there are about 130 of waste dumps, which occupy the area of more than 1000 ha. Lack of green areas of general use is – 905 ha (42,8%). Forests and forest plantations Donetsk occupy 6 173 ha, that is 10, 82 % of the total area. The required value is 12.5 %.
Object of rasearch – the waste dumps g. Donetsk
Subject of rasearch – possibility to use the waste dumps as the restored elements of ecological network of the city.
Currently, there are elaborations on the creation of regional ecological network in the Donetsk region, and Donetsk is a part of this network as a potential frame natural kernel. This suggests that the creation of the ecological network in the Donetsk is vital and paramount.
During the creation of local econet is planned to increase the area of green plantations, restore anthropogenically disturbed lands, to take under the special protection of the landscape sections, which will serve as structural elements, that as a whole will not only strengthen the position of the Donetsk, as the potential of the frame of the regional environmental network, but also will improve the ecological condition of the city.
Eco-network is a single territorial system, which is formed with the purpose of improvement of conditions for formation and regeneration of the environment, increase of the natural-resources potential of the territory of Ukraine, the conservation of landscape and biological diversity, place of residence and the development of valuable species of flora and fauna, genetic fund, ways of migration of animals through a combination of territories and objects of natural-reserve fund, as well as other areas of special value for the protection of the environment and in accordance with the law and international obligations of Ukraine subject to special protection [1].
Object econet is considered a separate part, which has the signs of a spatial object – a certain area, boundaries, characteristics etc. To the objects econet include the territory and objects of natural-reserve, water, forest funds, extensive use of agricultural land (pastures and hayfields) [3].
Important elements of ecological network is divided into five steps, or levels: the biosphere, pan European (mainland), national, regional, local [4].
Structural elements of the econet – this is the territory of the ecological network, different functions. To the elements of the National environmental network of national importance include [1]:
- key areas of the ecological network of natural reserves, wildlife management areas, biosphere reserves, national natural parks, regional landscape parks, other significant area valuable natural territories with a strict protection regime, which are combined into a single territorial system of using natural corridors;
- natural corridors – natural or given to natural as areas of land or water surface, which at different levels of the spatial organization of the ecological network provide for the environmental conditions of the continuity, the system of unity and implementation of functions of биокоммуникации. The main natural corridors in Ukraine are of the river Dniester, Southern and Western Bug, the Dnieper river and the Seversky Donets;
- renewed territory, they are separated within the natural complexes, which have undergone to changes under the influence of anthropogenic factors or natural disasters, and which can be recovered through the implementation of relevant activities. Renewed territories are also eroded lands, lands subject to revegetation and etc. The renewed territory ensure the spatial integrity of econet;
- the territory of the buffer allocated with the purpose of prevention of negative impact of economic activities on valuable natural complexes and objects. Buffer areas provide protection key and connective territories from external influences. The buffer zone is the area with the natural or partly altered the landscape that surrounds the most valuable areas of the ecological network and protects them from the effects of adverse external
- The Law of Ukraine "On ecological network of Ukraine" (N1864–IV dated June 24, 2004.);
- The Law of Ukraine "On National program of forming the national ecological network of Ukraine for years 2000–2015" (N1989 from 21 September 2000.);
- Resolution of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine dated 29.11.2001 no.1603 "On establishment of the Coordination council on questions of the formation of the national ecological network";
- Order from 16.10.2009№ 545 "On approval of the List of rare and being under the threat of disappearance, and typical natural plant communities, which are subject to protection and are listed in the Green book of Ukraine";
- Order from 13.11.2009№ 604 "On approval of Methodological recommendations on the development of regional and local schemes econet".
With regard to sources of information on issues of creating econet, it is possible to say, that they are not so many and they all have a certain hierarchy.
The main text is a pan-European strategy for biological and landscape diversity, go further the concept of the establishment of separate national networks of European countries (in Ukraine it is listed earlier in the text normative-legal acts). National concepts are divided into regional (for example, in Ukraine by regions) and local (by individual cities) program.
Access to these sources is limited. The texts of regulatory acts at the level of the country there are no problems, but if the concept still at the design stage – then it represents a series of publications from different authors in different collections of scientific conferences, scientific journals, etc. It is characteristic for regional and local eco-networks. So, in the internet you can find links to the already adopted a programme for regional eco-networks (Odessa, Dnipropetrovsk regions), but there is no direct access to the text of these programs.
In my opinion, it is necessary to create an information portal in the internet, which have concentrated all of these concepts and programs in one place. It is much would accelerate the development in the direction of creating eco-networks of different level, and the pan-European ecological network, as a whole.
In the process of coal extraction by underground way to the surface is the breed of preparatory and clearing works, cleaning and restoration of mountain developments, that the usually in one blade. Its quantity depends on the development system, the mining-geological conditions, method of dredging of coal and etc. Issued on the surface breed is stored in the different size and the form of dumps (conic, flat, combined). They occupy large areas of agricultural land, reduce the performance of adjacent land, pollute the atmosphere gases and dust, violate the hydrogeological regime areas. In addition, water (mainly toxic), flowing down from the heaps, and destroy the vegetation on the adjacent territory. Dumps, located in the vicinity of settlements, worsen sanitary-and-hygienic conditions of life of people[6].
Violations of the earth's surface directly associated with the production of mining works are not limited to the areas of mining leases and territories, which are allocated for the disposal of waste production, but also have an impact beyond their borders. Actually dimensions of the disturbed lands considerably exceed those areas occupied by the objects of the enterprise.
Waste dumps consist of a mass of dry substances (overburden and coal carbonaceous shale) and foundations (part of the earth's surface). In the period of its existence the dumps do not remain constant. Their surface and form for a variety of reasons change [7].

Fig.1
– Cone rock dump

Fig. 2 – Flat rock dump
The
main factors of
negative influence of waste dumps on the
natural
environment are:
Fig. 2 – Flat rock dump
- violation of the natural landscape of the earth's surface;
- pollution of the atmosphere;
- violation of the hydrogeological regime of the surrounding areas.
- chemical
and radiological pollution soil and water.

Fig. 3 – The burning rock dump
The proposed technology takes into account interests:
- land owners and land users (no need to change the form of ownership);
- the local population (improvement of living conditions);
- power (participation in the implementation of the national program of ecological network);
- biocenosis (contributes to the restoration of biodiversity, reduction of pollution of the environment).
In Donetsk there are about 91 rock dump coal enterprises. These dumps occupy nearly 800 hа square of the city. Feature of their forms and status can be seen on the diagram (fig. 4).
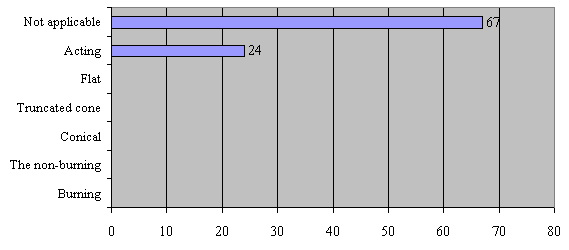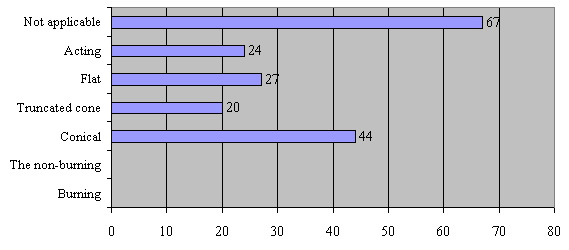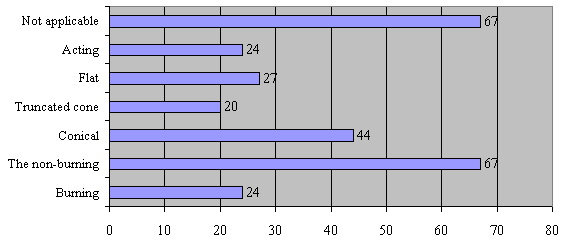
Fig.
4 – Diagram of
performance
At the diagram we can see that the majority of waste – not applicable (67 with 91 units.), the majority of waste – burn (53 units with 91). The most common form conical (44 units with 91 units.).
The recovered territory is the territory subjected to changes under the influence of anthropogenic factors and natural disasters, and which can be recovered through the implementation of relevant activities. Renewable territory ensure the spatial integrity of ecological network[2].
In the submitted work is also used the term "technogenic recovered element". What does it mean?
Landscape – the basic unit of the physico-geographical zoning of – genetically uniform spaces with the same relief, geological structure, climate, the general character of the surface and underground waters, natural combination of soil, plant and animal communities.
Technogenic landscape – modified or artificially created by man on the basis of natural landscape, natural balance which is constantly kept in the man [8].
Similarly, it is possible to assert, that technogenic recovered landscape – it is artificially restored, to establish the natural balance, disturbed landscape.
In our case, the word "landscape" is substituted for "element", to emphasize that this territory is part of the ecological network as its structural element.
First of all, in the econet you can include non-performing non-burning dumps. At the moment, these objects are characterized by the various states, as you can see in the diagram (fig. 5).
Fig.
5 – Chart
characteristics
not applicable not burning dumps
The chart indicates that most of the dumps are not involved and not converted.
For the inclusion of non-burning of non-performing dumps (43 units) in the structure of econet, they must be remediate: to reform, to fall asleep the ground of corresponding quality and properties, and to plant perennial plants. At the most favorable result reclamation, these areas must submit landscapes and biodiversity of the area, with the purpose of their further use as a natural cores.
In turn, recultivation (without reconfiguring) not burning of non-performing dumps will allow to increase the area of green plantings on the 156,77 ha. And given the size of the sanitary protection zone in the amount of 300 m along the perimeter of each of the blade, then much more. These measures are very actual in the conditions of deficiency of green plantations and forest land in the city of [9].
To determine the extent of reclamation works in the first place it is necessary to estimate the degree of landscaping rock dumps at the moment. For this purpose it is proposed to apply the greening heaps (using, as a helper program Google Earth), which characterizes the ratio between the area of green plantations in the area of rock dump, free from planting(%).
Determination of the coefficient of landscaping dumps is one of the primary operations of the econet of the Donetsk city.
On the basis of the obtained for each blade factors, you can determine the order of re-planting and the degree of necessary additional landscaping, taking the benchmark blade, which most accurately represents landscapes and biodiversity of the area.
The non-burning dumps, mainly, are the source of the formation of dust. It is known that the average of 1 square meter of surface rock dumps is blown off by about 50 mg of suspended solids per day.
Solid aerosol particles deposited on the leaves, stems and branches of plants and the amount of dust accumulation, especially on the leaf surface for various breeds of plants, different.
Table
1 – List of plants and
their
properties dust
removal
Analysis of the data in the table shows, in the first place, at a very low dust collecting properties of the bushes, second, the mass of dust accumulation is not in direct dependence on the total area of leaf surface.
It is possible to draw a conclusion, that the most effective catching dust is ash green, mulberry tree, maple yacenelistnyii, canadian poplar and willow, which are recommended for the creation of the sanitary protection zone within waste dumps [10]. At the same time, SPZ immediately gets a role of the buffer zone as an element of ecological network.
Thus, turning waste dumps in the elements of ecological network, we not only ensure the usefulness of its structure, but also solve one of the main problems of Donetsk: the problem of waste dumps mines, which occupy a huge area of land resources and damage the environment and health of the population.
A huge man-caused load on Donbass forces with the issue of the use of the breed, which is extracted and problems of the existing rock dumps, because the successful solution of these tasks leads to:
1) the decision of environmental problems:
- reduction of air pollution by toxic gases, dust and etc.;
- reduction of water pollution Donetsk region sinks with heaps;
- decrease in extraction of various natural resources and the conservation of natural resources for future generations by developing resources, which are already there;
- reduction of deformations of the earth's surface (ground failures, houses, to the ravines and etc.)
- he reduction of contamination of arable land area, outside the city, which could be used for agricultural land.
- warning cluttering up land in the city, which could be used for better purposes;
- the emergence of workplaces;
- improve the health of people, living on the territory of Donbass;
- improve the condition of the city.
The problem of waste dumps finds its place in their transformation into elements of the econet of the city with the prior artificial regeneration.
- Закон України "Про екологічну мережу України" від 24 червня 2004 p. № 1864–IV//Урядовий кур'єр. — 2004. — 14 вересня. — № 172.
- Закон України "Про Загальнодержавну програму формування національної екологічної мережі України на 2000–2015 роки" від 21 вересня 2000 р. №1989 111//Урядовий кур'єр. — 2000. — 8 листопада. — № 207.
- Остапко В. М., Глухов О. З., Блакберн А. А., Мулєнкова О. Г., Ендеберя А. Я. Регіональна екологічна мережа Донецької області: концепція, програма та схема/Під загальною ред. Остапко В. М. – Донецьк: Видавництво – ТОВ ТЕХНОПАРК, 2008. – 96 с.
- Гавриленко О.П. Екогеографія України: Навчальний посібник. – К., 2008. — 646 с.
- Екомережі – Інформаційний екологічний портал ECOLOG [електроний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://ecolog.at.ua/index/0–21
- Охрана окружающей среды в горной промышленности. В.И. Николин, Е.С. Матлак. – Д. : Вища школа. Головное издательство, 1978. – 192с.
- Техногенные последствия закрытия угольных шахт Украины: монография/Ю.Н.Гавриленко, В.Н.Ермаков, Ю.Ф.Кренида и др. – под ред. Ю.Н. Гавриленко, В.Н. Ермакова. – Д.: «Норд-Пресс», 2004. – 631 с.
- И. Добровольский И.А. Эколого-биогеоценологические основы оптимизации техногенных ландшафтов степной зоны Украины путем озеленения и облеснения (на примере Криворожского железорудного бассейна). Автореф. ... д. б. н. Днепропетровск, 1979.
- Поволоцкая И.В. Рівень озеленення міста Донецька як екологічний показник сталого розвитку – Охорона навколишнього середовища та раціональне використання природних ресурсів – 2010/Матеріали ХХ Всеукраїнська наукова конференція аспірантів і студентів. – Донецьк, ДонНТУ – 2010.
- Поволоцкая И.В. Озеленення прилеглих територій породних відвалів – засіб покращення навколишнього середовища – Сучасні проблеми екології та геотехнологій – 2010/Матеріали VII Міжнародна наукова конференція студентів, магістрів та аспірантів. – Житомир, ЖДТУ – 2010.