
Yungina Irina
Faculty ecology and chemical technologies
Department of applied ecology and environmental protection
Speciality "Ecology of chemical technologies"
Monitoring of heavy metals in the ponds of city Makeevka
Scientific adviser: professor's assistant Troshina Olena
Introduction
The pollution of natural water makes threat to life and health, as well as the existence of the biosphere as a whole. That’s why the estimation of state of water ecosystems under the influence of anthropogenic factors is one of the most actual tasks for the protection of surface water resources.
1. Aim and tasks
The aim of the work is studying of existing condition of ponds of town Makeevka with the object of analysis and estimation of quality of their water as reservoir of culture and welfare usage.
2. Actuality
Water resources of rivers and lakes in the Donbass region very modest. If, moreover, take into account the small amount of rainfall and high evaporation them, it becomes clear why the problem of water supply for the region is the number one problem.
In the Donbass region daily use large amounts of water. The use of large volumes of water, pollution sources, sewage and waste cause great harm to water bodies.In conditions of high developed industry and large quantity of population of Donbass they use here large quantity of water everyday.
The Donetsk region takes first place in Ukraine at dropping of poluted waste water. The main polluters are plants of metallurgical, chemical industry, heat–power engineering, coal mines. Discharge of large quantity of untreated waste water, and long–term accumulation of polluted substances led to the fact that most water bodies area is classified to the category of dirty and very dirty ones.
3. Science novelty
In first time carried out estimation of water in natural reservoirs located in the city of Makeevka and study the dynamics of changes in water quality ponds.
4. Review of literature and elaborations on a theme
Valuation of water quality in rivers and lakes has been made in accordance to "Sanitary rules and standards of protection surface waters from pollution" [1-3]. These rules set Two categories of reservoirs (or its parts):
- drinking water and cultural purpose;
- water fish–utility vehicles.
Ingredients and properties of water of water bodies of the first type should corresponded standards alignments, located in the watercourse at a distance of 1 km above the nearest stream, and not flowing bodies of water – in a radius of one kilometer from the place of water use [4-7]. The ingredients and properties of water in fish–ponds have to conform to the standards in place of release of waste water at the scattering release (the presence of currents) in the absence of a scattering of release – no more than 500 meters from the place of registration.
Standardized values of water reservoirs [8]:
- content floating impurities and suspended solids;
- smell, taste, color and temperature of the water;
- pH value, the ingredients and concentration of mineral impurities and dissoled oxygen;
- biochemical oxygen demand;
- pathogens, the concentration and composition of toxic and harmful stances.
- discharge waste water into waters, if it can be alloided (using sound technologies, processes and systems, waterless, and defense re–supply);
- if waste water contain valuable wastes which may be recycled;
- if waste water contain raw material, reagents and products of enterprises in quantities, exceeding technological losses;
- if waste water contain substances for which MPC is not established.
- The state of coastal areas considered surface water of the city Makeevka is unsatisfactory, except in the pond "Divo. "
- The main sources and courses of ponds pollution are: systematic water pollution by sewage from nearest houses, agricultural fields and horse farm, the closeness of ponds to the car line, washing cars in ponds, the presence of petrol–station, closeness to plants and mines.
- The usage of examined reservoirs (except pond «Divo») is not expedient for cultural and welfare aims.
- Лукашевич О.Д. Экологические и технологические аспекты оценки качества природних вод для производственного и хозяйственно–бытового использования // Вода и экология, 2007. – Т. 1, вып. 1. – С. 3–16
- Felfoldy L. J. M. A new system for the biological qualification of water // research in water quality and technology. – Vol.3. Research center for water resources development. III Institute for water pollution control. – Budapest, 1976. – 37 p.
- Felfoldy L. J. M. A biological vizminosites. 3 Javitott es bovitett kiadas // Vizugyi hidrobiologia, 9 kotel. – Budapest, 1980. – 263 p.
- Статистичний щорічник Донецької області за 2008 рік. – Д., 2009. – 100 с.
- Ободовський О.Г. Гідролого–екологічна оцінка руслових процессів: (на прикладі річок України). –К.: Ніка–центр, 2006. – 274 с.
- Общественный экологический Internet-проект EcoLife [электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа:
http://www.ecolife.org.ua/index.php - Пельтихин А.С. Особенности рек Донбасса и рекреация. Сб. материалов научно-практической конференции «Туризм – перспективная отрасль экономики Украины». – Донецк, 1995. – С. 123–124.
- Паладий И.П., Молодан Г.Н. Социально-экономические аспекты сохранения аборигенной биоты реки Кальмиус. Конференция ДонНТУ, 2004. – с. 17–21.
- Программа восстановления и поддержания чистоты и водности малих рек Донецкой области/ под ред. Яцика А.В. – Донецк, 1999. – 415 с.
- Сафронова Н.С., Веницианов Е.В. и др. Комплекс аналитических методов для определения содержания и форм существования тяжелых металлов в природных водных объектах. //Водные ресурсы. Т.24. № 4, 2007. – с. 477 – 485.
Harmful and poisonous substances are normed at the principle LHI (limiting harm index), i.e. the most probable harmful effect of each substance [9-10].
«Sanitary rules and standards of protection surface waters from pollution» prohibit:
It is extremely important for the state of water bodies is to monitor heavy metals. The term "heavy metals" is associated with a high atomic mass of element. One of the signs, which allows to refer to heavy metals, is their density.
Estimation of the level of reservoirs pollution by hard metals is actuale problem. It is connected with that hard metals have cumulativeness and toxycologess for all alive organisms and hidrobionts privately.
Assessing the level of water pollution by heavy metals is an actual problem [11]. This is due to the fact that heavy metals have cumulativeness and toxicity for all living organisms and aquatic organisms, in particular. The table shows the rates MPC for heavy metals in water bodies for various purposes.
Table – Maximum permissible concentration of some heavy metals in water reservoirs
| Name of element | Maximum possible concentration, mg/dm3 | Class of dangers | |
| for reservoirs of the drinkable and cultural and welfare appointment | reservoirs of the fishing appointment (for seas) | ||
| copper | 1,0 | 0,001 (0,005) | 3 |
| zinc | 1,0 | 0,01 (0,05) | 3 |
| lead | 0,03 | 0,006 (0,01) | 2 |
| cadmium | 0,001 | 0,005 (0,01) | 2 |
| cobalt | 0,1 | 0,01 (0,005) | 2 |
| chrome (III) | 0,5 | 0,07 | 3 |
| chrome (VI) | 0,05 | 0,02 | 3 |
| nickel | 0,1 | 0,01 (0,01) | 3 |
| manganese | 0,1 | 0,01 (0,05) | 3 |
| mercury | 0,0005 | 0,00001 (0,0001) | 1 |
| iron | 0,3 | 0,1 (0,05) | 3 |
| molybdenum | 0,25 | 0,001 | 2 |
5.Received results
It was examined five ponds, situated at the territory of the town Makeevka: Municipal pond №1, 30th pond, pond «Cheremushki», Municipal pond «Gorki» and pond «Divo». According the official data, throwing of waste water into these reservoirs is not made. But for today the flowing of waste water from country settlement, the closeness to car line and petrol–station, seasonal washing of cars in all ponds, except pond «Divo», replacement of uncontrolled dumps near the reservoirs have place. Besides, at all ponds, except for the pond «Divo», beach territory is in bad condition: absence of sand, urns, beach equipment and drinkable fountains, the territory is polluted, their cleaning is not made.
Researching of the water quality in reservoirs of cultural and welfare appointment has been made in a period from 2006 till 2011 year. For making analysis the data of the systematic researches has been used, which has been made by municipal Sanitary Station. The control has been made according to following factors: smell, presence of admixtures, maintenance of suspended elements, hydrogen index pH, mortal oxygen, biochemical oxygen demand (BOD full), chemical oxygen demand (COD), pathogenic organisms, maintenance of iron, chlorides, ammonia, nitrites, nitrates, phenols, oil products. The results of analysis the water in ponds of town Makeevka are at the picture:
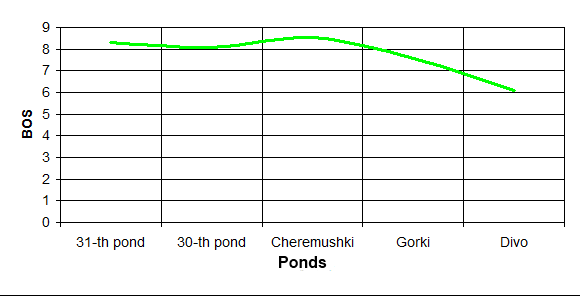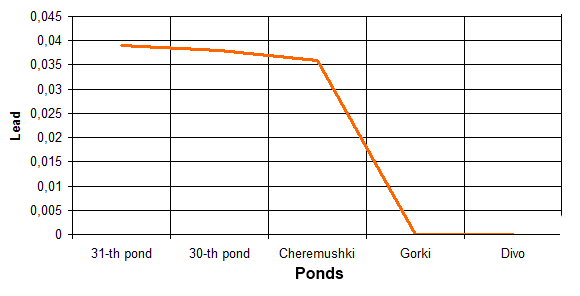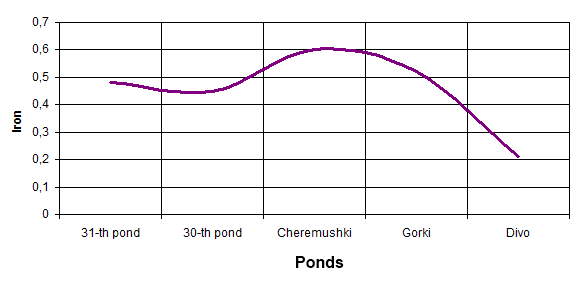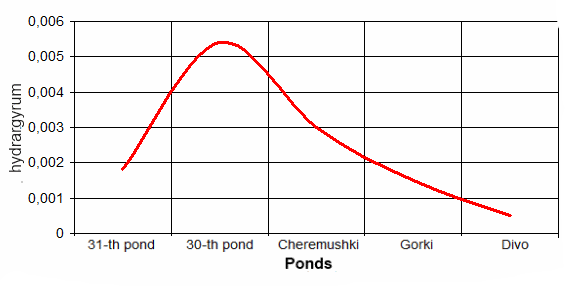
The results of the analysis of water ponds Makeevka
Conclusion
Thе following conclusions have been made as a result of made work:
In writing this abstract master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2011. Full text of the work and materials on the subject can be received from the author or his manager after that date.