|
|
|
| DonNTU | Master's portal |

| Resume |
The purpose of master’s work — working out and research of new methods of processing of production wastes of the limestone stored in sailings.
Idea of work — the complex approach to working out of technology preparation limestones for maintenance of improvement quality production according to requirements of metallurgical and building industries.
Problems:
studying of physicomechanical properties of the consolidated production wastes of the limestones, which are a mix of limestones by fraction of 0-15 mm and a sandy-argillaceous material;
the analysis results of the spent researches of selective crushing, as method of enrichment the consolidated waste;
studying of design features the rotoring thrower, which principle of work – selective crushing;
research of interaction of conglomerates with rotor's blades of the thrower;
calculation parameters of the effective form of a casing of the thrower (providing repeated impact of conglomerates);
calculation probabilities of realization the central and excentric blows blade rotoring thrower on conglomerates depending of size an initial material, quantities blades and frequency of rotation of a rotor;
definition the reasons of low efficiency of the thrower at destruction of large conglomerates;
working out of a complex technical actions for increase of efficiency this mineral process;
research of the problems arising at sifting production wastes of limestones, concerning to difficultly mineral process to materials because of high humidity and the big maintenance of ilisto-clay materials;
the review new types of sifting surfaces and racket with purpose of increase efficiency of process dry sifting;
recommendations about carrying out of production tests new types of sifting surfaces and rackets.
Object of research — the consolidated production wastes of limestones stored in a sailing.
Subject of research — technology of enrichment of the consolidated production wastes of the limestones stored in a sailing.
In connection with exhaustion of mineral resources the especial urgency is got by a solution of a problem of rational use stocks of mineral raw materials, application of technics and technology which will allow to overwork both earlier stored in sailings, and a current waste of mountain manufacture under a condition observance of requirements State standard’s and consumers to quality of production.
Among many technological and organizational problems which are connected with rational use of bowels and the extracted mineral raw materials, prolongation of service of deposits of limestones, reduction of losses of a mineral, at all stages of technological process concern the sharpest. In hills of limestones there are clay impurities. Such structure of deposits at carrying out of mining works causes the considerable maintenance of harmful impurity both in raw materials, and in finished goods. Search of new methods and technologies of enrichment of limestones is necessary for the decision of this problem and before the formed waste of their manufacture.
On the majority of the mining enterprises of limestones carrying out extraction the most part of mineral raw materials is enough not only isn't used, but also demands expenses for its warehousing, and also worsens an ecological situation of the given region. As a rule, this waste represents difficultly mineral a mix of the recrushed limestones and ilisto-clay materials [3].
Processing of production wastes the limestones stored in sailings, raises efficiency of a national economy, improves ecological conditions of the given region.
introduction of selective crushing as enrichment method at processing of sailings of production wastes limestones and definition of its characteristics;
the theoretical substantiation of design features the rotoring thrower as equipment for selective crushing of conglomerates and decrease in the maintenance of sandy-argillaceous materials in rubble at the expense of reduction of a thickness of the clay cover covering each piece of rubble on all its surface.
Survey of researchData on application of enrichment by a method of selective crushing (branch of sandy-argillaceous materials from limestones) at processing difficultly mineral processing at dry classification of the consolidated production wastes of limestones in domestic and world practice aren't revealed.
In DonNTU of data on working out and existence of such method enrichment of production wastes of the limestones stored in a sailing, it is not revealed.
Production wastes of limestones represent a mix of the explosion recrushed by energy and mechanical crushing of limestones with accompanying harmful impurity: clay, slates, sand, loams fraction of 0-15 mm [7].
The waste of limestones stored in a sailing is difficultly mineral processing for following reasons:
for decades of storage of a waste there was their consolidation (possesses coupling 30-50 MPа) – for this reason for processing a considerable quantity of conglomerates arrives. Such conglomerates don't collapse sifting and considerably pollute rubble a lime, raising the maintenance in it of harmful siliceous impurity for maximum permissible values;
high humidity of a waste in aggregate with the maintenance of ilisto-clay particles complicate their classification sifting for the account sticking deck;
the limestone surface is covered by a clay cover in the thickness of 1-3 mm which doesn't leave sifting [7].
Way of enrichment applied under such circumstances is wet screen separation. However in Donbass water resources are limited, as building elutriator of slurry is undesirable. The main reason which doesn't allow to apply wet screen separation, absence of a commodity market wet slurry is. Therefore perspective ways are dry ways of processing of a waste of the limestones stored in a sailing.
In the Company "VIDIS" which are carrying out processing of a sailing of flux limestones of Dokuchaevsky fljuso-dolomitnyj industrial complex, for the purpose of destruction of conglomerates and removal of a clay cover from a rubble surface the method of selective crushing with application rotoring thrower MM-1 (the non-standard equipment) is introduced [8].
The Rotoring thrower MM-1 represents an all-metal rotor on which four demountable blades, placed in the case from a wearproof steel are fixed. In process of deterioration of the blade are replaced with the new. Average term of their operation six months at a continuous operating mode.
The thrower is established between dumping drum of the tape conveyor (submitting a initial material on the equipment) and a roar on which extraction from rubble fraction of fraction of 5-15 mm of 0-5 mm, formed is carried out at destruction of conglomerates and a clay cover of rubble (picture 1).

An initial material (rubble fraction of 5-40 mm) moves the conveyor on directing plate which provides initial material giving on the center rotoring the thrower. After blow about the blade rubble pieces, many times hitting about case walls, unload below on a racket. As a result of blow small durability clay inclusions, clay and conglomerates collapse, and limestone (stronger) thus doesn't collapse.(picture 2).

In that case there is a selective crushing – the basic way of enrichment different durability a stone material in the course of its processing. Selective crushing is carried out as a result of more intensive destruction of less strong breeds in the course of crushing and the subsequent branch of the crushed material.
Process of destruction of a material depends on a piece arrangement rather blade a rotor and from depth of its penetration into a working zone of a rotor. If depth of penetration exceeds half of size of a piece (that is direct central blow): in the first phase cracks are formed, in the second — making a start one from another, piece parts are rejected blade with different speeds (picture 3).

If depth of penetration of a piece less than half of its diameter (that is blow eccentric): resistance blade is given only by weight of a chopped off part A, and last part of a piece Б, remaining in rest, "does not accept" participation in shock process (picture 4) [1].

Table 1 — Dependence of overall performance of the thrower on humidity of a material and frequency rotation of a rotor of the thrower
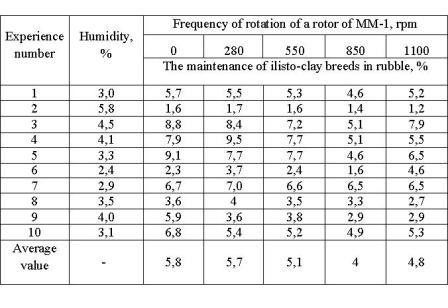
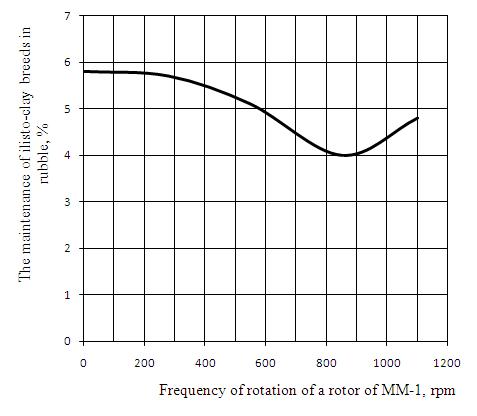
Optimum frequency of rotation of a rotor is frequency at which energy of blow of blades on a processed material is sufficient for destruction clay, conglomerates and a clay cover of rubble, but isn't sufficient for destruction of rubble of limestone. As a result of the spent tests it is established that for the designed throwing car frequency of 850 rpm is optimum (picture 5). Decrease in efficiency of application of the throwing car at frequency of rotation of a rotor over 850 rpm is caused by sharp increase in speed of the air stream created by blades which carries away rubble pieces, interfering with blow beat a rotor on rubble. At frequency of rotation 850 rpm energy of blow there are less doesn't allow to destroy conglomerates. At frequency of rotation of a rotor over 1000 rpm it is observed not only destruction of conglomerates and a clay cover of rubble, but also the limestone.
Productivity the rotoring thrower depends on its diameter, numbers and forms blades; size and physical properties initial and levigated a product; uniformity of a initial material; design features [4].
The made of Company "VIDIS" calcareous rubble is a mix of the rubble allocated at processing of a sailing of a waste and rubble, allocated at processing of a current waste drobilno-obgatitelnoj factories.
The rubble allocated at processing of a current waste, contains 1-2 % of ilisto-clay particles, on its surface there is no clay cover.
Introduction of selective crushing at enrichment of production wastes of limestone in Company "VIDIS" has allowed to lower the maintenance of ilisto-clay breeds in rubble to 4 %.
At mixing of two kinds rubble the received mix meets requirements operating State standart to the maintenance of clay particles in rubble [2].
Increase of efficiency of enrichment of the waste stored in a sailing, is a priority problem as decrease in clay particles in rubble to 3 % will allow to realize rubble taken of a waste without its mixing with rubble, taken of a current waste. Thus, the factor of dependence of capacity of the enterprise from quantity of a waste of drobilno-concentrating factory arriving for processing is eliminated.
At the enterprise the throwing car has been made and introduced, but the received results specify in presence of the constructive lacks which elimination is possible only after calculation and the analysis parameters of occurring process of selective crushing.
Selective crushing is effective, but not in the unique way of enrichment of the waste stored in a sailing.
Now at the enterprise there is no technical substantiation of introduction or refusal of introduction of innovative technologies sifting and new types of sifting surfaces (self-cleared in the form of a harp corrosion-proof decks [5]).
So introduction of the equipment, allowing to make division on smaller fractions, will allow to increase volume of output of rubble and to lower volume of output of limestones fraction of 0-5 mm that will raise economic indicators of manufacture at the expense of a difference of the prices realization of production.
Innovative multifrequency rackets of technology Kroosh are intended for division into classes fraction difficult mineral procession (damp and clay) materials.
Technology Kroosh is the vibrating technology representing set of ways and devices for polyfrequency influence on loose (in this case) environment. At the heart of technology the influence principle on the loose body passing through a roar, the spectrum of the frequencies corresponding to a frequency spectrum of the given concrete loose body lies. As a result the loose body gets properties of a liquid. Outwardly it looks as movement turbulent a stream of a layer of a loose material on a sifting surface. In such condition in a layer the phenomenon of a segregation and small particles for very short time sharply becomes more active pass through a layer to a grid and further through grid cells.
On the loose body which is on a racket, the body which is with it in direct contact can influence only, such body is the sieve. The grid which transfers to a loose body of fluctuation of the big energy and a wide frequency spectrum, itself fluctuates in a multifrequency mode, and, depending on a solved problem, receives peaks of accelerations from tens to hundreds (for comparison — acceleration of a sieve and a box inertial rackets — no more than 5 g). Besides that these accelerations are transferred to a loose body, they provide continuous self-cleaning deck in a roar operating time. It is the second basic feature of technology Kroosh [6].
As a result of operation of the throwing car within 2009-2010 it is established:
conglomerates in diameter of 5-35 mm collapse completely;
pieces dry clay in diameter of 5-35 mm collapse completely;
pieces damp and fat clay of 5-35 mm collapse on 40-50 %;
conglomerates in diameter of 35-100 mm collapse partially (the size of conglomerates decreases for 10-30 %);
the clay cover covering each piece of rubble, collapses on 20-30 %.
From results of operation it is visible that application of the throwing car at processing of sailings carbonate breeds effectively, is available potential for improvement of quality of processes of processing and accordingly improvement of quality of a made commodity output.
Thus, the theme of studying of theoretical bases of work of the equipment for selective crushing for the purpose of its modernization and hanging of its efficiency is industrially claimed.
|
When writing this abstract master's work is not done yet. Final completion: December 2011. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after stated date. |
Роторные дробилки. Под ред. В.А. Баумана. – М.: «Машиностроение», 1973. – 272 с.
М.А. Зимин, Ф.В. Панфилов, А.А. Матросов, И.А. Афонин. Руководство по обогащению отсевов дробления и разнопрочных каменных материалов. – М.: СОЮЗДОРНИИ, 1992. – 66 с.
ГОСТ 23845-86 «Породы горные скальные для производства щебня для строительных работ. Технические требования и методы испытаний».
Серго Е.Е. Дробление, измельчение и грохочение полезных ископаемых: Учебник для вузов. – М.: Недра, 1985. – 285 с.
Промышленные сита. — [Электронный ресурс] — режим доступа: http://www.sitoprom.com.ua/products/industrial%20screens/Metalevi/arfoobrazni_sita
Опыт применения технологии Kroosh для просеивания нерудных сыпучих материалов. — [Электронный ресурс] — режим доступа: http://www.kb-intel.com.ua/product/19/
| Resume |