Abstract
- Introduction
- 1. History of studying of a problem
- 2. Results robots
- 2.1. Characteristic of Polezhakovsky dumps of DSP
- 2.2. Impact of DSP and Polezhakovsky dumps on a surrounding medium
- 2.2.1. Atmosphere
- 2.2.2. Soil
- 2.2.3. Hydrosphere
- 3. Recommendations about improvement of a state of environment
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Work urgency: оOne of manifestations of anthropogenous environmental impact is change of speed and an orientation of geochemical processes. The balance of metals in the territories which are affected the mining and metallurgical enterprises rather sharply changes. Donbass belongs to the most densely populated and industrially developed regions of the world on scales of mining and their processing, and also a wastage by training. Except mining and processing industry in formation of a wastage makes the contribution and ferrous metallurgy, also well developed in our area. Metallurgical slimes of the enterprises of Donbass are stored in shlamonakopitel by total capacity more than 40 million m3 which practically all are overflowed. The loose capacities near the enterprises aren't present, and the warehousing organization in the distance will lead to the considerable material inputs and an aggravation of symptoms of a surrounding medium.
Work purpose: the purpose of a master's thesis consists in an assessment of influence of steel works, and also their wastage on a surrounding medium.
Research problems:
- Analysis of the current state of a problem of environmental by metallurgical branch.
- Studying of influence of Donetsk steel plant on the hydrosphere, a lithosphere, the atmosphere.
- An assessment of extent of influence of a wastage of Donetsk steel plant on the hydrosphere; .
- Establishment of regularities of change of chemical composition of underground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps of DSP during the period 2006–2010.
- identification of the centers of pollution of underground waters and the reason of the increased concentration in them.
- optimization of a local network of supervision, for improvement of monitoring of underground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps of DSP
Object of researches: the surface and underground water in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps.
Subject of these researches: monitoring of a condition of the hydrosphere in a zone of influence of a wastage of ferrous metallurgy.
Research techniques which were applied in this work:
- Systematization and analysis of data.
- Methods of statistical data processing.
- Calculations of complex indexes of pollution.
- Methods of the space analysis.
Scientific novelty of work: complex impact of metallurgical industry on a surrounding medium provides communication between concrete types of industrial wastes and structure of available pollution of ground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps.
Practical value: пthe obtained data can be used further, for perfecting of technology of warehousing of a wastage, and as for development of recommendations about decrease in pollution of the atmosphere and the hydrosphere. Results of a mapping can be used at research of quality of a surrounding medium in the adjacent territory.
Personal contribution of the author: it is settled an invoice an integral index of pollution, basic elements pollutants are defined, dynamics of change of a condition of underground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps is traced.
1. History of studying of a problem
Long-term researches of the Soviet and foreign scientists (to Yirzhel V., Balek Ya., Tyutyunova F.I) is established that underground waters of the urbanized territories are exposed to essential changes in the quantitative and quality relations [1, 2, 3]. It is everywhere noted reductions of operational stocks of fresh underground waters owing to an intensification of water selection and their pollution. Such changes grow out of global processes of an urbanization and production integration [4].
The urbanized territories where lives now 42 % of urban population of the globe, make only 4 % of the area of our planet at what its annual increase is at level of 0,05–0,4 million hectares [4]. Body height of the cities and city agglomerations is accompanied by alienation of arable lands, concentration of industrial production, increase in dumping of industrial and household wastes and, therefore, pollution of underground waters.
Metallurgical industry of Ukraine on volume of production takes the seventh place in the world. Production capacity of mining and metallurgical complex of Ukraine in recent years – a base element of economy of the state. The mining and metallurgical complex is the main donor of the budget, providing more than 40 % of receipts of currency. Its part in gross domestic product comes nearer to 30 % [5].
In ferrous metallurgy of Ukraine the integral amount of annually loss iron makes 35 million t, a half of its losses is the share of the mining industry where it generally contains in the wastage representing low-magnetic oxidized ores not giving in to enrichment of processing applied in the ways of iron-ore raw materials.
Need of development of dumps of metallurgical production is predetermined by social and economic, sanitary-and-epidemiologic and ecological conditions of their placement and the existing scheme of operation. In recent years options of utilization of all quantity of a being formed wastage [6, 7] were developed.
Following authors were engaged in questions of a salvage of metallurgical manufacture: V.I.Rostovsky, А.С. The cooper, O.I.Radzhi, A.V.Kravchenko [8, 9].
Environmental problems of metallurgical production are shined in Gruzdev V. works of Page [10], Matveev A.N. [11], etc. authors.
Scales and nature of pollution of environmental environment the enterprises of a metallurgical complex are bound to level of applied technologies, their environmental friendliness, quality and quantity of used raw materials, volume and structure of emissions, dumping and a rigid wastage, a geographical position of the enterprises, nature of dispersion of pollution and influence on landscapes, ecosystems and their components [10].
The main source of information which covers environmental problems of a studied site (Polezhakovsky dumps of DSP), reports on earlier carried out works [12, 13] are. Dumps and a slimestore are located in an environment of various objects: the farmland to the South from them, inhabited sector of the settlement of Polezhakovo, a pond in the Anonymous beam, power lines, highways, production sites, buildings and constructions of the various enterprises. Some of them are in an influence zone from dumps. Influence of dumps is expressed in distribution of dust emissions to free air, their deposition on soils and a vegetative cover and in pollution of the surface and underground water. The farmland and inhabited sector of the settlement of Polezhakovo is outside of the established sanitary and protective zone and actually a zone of influence of the dumps provided to development.
Thus, the problem of influence of a wastage Donetsk on a surrounding medium and, in particular, on the hydrosphere, was given not enough attention. This master's thesis also is devoted to this problem. In further researches it is necessary to establish structure of an underground and surface water, its dependence on DSP wastage, to establish possibility of recycling of a wastage of ferrous metallurgy in a national economy.
2. Results robots
2.1 Characteristic of Polezhakovsky dumps of DSP
The pedigree and slime dump is difficult by the inhomogeneous wastage on structural and real parameters. In the course of researches three most widespread groups of waste products were allocated:
– the wastage of coke-chemical production lying in the basis of a dump, fragmentary leaving a surface of a slope and presented by a different scrap unassorted pedigree material with traces of aeration and oxidation which are shown in change of primary dark gray coloring to yellowish brown, brown and reddish-brown;
– the ferriferous wastage of metallurgical production prevailing in an upper of a dump, presented to dense friable shallow and short-grained sand-alevritisty a material from dark gray to black color;
– an other wastage among which the wastage of structural materials presented by the beaten brick, the beaten glass, concrete prevail, etc.
Delivery of a wastage to a dump is carried out aroundly the clock generally by rail and partially by motor transport. During winter time prophylaxis against regelation of a wastage is made.
2.2 Impact of DSP and Polezhakovsky dumps on a surrounding medium
2.2.1 Atmosphere
The main source of pollution of the atmosphere from DSP, is the arc furnace of a wood particle board No. 1. Of total of the harmful substances entering in the atmosphere from steel works, about 20 % make a dust and about 80 % harmful chemicals. In turn harmful chemicals include: 78 % of dioxide of carbon, 15 % of sulfur dioxide, 6 % of dioxide of nitrogen, 0,7 % hydrocarbons.
Emission of pollutants nonuniformly on the melting periods, a maximum of a dust to allocate falls on the periods of melting and a bath purge oxygen and at work of gasoxygen torches.
The greatest emission of gaseous pollutants is observed when smelting foundry cast iron for production of molds.
Results of an assessment showed that the considered territory on mid-annual values of meteorological parameters is characterized low pollution the atmospheres, during the summer period (in connection with body height of number of inversions) – moderate, and in the inferior years – raised. It is important to note also that in summertime pollutants are poorly washed away by settlings.
Level of pollution of free air at development of Polezhakovsky dumps doesn't exceed the established sanitary standards on border of a sanitary and protective zone of dumps. Upon termination of operation of considered sites of Polezhakovsky dumps their complete isolation and gardening is planned.
2.2.2 Soil
Soils the studied territory test both physicomechanical, and the physical and chemical transformations expressed in change of primary structural and real signs and in formation of new type of soils. The most intensive changes are fixed visually on the color, the characteristic development of new mineral types.
Pollution soils the adjacent territory from dumps probably only in the course of a dispelling of pulverous particles of a wastage by a wind. It proves to be true well consistent directions of propagation of the allocated aura of integral pollution of soils from a pedigree dump with prevailing east directions of winds. Thus distribution of elements round a polluter – dumps – is caused by gravitational differentiation of pulverous particles.
The zone of influence of a pedigree dump and slimes dump, Zc allocated on an integral index, repeats a contour of a dump and is coordinated with prevailing east direction of winds extends to the west. The highly hazardous extent of pollution established within a slimes store of ESPTs, doesn't leave for its borders and is bound to a shallow layer of the slimes placed at the bottom of its bowl. The basic anomaly formation elements are cadmium, lead, Hydrargyrum and the manganese which auras have various abundance and a space priurochennost. It allows to argue that their formation is caused by the various sources not bound to dumps. Auras of lead, Hydrargyrum and cadmium have regional nature of manifestation and, possibly, are bound to the raised city hum noise. Iron, the main component of dumps, doesn't form significant abnormal zones within the studied territory.
2.2.3 Hydrosphere
Before starting more detailed analysis of influence of waste products of DSP on an underground and surface water, the analysis of accumulation of pollutants in time, during the period 2006–2010 was made.
Below 2 graphics reflecting composition of underground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps are presented.
On fig. 2.1 dependence SPKorg clearly is visible. from the content of iron in water, dynamics of their accumulation is similar. Factor of concentration of iron in 2006 year exceeded value of maximum concentration limit in 2 times, in 2010 year this value decreased to norm. Concentration of chlorides for 5 years is almost invariable, but by the end 2010 year it reached border of excess of maximum concentration limit, but isn't considerable – in 1,2 times. The content of sulfides exceeds maximum concentration limit in 2,7 – 3,5 times.
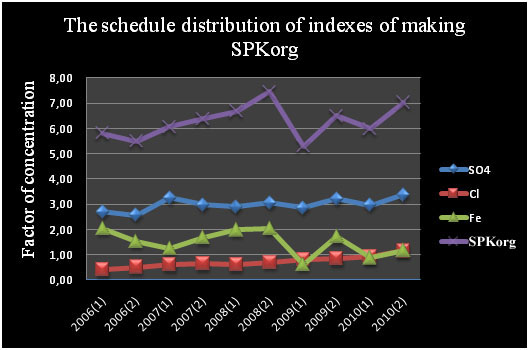
Drawing 2.1 – the Content of sulfates, chlorides and iron, SPKorg.
Fig. 2.2 comprises dynamics of accumulation of Hydrargyrum, cadmium and value of a mineralization and water hardness. Sharp decrease of concentration of Hydrargyrum in underground waters is observed, in 2006 of value exceeded maximum concentration limit that it is not observed for the next years. Probably, such change of concentration is caused by change of the fuel used at operation of furnaces. The considerable changes of the content of cadmium it is not noted, factors of concentration fluctuate from 1 to 1,5.
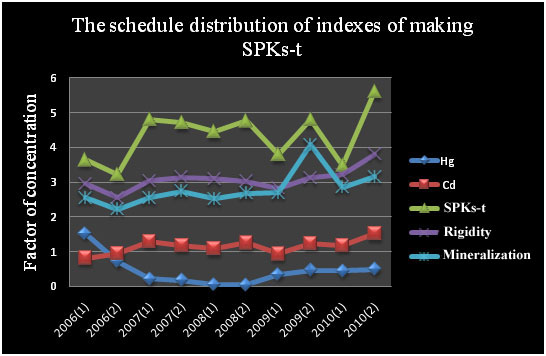
Drawing 2.2 – the Content of Hydrargyrum, cadmium, SPKs-t, a rigidity and a mineralization.
Apparently from schedules, the composition of underground waters for 5 years essentially doesn't change, it speaks about a stable ecological situation in the studied territory.
The detailed assessment of a condition of an aqueous medium in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps begins with the analysis of features of the quantitative value distribution of indexes.
Having compared concentration of chemical elements in an aqueous medium as a whole, to the marginal concentration taken according to Sanpin 4630–88, we received the following results (tab. 2.1)
| Sign | Indexes |
| Don't exceed maximum concentration limit | Co, Ni, Cr, V, NO3-, NH4+, Cu, Zn |
| Exceed maximum concentration limit on a minimum | SO42-, rigidity, mineralization. |
| Exceed maximum concentration limit on an average | Pb, SO42-, Cl-, Fe, rigidity, mineralization. |
| Exceed maximum concentration limit to the maximum | Pb, Cd, Hg, SO42-, Cl-, Mn, Fe, rigidity, mineralization. |
The raised content in waters of a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps of lead, iron, sulfates, chlorides is bound to carrying out of these components with sewage of steel works, chemical productions, mines.
As showed the carried-out researches, integral pollution of an underground and surface water by components of a sanitary and toxicological limiting sign is characterized by moderate and high degree (fig. 2.3). The abnormal zone is allocated from the northwest to the southeast, completely covering east part of the territory. Within the formed aura settle down a slimes store, slimes dump and a site of an unauthorized dump which is between them.
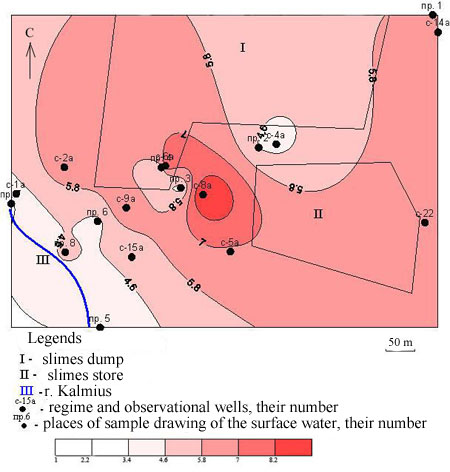
Drawing 2.3 – the Card of distribution SPKS-t, mg/dm3
The principal components influencing SPK, lead, cadmium and Hydrargyrum are. On all territory of approbation maximum concentration limit excess for Hydrargyrum makes 1,2–1,6 times. In this territory the site of an unauthorized dump settles down.
Integral pollution by the components influencing organoleptic indicators of water, on the most part of the studied territory corresponds to high degree (fig. 2.4). Local punctual anomaly extremely - high extent of the pollution, located from the North-West from a slimes store is allocated. The scale aura of high extent of pollution extends from the northwest on the southeast, covering in the borders a slimes store, an unauthorized dump of a household wastage, and as slimes dump.
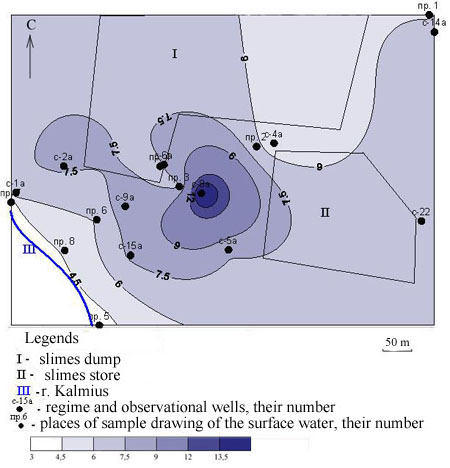
Drawing 2.4 – the Card of distribution SPKorg., mg/dm3
The main pollutants defining level of integral pollution in the studied territory, sulfates (excess of maximum concentration limit reaches 3,5 times), iron (maximum concentration limit excess to 2 times), chlorides (maximum concentration limit excess to 1,5 times) and in minimum degree manganese are.
As a result of the carried-out researches it is possible to argue that the main source of pollution of the hydrosphere in this territory is the slimes store as basic elements which make an integral indicator of pollution, sulfates, chlorides, iron manganese, lead, cadmium which are characteristic for a wastage of ferrous metallurgy are. Besides, waters of this area have the raised mineralization and a rigidity. Extraneous sources of impact on underground waters in the studied territory are unauthorized dumps of a various wastage and the garbage, located on all periphery of dumps. T.O., negative influence of a wastage of Donetsk steel works on the surface and underground water that causes of continuous monitoring of a condition of the hydrosphere in a zone of their influence is established.
3. Recommendations about improvement of a state of environment
For the maximal decrease in harmful effects on a surrounding medium performance of the following actions is provided:
- gardening of slopes of an existing dump;
- branch of the surface drain from the territory located above a dump;
- dump formation by circles with the device of an armor rekultivatsionny coat from loam on a dump slope;
- humidification of a wastage at their humidity less than 10 %;;
- having watered warehousing territories at cargo handling works.
Sites of warehousing of a wastage are designed taking into account borders of SZZ established for Polezhakovsky dumps.
Carrying out the regular monitoring of a condition of free air, the soils which are surface and underground water in a zone of influence of dumps is necessary.
For improvement of carrying out monitoring and more authentic results of its carrying out, the author of work offers optimization of a local observational network. It is necessary to reconstruct and restore wells which were put out of action, namely – hard currency. 1а, 2а, 4а, 5а, 6а, 8а, 9а, 14а, 15а, 22 – reconstruction are subject, to hard currency. 11, 12, 18, 20 – are subject to restitution. Follow-up to available wells, it is necessary to equip 5 more wells – hard currency. 23, 24, 25, 26, 27. It will give more reliable data about a condition of underground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps.
Conclusion
As a result of the carried-out work the following conclusions were received:
- The analysis of a condition of a problem of environmental was carried out by metallurgical branch, and was established that the matter is rather actual not only in our region, but also in other countries of Europe.
- Impact of DSP on the atmosphere, the soil and the hydrosphere is established.
- It is defined that DMZ wastage negatively influences a hydrosphere condition. The indexes exceeding maximum concentration limit, namely SO42- in 3,5 times, with Fe – in 2 times, Cl- – in 1,5 times, Hg – in 1,6 times are allocated.
- It is established that essential change of composition of underground waters in a zone of influence of Polezhakovsky dumps during the period 2006–2010 it is not observed;
- The main centers of pollution of underground waters which are dated for a slimes store and slimes dump that confirms their influence on the increased concentration of pollutants are revealed.
- Actions for optimization of a local network of the supervision, allowing to improve system of monitoring of underground waters in the studied territory are offered.
References
- Врба Я., Йиржеле В., Балек Я. Экологические последствия влияния техногенных факторов на качество подземных вод//Тр. 27-го Междунар.геол.конгр. С–16. Гидрогеология. М.: Наука, 984 с.93–100
- Режимные инженерно-геологические и гидрогеологические наблюдения в городах. М.: Наука, 1983. – 160с.
- Тютюнова Ф.И. Современное состояние и основные направления исследований загрязнения подземных вод в пределах городов и городских агломераций//Методы типизации и картирования геологической среды городских агломераций для решения задач планирования. М.: ПО «Стройизыскания», 1981. – С.42–45
- Тютюнова Ф.И. Гидрогеохимия техногенеза. М.: Наука., 1987. – 335с.
- Мазур. В.Л. Потенциал и проблемы ГМК Украины / В.Л. Мазур // Нові матеріали та технології в металургії та машинобудуванні. – 2008. – №1. – С. 144–147.
- Технико-экономическое обоснование инвестиций развития Полежаковских отвалов и эскизный проект санзоны. Книга 1. ГНИПИ «Гипросталь». Арх. № ТМ-100196. Харьков, 1998.
- Оценка воздействия на окружающую среду выбросов вредных веществ в атмосферу от источников Полежаковских отвалов и отвала промышленно-производственных отходов металлургического производства ОАО «Донецкий металлургический завод». Отчет по научно-исследовательской работе. ОАО «УКРНТЭК». Харьков. 2000.
- Комплексная утилизация заскладированных отходов черной металлургии. В.И. Ростовский, А.С. Бондарь, О.И. Раджи, А.В. Кравченко, Донецкий государственный технический университет, Украина
- Оптимизация рециркуляции отходов в черной металлургии. Клягин Г.С., Ростовский В.И., Мороз Е.О., Кравченко А.В. Донецкий национальный технический университет
- Груздев В. С. Комплексная оценка техногенного воздействия предприятий черной металлургии на окружающую природную среду центра европейской России.
- Матвеев А. Н. Оценка воздействия на окружающую среду : учеб. пособие / А. Н. Матвеев, В. П. Самусенок, А. Л. Юрьев. – Иркутск : Изд-во Иркут. гос. ун-та, 2007. – 179 с
- Технико-экономическое обоснование развития шлаковых отвалов металлургического производства ЗАО «Донецксталь»- металлургический завод». Этап.4. Книга 1. Пояснительная записка. ПГП «Артемовская гидрогеологическая партия», Донецк, 2006.
- Технико-экономическое обоснование развития шлаковых отвалов металлургического производства ЗАО «Донецксталь»- металлургический завод». Этап.3. Отбор проб, лабораторные исследования, оценка степени загрязнения почво-грунтов,поверхностных и подземных вод. ПГП «Артемовская гидрогеологическая партия», Донецк, 2005.
- М.Г.Ладыгичев, В.М.Чижикова. Сырье для черной металлургии. Том 2. Экология металлургического производства. Изд.: Теплотехник – 2005, 790с.
- А.Б. Макаров. Техногенные месторождения // 2000. Т. 6. № 8. С. 76–80.
- А.К. Зайцев, Ю.В. Похвиснев. Экология и ресурсосбережение в черной металлургии. Московский государственный институт стали и сплавов (технологический университет).
