Abstract
Contents
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose of the idea and objectives of the study, expected results
- 3.Predpolagaemaya scientific novelty
- 4. A review of existing research and development on the subject
- 5.Tekuschie and planned rezltaty
- Conclusion
- Source List
1. Relevance of the topic
Fresh water – one of the most important mineral resources. Its reserves are unevenly distributed, and consumption is increasing due to the limited possibilities of its replacement in kind of technology.
The extreme seriousness of the problem of economic – drinking water purchased for the Donets Basin, where the main source of fresh water (80%) is the channel of the Seversky Donets – Donbass with a very worn–out infrastructure, resulting in great loss of flow. Other sources of water that could cover the deficit of water in the Donbass, no. In these circumstances, the search for alternative sources of economic – drinking and technical water supply in the region is very important. [1]
One of these sources may serve as a mine water mining, which is pumped into the volume of 900 million m3 / d, which is comparable with the volume of water transported through the channel Seversky – Donets Donets Basin.
Extension of the coal enterprises and the use of mine water on their own economic – drinking and industrial needs with a corresponding reduction in potable water from its natural sources is both an important conservation value, since it can be seen as an important contribution to solving environmental problems – to prevent depletion of water resources .

Figure 1 – Installation Demineralizatsionnye
Currently, only 13–15% of mine water is used for technological needs and did not use for drinking purposes because of their pollution particulate matter, mineral salts and bacterial impurities. Consequently, the realization of the possibility of using mine water for the needs of the economy requires that they be pre–stonecrop on the above ingredients.[2]
At first glance (and the opinion of DonUGI Dongiproshah) problem clarification of mine water from the suspended matter is solved. However, analysis of the experience lighten mine water by conventional water treatment plants, located on the surface of the Earth, points out that this question is removed from the agenda was premature for the following reasons:
– the total excess concentration of the Rural Lands in the pumped water (300 mg / l), which quickly snizhet effectiveness and reliability of surface brightening structures, thus determines the project does not match the actual effectiveness of the latter (as a rule, in–situ real effectiveness is much lower real);
– the presence of water trudnoosadimyh fine clay fractions (more than 50% for the deposit of coal grades K, OS X, D, T and G), so that even the use of chemicals does not provide the desired degree of lightening;
– a variety of properties of suspended solids density, particle size composition, ash content, which also narrows the scope of the treatment facilities;
– uncertainty (often) information about the actual degree of clarification of mine water.
– the complexity of the technological schemes and application design of treatment facilities;
– lack of flexibility to respond to the treatment plant changes in the conditions of polluted water to enter sewage treatment plants, namely, the change in the quantitative and qualitative composition of impurities as well as the volume of pumped mine water;
– rejection of significant land areas under the treatment plant. [3]
Reported shortcomings point to the need for improved approaches for mine water free of suspended solids.
To an even greater extent than clarification and disinfection of mine water is not resolved over several years, the problem of mine water demineralization. It can be noted that in this region suggested the physico–chemical methods for mine water demineralization: ion exchange, membrane methods (electrolysis and reverse osmosis) and distillation. Among them is the most technologically versatile meod distillation.
At the same time a number of benefits is the application of membrane technology based on the method of reverse osmosis which include: low power consumption mode, its high efficiency, full bactericidal treatment of water, the simplicity of the scheme, which can easily be automated, technologically simple control of the quality of purified water (conductivity ), low operating costs. The disadvantages of reverse osmosis method, as well as other methods listed above, demineralization include high capital costs for construction of facilities. However, low operating costs with the use of this method contribute to rapid return demineralizatsionny installation. [4]
Thus, the results of the analysis show that the purely technical issues demineralization problem can be solved. The question is. In the state of a particular coal mining company on its own to carry out full demineralization of pumped mine water, and processing at the output of generators to the state of the dry brine soleproduktov.
As analysis of the experience and made the calculations, the solution in such a setting for economic reasons, is practically impossible. At the same time a partial solution to the problem, in our opinion, perhaps, if you follow the direction of the use of demineralized water instead of drinking, ie, partial solution to the problem. With this approach, firstly, there is no need of processing brine: they dropped the hydrographic network.
Secondly, there is economic compensation due to:
– failure of the process of clarification of mine water by capturing and using conditional–clean sediment from the mine water flowing out space mines, this approach falls down the need to build expensive lighting facilities;
–out the consumption of expensive fresh water for industrial needs of the mine (at today's price of 9 grn/m3 and consumption of fresh water for the mine, "Deep–Yasinovka" 101.6 thousand m3/year it will be 915 UAH / year);
– low operating costs in the case of choice for the demineralization of water by reverse osmosis, which promotes rapid return on the installation. [5]
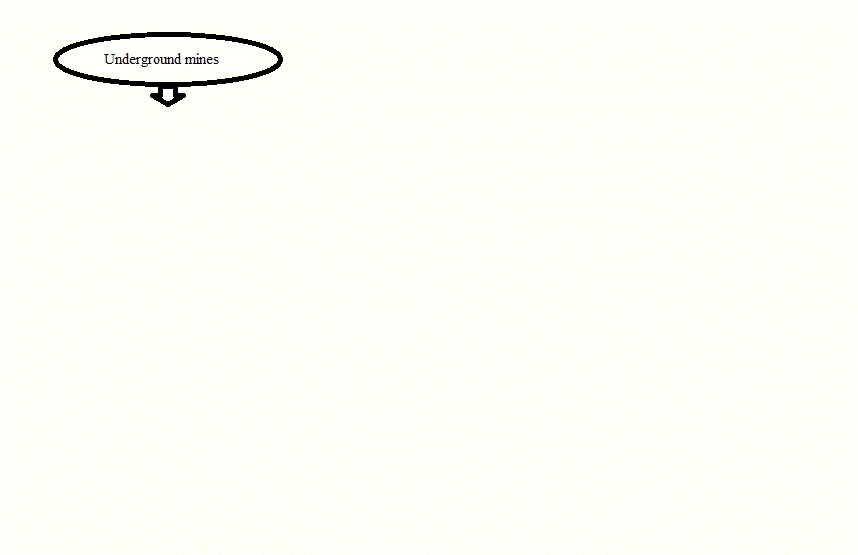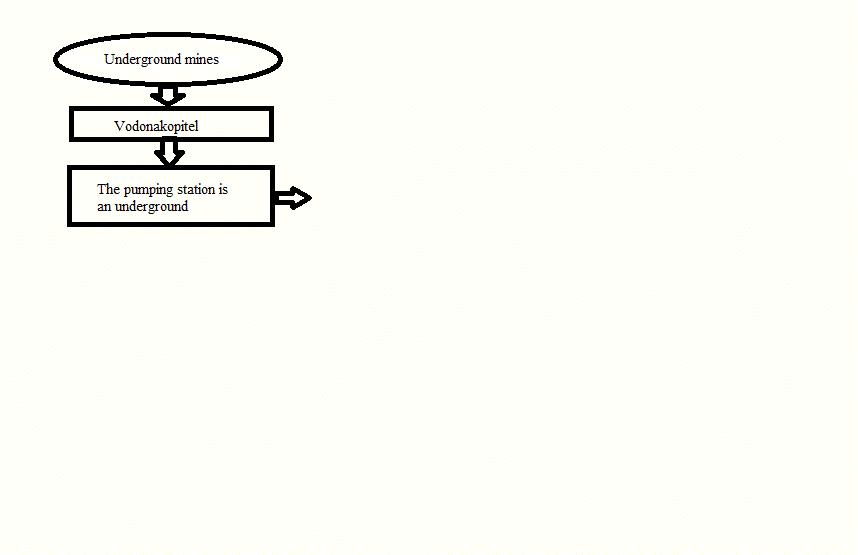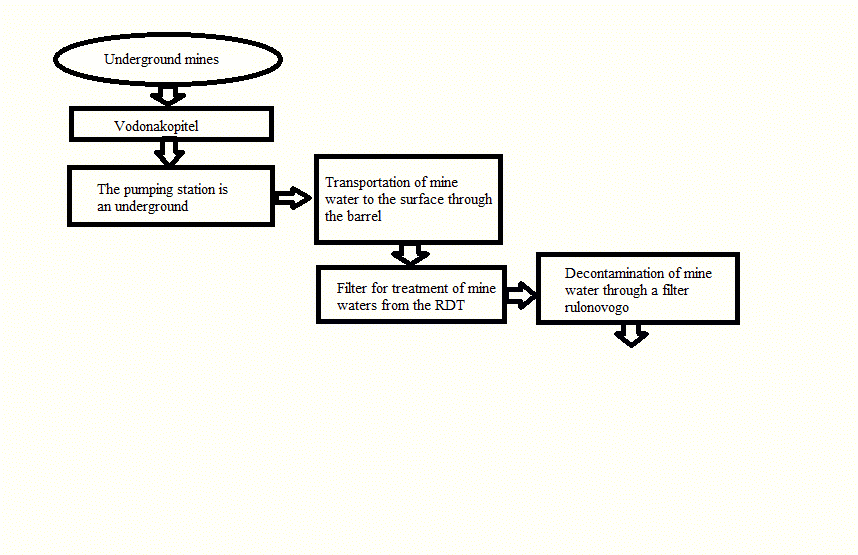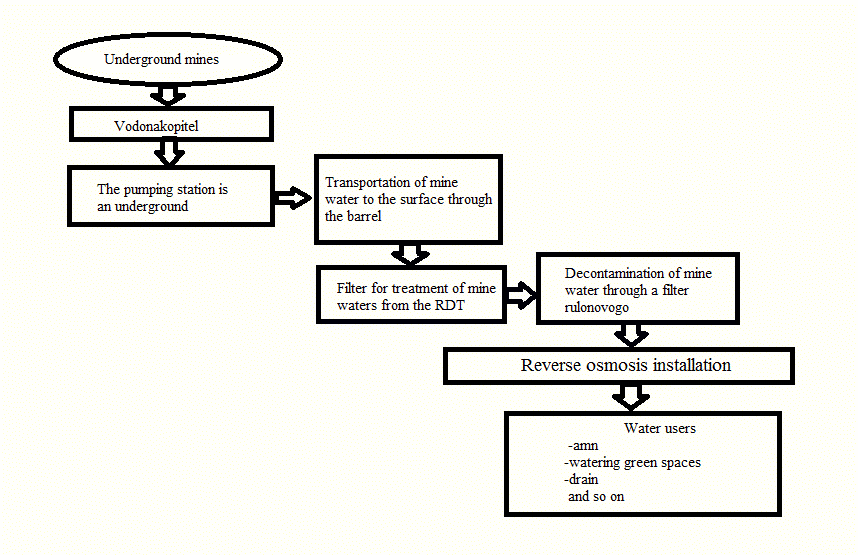
Figure 2 – Shema planned rabot
Thus, the use for drinking and industrial purposes without the conditioned mine water treatment brine instead of expensive drinking water will significantly reduce and offset the cost of concrete in the water treatment company, and thereby obtain a reliable alternative source of supply of the mine.
2. The purpose and objectives of the study, expected outcomes
The purpose of the work – the choice and justification of technological measures on the use of relatively clean mine water supply for industrial enterprises, "Deep–Yasinovka"
Objectives:
–the study of assessment of the situation with the mine water;
– analysis of the experience of using mine water for the needs of the economy;
–establishment of the general and specific requirements for spending and the quality of mine water used to supply the mining company for technical and household drinking water;
– use of the possible uses of treated water at the mine;
– study of the conditions of formation and transport of mine waters in underground mine workings;
– use of physical–chemical composition and kinetic properties of the components of groundwater;
– siting of underground mine workings for the construction of underground water storage;
– development of a hydraulic circuit transport water from the underground mine vodonakopitelya to develop up to the pump station to pump water to the surface;
– choice of equipment and automation of the underground pumping station;
– development of a surface complex technological scheme of the purification of ground water of suspended solids (by direct filtration), and air conditioning water, ie adjustment of different composition, (reverse osmosis), if necessary, as set out in the course of work;

Figure 3 – Filter clarifier FOV
– selection of water treatment equipment in accordance with the component parts of complex technological seme water treatment;
– determination of economic effectiveness of recommended measures for the use of mine water for the needs of the enterprise.
The object of study, the mine water control.
The subject of study – the technological processes of cleaning and the use of mine water.
3. Expected scientific innovation
1.Razvitie new concepts of technical and economic possibilities of the use (after purification) simultaneously extracted groundwater for its own needs of the mining enterprise.
2. The establishment of an integrated technological dependency of conditioning and purification of groundwater.
3.Obosnovanie uses of mine water in a real business.
4. A review of existing research and development on the subject
To date, obbem scientific and technical information about using mine water is not significant. increasingly accumulated information about the treatment of mine waters, primarily in the earth's surface. It is devoted to clarification, disinfection, and mine water demineralization. In this issue of clarification and disinfection of water in a large number of works, rather than demineralization. In the first case to be called a work of coal VNIIOS institutions (Perm), DonUGI, Dongiproshaht, and the second of the Institute of Colloid and Water Chemistry (Kiev, Inc. UkrNTEK (Donetsk). [5] [6]
In the late twentieth early twenty–first century, made deep cleaning work on mine water is not in the surface and in underground mines. First of all, it should be called robots and DonNTU Shakhty branch Novocherkassk Polytechnic Institute (Mines).[7]
System analysis of the results of these papers identified topicality of this master's work, its purpose, the idea of the problem, the description above, and select from a large number of well–known so far in practice, the most applicable for the purification of mine waters from suspended solids (the method of direct filtration), and air conditioning ie adjusting a composition of water (reverse osmosis method). [8]
5. Current and planned
To date, the following conditions:
– investigated the situation with water mines, identified sources of water consumption of fresh water, estimated costs;
– analyzed the experience of using mine water for the needs of the economy as a whole;
– study eligibility mine water for drinking and industrial water supply;
– examined (pre–) conditions for the formation of threads of mine waters in underground mine workings;
– formed the technological approach to the preparation of mine water for their consistent use of the needs of the enterprise;
– identifying possible directions for use of mine water at the plant. [9]
In turn, the following steps:
– a detailed study of waterway mine water in the underground mine workings, their volumes, physical – chemical composition;
– site selection for the construction of an underground vodonakopitelya;
– development of a hydraulic circuit transport transportation of groundwater to the surface of the mine with the help of an automated underground of the pumping station;
– development of technical scheme of the surface post–treatment and conditioning of underground water;
– choice of after–treatment and conditioning of underground water, equipment to implement them in the process flowsheet;
– determination of the economic effectiveness of the use of trained mine water in the mines developed in this master's work. [10]
Conclusion
Given the above arguments – the relevance of the problem, a sufficiently high scientific level of problem solving treatment of mine waters from suspended particles and mineral salts, the increased price of water for various purposes and quality – you can make a conclusion about the existence of technical and ecological and economic prerequisites for the development of large–scale programs prevent discharges into water bodies Donbass untreated mine water on the basis of their complex processing.
introduction of complex processing and conditioning of mine water will not only radically solve the problem of water protection from pollution, but also provide a market for processed products derived products, to create competitive conditions for water users, which ultimately will benefit the economic development and pridpriyatiya environmental conditions.
Source List
- ES Matlak, Maleev VB Reducing contamination of mine waters in underground conditions–K.: Engineering, 1991.
- Physico–chemical basis of technology and decontamination of mine waters: monograph / [Grebenkin SS, VK Kostenko, ES Matlak and others]; under. total. Ed. Kostenko VK – Donetsk, "VIC", 2009.–438s.
- Maydukov GL, Grigoryuk ME Mine water as a natural resource / Coal Ukrainy.–2006. – ╣ 12, p.22–28
- program and construction of a mine water demineralization plants in major coal basins of Ukraine, as well as the use of mine water for the needs of the economy. Explanatory Note PP–510–1–13, Dongiproshaht, Donetsk, 1992.
- Reznikov Yu, VV Kulchenko Using mine water – a promising direction of saving water and reducing the costs of enterprises. Sat scientific work "Improvement and development of new technologies and equipment for environmental protection. JSC "Ukrainian Scientific Center of Technical Ecology", Donetsk, 2000. S. 10–14.
- ES Matlak, VK Kostenko, OV Lunova. Before the power of mozhlivu zm│nu reg│onalnih standards yakost│ mine water, scho skidayut, that osoblivost│ ┐h vikoristannya / / Problems ekolog│┐. – 2010. – ╣ 1–2.–pp.46–50.
- Sinyavsky SA The problem of mine water demineralization / Coal of Ukraine. – 2010 – ╣ 2 – p.22–24.
- Omelchenko, NP Kovalenko, LI New technologies lighten mine water to reuse. Zagalnoderzhavny Naukova tehn│chny–journal "Problems of ekolog│┐." – Donetsk: Donetsk National Technical University, ╣ 1–2. – 2008. S. 8–12.
- ES Matlak, Romanov, VY The use of mine water in the technical, economic and domestic water supply – a new approach to solving the problem of water scarcity Donbass. DonNTU.
- AA Minaev, ES Matlak, GV Averin The maximal involvement in the economic shahtn│h water supply Donbass / Zb│rka dopov│dey Naukova–praktichno┐ konferents│┐ "Ohorona dovk│llya that ekolog│chna BEZPEKA", Vol 1 – Donetsk, 2001. – S. 206–210.
