Abstract
Table of contents
- Introduction
- 1. Actuality and novelty
- 2. Planned results
- 3. Review of existent decisions
- 3.1 Review of existing solutions on an international level
- 3.2 Review of existing decisions at the national level
- 3.3 Review of existing decisions at the local level
- 4. General Part
- Conclusion
- Literature
Introduction
At present, the developed world there is a steady trend towards the rapid development of telecommunication services Triple Play. The first place for telecom operators face the problem of providing services to subscribers high-speed Internet access, IP-TV, data, video telephony and video conferencing.
1. Actuality and novelty
The decision of these tasks is especially actual for the operators of off-wire mobile communication – at providing of access additional complications that are absent in wire fixed communication networks appear to the network. To these complications it is possible to take multibeam distribution of signal, that results in the slow and rapid stopping beating, dispersion of energy, in an atmosphere, absorption by the crowns of trees, reflection from building, water surfaces and other planes. In addition, the fact of mobility of subscriber complicates the reception of signal, in particular, at moving of subscriber between cells, when it is needed to save quality of the given services.
In developing such networks an integral part of algorithm design is the use of software tools to verify the calculations the number and type of equipment for the network. For example, to verify the calculation of the radio coverage area using special software packages, which you can specify the characteristics of antennas (a type of pattern, the slope, the number of sectors), feeders, transceivers. Without the use of such software systems is difficult to calculate the required number of base stations to cover the territory. There are the analogical programs for the calculation of equipment from position of providing of capacity of network. But such programs are far fewer, in addition, a question about providing of parameters of QoS for the given services is decided partly or in general not decided.
Therefore, modeling of sections of the network and the network as a whole in order to verify QoS parameters to ensure the subscriber is an urgent task for the developer of telecommunications software. In addition, these complexes should also be realized the problem of optimizing the network. The use of these programs will significantly accelerate the process of developing the project network and optimize the amount of equipment. Thus, the purpose of master's work is to justify the possibility of building a wireless telecommunication network of third generation mobile communication environment for the city of Donetsk with the use of algorithms for simulation and optimization of the network sites.
2. Planned results
As a result of the implementation of the project will be submitted to a wireless network of third generation mobile communication for the city of Donetsk. The use of technology of UMTS/WCDMA is planned for realization of network.
In-process of my final work, the algorithms of design of different processes will be presented in a network, as well as optimization of the network sites in order to improve them.
The projected research results:
- The waiting time of the application for service extension.
- Bandwidth connection in the network congestion (for example, for temporary overload – during the various city events).
- The waiting time of the application for service extension.
- Time of handover in the network. Knowing the ability of controllers and base stations, we can estimate how quickly will the transfer of subscriber services, and how it will affect the quality of services, which at the time of handover the subscriber uses.
3. Review of existing solutions
Wireless mobile communication network of the third and fourth generations – hot topic for subscribers of mobile operators, equipment manufacturers, so this topic has been widely discussed developments in the world.
3.1 Review of existing solutions on an international level
A number of scientists involved and engaged in the research of mobile third-generation networks. Many of these studies conducted by researchers in the CIS: A. Babin, "Designing optimal radio network subsystem 3G/UMTS/WCDMA based on the theory of monotone systems" [1], S. Aksenov, "Investigation of the handover procedure on the quality of services in networks UMTS" (2008, St. Petersburg) [2]. Research groups worldwide developer of telecommunications equipment (Alcatel, Nokia, Siemens, etc.) involved in research issues of networking standards UMTS. In the CIS countries, as well as in Ukraine, there is also 3G-revolution. In Russia, the three largest operators have received licenses to provide cellular services in the standard UMTS: OJSC "Мобильные ТелеСистемы" (MTS), JSC "ВымпелКом" (Beeline trade mark) and OJSC "Мегафон".
ОOJSC "Мегафон" became the first Russian operator, running the third generation network into commercial operation. In early October 2007 the company has in place a network of 30 base stations in the city of St. Petersburg. In May 2008, MTS launched the commercial operation of a network of UMTS/HSDPA in St. Petersburg and later in other cities of Russia: Sochi, Kazan, Nizhnekamsk, Saratov, etc. Since September 2008, the Company "ВымпелКом" also began to deploy the networks 3G UMTS/WCDMA throughout Russia: St. Petersburg, Nizhny Novgorod, Samara, Chelyabinsk, etc.
3.2 Review of existing decisions at the national level.
In Ukraine already there are a few decisions of tasks of grant of mobile high-speed access to the network the Internet:
- МТS is the largest operator of mobile communication; an off-wire mobile communication network is built on the standard of GSM. Presently МТS gives services of the mobile Internet in technology 3G CDMA 450 EV-DO.
- Kyivstar – the network of this operator is also built on technology of GSM, gives services of access to the network the Internet and IP-TV on technology 3G UMTS on the base of operator Utel.
- Life:) – basis of network is GSM, building on above GSM is subnet 3G UMTS/WCDMA.
- Beeline is a network, analogical Life:) is a basic network of GSM with building on 3G.
- Utel is a separate operator of mobile communication of the third generation the network of that is built on technology 3G UMTS/WCDMA.
- PEOPLEnet is an operator a network of that is fully the network of the third generation, built on the standard of CDMA2000 1x EV-DO Rev.A; gives services of access to the network the Internet.
All basic operators of mobile communication use the standards of the third generation for realization of high-speed access to the network the Internet. But this direction is literal it is not too developed for all operators. For example, the mobile Internet from МТС does not allow to load large files, look over videocontent – actually, there is possibility only to look over web-pages. It is related to that amount of equipment 3G not enough for maintenance of all persons interested to get access to a 3G network of subscribers the amount of that increases constantly.
In addition, a price on services of the mobile Internet remains in most yet very high. The Ukrainian operators have problems of other character also. For example, for an operator Utel direction of vocal connection is poorly developed is a cost of rings on other operators costs too expensive. PEOPLEnet gives exceptionally services of access to the network the Internet, and possibilities of vocal connection are absent in general.
3.3 The projected research results
In-process of my final work, the algorithms of design of different processes will be presented in a network, as well as optimization of the network sites in order to improve them:
- Michael Okhrimenko (TCS-09M), "Study of the techniques of building and development of next generation networks for mobile operators" (development of the network standard UMTS).
- Lubov Shapovalova (TCS-09M), "Research and development of the model data in the radio access network based on WiMAX technology with regard to quality and safety".
- Olga Bordunova (TCS-10M), "Development and study of optimization techniques in the networks CDMA".
4. General Part
Features of standard of UMTS
It is not a secret that a situation with distribution of frequency stripes in Ukraine is extremely tense (however, as well as in any other country). Therefore purchase of frequency stripe sufficient for forming of frequency plan of the system frequency-division channels attended with a necessity to free ranges or to redistribute them, to get a whole stripe. So, planning, for example, of communication of fourth-generation (LTE or WiMAX) networks as early as beginning meets with serious obstacles. Less high-usage ranges higher 3,5 GHz possess other defect – the base stations in this range have a small cruising radius, so, the amount of equipment for such network is needed.
A simpler situation is with communication systems with code division multiplexing (UMTS, CDMA2000). Here the signals are "user-base station" transmitted on one frequency, and channel separation is carried out with the help of technology CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access – Multiple Access, CDMA) (Figure 1).
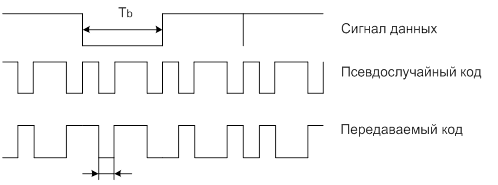
Figure 1 – Example code transmitted using CDMA technology
Each transceiver has its own pseudo-random code, so that the receiver recognizes its "own" the signal by using a combination of the received signal and the operation code using XOR. Signals from other transponders are ignored. Thus, due to the fact that the transceivers operate at one frequency, CDMA systems have a high bandwidth. In addition, the CDMA system has other advantages. Due to the fact that the pseudo-random code pulse T is much less than the pulse width of transmitted data Tb, the width of the signal transmitter is much larger than the width of the signal data. Thus, the received signal is broadband, which means – noise-like, so the noise model, which often acts as Gaussian white noise can significantly degrade the signal quality.
These systems are highly secretive transfer – without the knowledge of pseudo-random code to decode the received data is impossible.
Develop a plan for network design
Task of planning of off-wire TCN of mobile communication – one of the most intricate and responsible problems of opening out of network. It is needed to define the amount of equipment, place of his location, distribute frequency channels, coming from the combined criterion efficiency-cost. From one side, the excessive placing of the base stations will be unprofitable, as will result in superfluous expenses, on the other hand the too rare location of the base stations can cause appearance of the unserved zones or shortage of resources for maintenance of subscriber traffic (that, apparently, and observed in the Ukrainian networks.
In addition, functioning of these networks is characterized by a next circumstance – at the increase of amount of active subscribers in a cell the radius of her zone diminishes. Thus, planning of mobile communication network requires iteration approach in calculations, in the process of that mathematical methods and methods of computer design are used.
So, the plan of development of mobile cellular communication network is such:
- Calculation of amount of the base stations with the use of mathematical models.
At first it is necessary to expect coverage of territory of planning object – so, to define a radius cells coming from the requirement of coverage of territory the signal of sufficient level. On territory there must not be areas with the weak level of signal, that less sensitiveness of subscriber device, black-out areas (from high building, for example), areas without coverage. Many models of distribution allow to take into account the different features of object. It is expedient to expect coverage on a few models. It is further necessary to estimate the capacity of the got network of radioaccess, thus for every technology of network the methods of calculation. And, if the greater amount of the base stations is required, to correct the calculation. - Preparation of frequency-territorial plan of the network.
- Using special software to evaluate the radio coverage of the network with the previously calculated number of base stations. In the end, and adjust the amount of equipment.
- The calculation of adjusted net capacity. There are also software packages that allow to specify the parameters of the intensity of traffic for different services, and evaluate network capacity. If the specified number of stations can not handle the expected load of the subscribers must be added to transceivers or base stations. Or, it may be sufficient redevelopment location of stations. If the base station is too much for the calculated load, it is necessary to reduce this number, making changes in planning in a location of base stations, changing the height of the suspension, the angle of antenna patterns and changes in other parameters. This section also plan to use the model to simulate the idempotent of the algebra of networks and their subsequent optimization of the parameters in order to provide QoS.
- Repeated realization of radioplanning and subsequent adjustment of amount of equipment.
- Re-calculation of network capacity.
- A process proceeds until it will not be succeeded to attain an optimal decision.
Design of UMTS network for a business center of Donetsk
For the conditions of the business center of Donetsk designed network of UMTS. Design was carried out according to plan, design:
-
According to the model Okamura-Hata is designed for the average radius of the cell parameters of the base station UMTS, the conditions of the city of Donetsk and the sensitivity of the subscriber station –140 dB (Figure 2).
The radius of cell, it is estimated that 1 km. The required number of base stations at the same time 17.
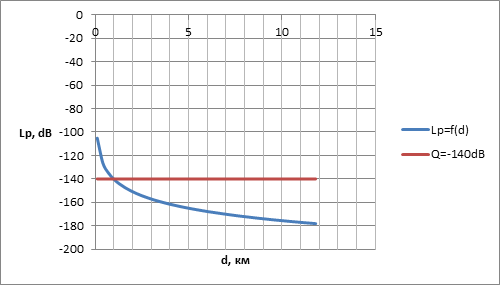
Figure 2 – Calculation of the radius of the cell base station for the conditions in Donetsk
- Based on the conditions for capacitance [3], to 40–50 base stations. The project adopted the maximum number N = 50.
- Calculated from the rest of the equipment, made up a block diagram of the network (Figure 3).

Figure 3 - Block diagram of a UMTS network for the conditions of the city of Donetsk
Using of models of an idempotent algebra for modeling and optimization
Idempotent algebra or max-plus algebra is new mathematics being base on two basic operations – new addition that is equal to the maximum, and new increase that coincides with addition. Idempotent mathematics is a natural vehicle for the decision of tasks of optimization and optimal management [4]. The general going near optimization of processes in telecommunications consists in the calculation of optimal value of some parameter that in this task is the criterion of optimization of the network have specific nodes – sources and receivers applications. Let there is the network presented as the acyclic graph, where tops of count are knots of network, arc – routes on that requests can be passed on a network. In every knot there are a device of treatment of requests and buffer in that there can be expectation of treatment in a turn. There are the special knots – sources and receivers of requests in a network structure.
To formalize the process variables are introduced the following notation:
- τik – duration of service k-th request in the i-th node of the network;
- xi(k) – time completion of the k-th service requests in the i-th node of the network;
- ai(k) – the time of receipt of the k-th request in the queue for service in the i-th node of the network.
It is envisaged that τik – non-negative random variables with a certain expectation for all i=1…n and k=1,2….
For definiteness, we set the additional initial conditions of the process [5]: xi(0)=0, xi(k)=–∞ for k<0 and i=1,2…n;
Taking into account the adopted notation and assumptions, the dynamics of each network node is described in terms of max-plus algebra, as
xi(k)=τik⊗ai(k)⊕τik⊗xi(k–1)
So it will be calculated during the completion of the k-service applications in the i-th node network with different routes of passage of this application. This allows, first, to simulate the process of service requests by different routes, and secondly, to optimize this time, choosing the smallest route. The use of idempotent algebras and Petri nets allow the device to solve the problem of modeling and optimization of important parameters of a mobile customer service network 3G [6].
The above algorithm for modeling the service time of the application can be used to estimate the waiting time for adoption service subscriber [7], as well as for their subsequent optimization to minimize.
In addition, we can evaluate and optimize the following parameters:
- Delay in voice and video.
- Bandwidth communication channel with network congestion (for example, for temporary overload – during the various city events).
- Time of handover in the network. Knowing the ability of controllers and base stations, we can estimate how quickly will the transfer of subscriber services, and how it will affect the quality of services, which at the time of handover the subscriber uses.
Conclusion
When introducing or increasing the network, it is convenient to model and evaluate the performance of services provided to subscribers, and then, if necessary, to optimize the network for a specific criterion. This will greatly simplify the process of building the network, since it will be possible to avoid erroneous or suboptimal solutions.
Literature
- Проектирование оптимальной подсистемы радиодоступа сети 3G/UMTS/WCDMA на основе теории монотонных систем [http://www.rae.ru/snt/]. – Бабин А.И. // Современные наукоемкие технологии. – 2008. – № 2 – С. 52–56.
- Исследование влияния процедуры хендовера на качество услуг в сетях UMTS [http://www.pandia.ru/384505/]. – С.А. Аксенов, – Телекоммуникационные системы и компьютерные сети, автореферат диссертации на соискание ученой степени кандидата технических наук, Санкт-Петербург, 2008.
- Исследование особенностей и разработка методики построения сетей нового поколения для операторов мобильной связи [http://masters.donntu.ru/2010]. – Автореферат квалификационной работы магистра.
- Компьютерные инструменты в образовании. – СПб.: Изд-во ЦПО «Информатизация образования», 2000, № 6, С.12–18.
- Применение сетей Петри для моделирования механизмов обеспечения QoS в компьютерных сетях // Механов В.Б. – Материалы международного симпозиума «Новые информационные технологии и менеджмент качества» (NIT&MQ 2010) ФГУ ГНИИ ИТТ «Информика». – М.: ЭГРИ, 2010.
- Математичні основи теорії дискретно-безперервних систем: монографія // В.І. Бессараб. – Донецьк: ДВНЗ «ДонНТУ», 2011.
- Colored Petri Nets: modeling and validation of concurrent systems // Jensen A., Kristensen L. – Springer-Verlag, 2009.
