Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the work, expected results
- 3. Review of Researches and Developmentes
- 3.1 Review of international sources
- 3.2 Review of national sources
- 3.3 Review of local sources
- 4. Developing LTE network model
- 4.1 The network design algorithm
- 4.2 Creation of information network of the object
- 4.3 Calculation of network traffic
- 4.4 The transport network topology
- 4.5 Network topology
- 4.6 The choice of lines
- 4.7 Creation of the structural diagram of a network
- 4.8 Creation of the functional diagram of a network
- Conclusion
- References
- The need to introduce new data services because of the high saturation of the voice services market and high competition.
- Providing subscribers with multimedia services which have high bandwidth demands.
- 2G and 3G technologies do not provide the high-frequency performance, which is a serious problem to provide high quality services.
- Slower growth in customer base of mobile operators in the networks of 2G.
- The development of multimedia services that require high-bandwidth communication channels.
- The low efficiency of use of frequency resources in existing networks.
- To study the LTE technology and its features.
- Analyze market for mobile services in order to justify the need for the introduction of network LTE.
- Analyze existing networks of the second and third generation.
- Identify the problem of the evolution of the second and third generation networks to 4G.
- Analyze possible scenarios for the evolution of GSM technology to LTE.
- Creation of version of introduction of LTE-based abstract segment of the existing mobile network.
- Investigation of processes of LTE.
- Development of key recommendations for the implementation of LTE technology on existing GSM-network.
- The economic rationale of the introduction of LTE.
- Get a model of GSM network.
- Get a model of LTE network.
- Comparative analysis of models.
- Creation of information network of the object.
- Calculation of network traffic.
- The choice of transport network topology.
- The choice of network topology.
- The choice of lines.
- Creation of the structural diagram of a network.
- Creation of the functional diagram of a network [3].
- "Worker" – a subscriber who does not require high bandwidth. The most important service is voice service. It is also important is protection of bandwidth and high stability of the compound. Subscribers of this type have the highest priority of service. Airport employee uses this service to coordinate with other staff. Subscribers with the same requirements may be passengers of VIP- terminal, which needs the reliability of the information exchange.
- "Passenger" – an active subscriber which demands large for mobility services. It is characterized by unstable bandwidth requirements. Its priority is lower than that of other categories of subscribers. Typical services used by subscribers of this type – IPTV, watching videos and online games, which also have high requirements for the delay.
- "Security systems" – an important indicator of quality for this category is the video in real time, which requires high bandwidth and data rate.
- To support the rate of 100 Mbit/s.
- Reliable data protection.
- Ability to increase network.
- Network length of 500 m to 5 km.
- Fast Ethernet, 100 Mbit/s:
- 100BASE-ТX (IEEE 802.3 part 21; 25; ИЕЕЕ 802.3u);
- 100BASE-T4 (IEEE 802.3 part 21; 23; ИЕЕЕ 802.3u);
- 100BASE-FX (IEEE 802.3 part 21; 26; ИЕЕЕ 802.3u);
- 1000BASE-LX (IEEE 802.3 part 34; 36; 37; 38 ИЕЕЕ 802.3z).
- Gigabit Ethernet, 1 Gbit/s:
- 100BASE-X (IEEE 802.3 part 21, 24; ИЕЕЕ 802.3u).
- 10-gigabit Ethernet;
- 40-gigabit and 100-gigabit Ethernet [9].
- Transferring files online is the dominant traffic in the fixed IP-based networks, where delivers information using hypertext protocol HTTP.
- Traditional IP-based networks using multiple protocols for sending e-mail: SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) – only for sending messages , etc.
- In providing services to streaming video uses a series of relevant protocols RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol) – Protocol streaming video in real time; RTP (Real-Time Transport Protocol) – the transport protocol in real time, and others.
- For the organization of VoIP service requires the use of additional, in addition to IP, the protocols that will be responsible for establishing and maintaining connections. The most useful are two protocols: H.323 and SIP. For correct operation of the network, all equipment should be equipped with the appropriate ports, which support the appropriate technology.
- Based on the analysis of the literature highlights the main algorithms that can be used in designing and modeling networks.
- Designed a network based on LTE technology for the segment of the "International International Airport Donetsk".
- Simulation of a network segment, based on GSM technology for the segment of the "International Airport Donetsk".
- Design and simulation of a further network segment, based on GSM technology for the segment of the "International Airport Donetsk".
- Comparison of the simulated networks.
- The economic rationale for the transition to LTE technology for GSM standard.
- Development of recommendations for the introduction of LTE technology on the existing network standard, GSM.
- Тихвинский В.О., Терентьев С.В., Юрчук А.Б. Сети мобильной связи LTE: технологии и архитектура. – М.: Эко-Трендз, 2010. – 284с.: ил.
- Тихвинский В. О., Терентьев C.B., Минаев И.В. Стандартизация, спецификации, эволюция технологии и архитектура базовой сети LTE // Сети и средства связи, № 2(10). Специальный выпуск «Сети доступа». – 2009. – № 3.
- Методичні рекомендації до курсового проекту за курсом "Проектування засобів та систем телекомунікаційних мереж" для студентів заочної форми навчання по спеціальності 7.091402 "Телекомунікаційні системи та мережі" / Укл.: доц. Дегтяренко І.В., ас. Ступак Г.В., ас. Прядко Л.О. – Донецьк: ДонНТУ, 2007. – 58 с..
- Использование радиочастотного спектра сетями LTE и LTE Advanced В.О.Тихвинский, С.В. Терентьев. / / Электросвязь. – 2010. – № 5.
- 3GPP TR 23.882 System Architecture Evolution: report on Technical Options and Conclusions ( Release 8).
- 3GPP TS 29.272. Evolved Packet System (EPS); Mobility Management Entity (MME) and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) related interfaces based on Diameter protocol (Release 9).
- 3GPP TS 29.272. Technical Specification Group Core Network and Terminals; Evolved Packet System (EPS); Mobility Management Entity (MME) and Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN) related interfaces based on Diameter protocol (Release 9).
- Электронный ресурс. Режим доступа: Сайт «Сотовая связь. История. Стандарты. Технологии»
- Электронный ресурс. Режим доступа: Статья с сайта Wikipedia «Ethernet»
- Releases can be found on the 3GPP site
Introduction
To date, Ukraine has external communication channels with sufficient capacity, in almost every locality there are service providers access to an external network, however, the connection between them and the end user is still done mostly either with switched or dedicated lines. As a result – low rate of exchange of information, poor connection, limited connectivity. An important problem is cabling, sometimes it is impossible, inconvenient and economically feasible, especially in big cities. Relevance of this topic is to find solutions for the implementation of new technologies in modern telecommunication networks. The design of such a network is to choose the most profitable and high-quality data transmission technology. Recently in the field of telecommunications more and more attention was paid to technologies of fourth generations that have the best, compared to previous generations, the characteristics of quality, speed and greater range of services. One of such technology is LTE.
1. Relevance
Telecommunications market is rapidly growing, changing trends and its operators must react promptly to preserve their positions and have profit in a competitive environment.
The problems of mobile communications:
Obviously, using existing networks to satisfy customer requests is almost impossible, so we can identify the main reasons for the need to introduce fourth-generation networks:
2. The purpose and objectives of the work, expected results
The purpose of the work is the creation of a mobile network with a reliable radio coverage, new services, low latency and high bandwidth on existing GSM networks, the rationale for the introduction of technology LTE, searching of economically viable solutions for the modernization of the GSM-networks for the introduction of LTE.
The main objectives of the study:
The object of study: abstract segment of the existing mobile network.
Subject of study: the union of methods to reduce costs, increase economic efficiency in the implementation of the LTE networks to the networks of GSM-standard.
As part of the master work is expected get the actual scientific results scientific results in the following areas:
For the experimental evaluation of the theoretical results and the formation of the foundation of further research, as practical results will be:
3. Review of Research and Development
3.1 Review of international sources
МThe International Telecommunication Union (ITU) began studies on globalization of mobile communications in 1986 and established long-term requirements for the frequency spectrum for the future of third generation mobile communication systems. In the 1992 ITU World Administrative Radio Conference (WARC-92) distributed the 230 MHz spectrum in the range of 2 GHz, the global system of third generation mobile communication satellite and terrestrial segments. Thus began the development of mobile networks, which is embodied in Release 8 [5], which gave the start of work on the technical appearance of mobile networks of new generation coming after generation of 3G, which are designed to revolutionize conventional technology. Work on Release 8 were terminated in mid-2009, work began on Release 9 [6-7], which defined the second phase of the LTE development.
Improving the functionality of LTE in Release 9 is the realization of the two bands or multiband data in a single physical channel, the further development of the radio access network E-UTRAN, the introduction of new high speed data transfer scenarios. Work on Release 10 are aimed at further development of LTE technology and the creation of advanced technology LTE Advanced.
3.2 Review of national sources
In the works of national scientists, such as Tikhvinsky V.O., Terent'ev S.V., Yurchuk A.B. "Mobile networks LTE: Technology and Architecture» [1] describes the main structural characteristics of the technologies LTE, protocol stacks, the stages of technology development, the interaction of the LTE network to 3GPP access networks, and no-3GPP. The same attention paid to issues of standardization, the specification network LTE in[2].
3.3 Review of local sources
Donetsk National Technical University (Department of Automation and Telecommunications) studies technologies of 4 generations, including LTE. Articles of Degtyarenko V., Shakhov D., Knertsera D., Zaporozhchenko V., Gas'kova I. devoted to issues of self-organizing networks, LTE, radio coverage. Great attention to design and simulation of communication networks is given to employees of the department of AT, they established methodology for the design of telecommunications networks and systems [3], which are described in detail the steps of network design, the method is universal, allows you to design a network for any technology.
4. 4. Developing LTE network model
To achieve the objectives as a segment for the design of the mobile network has been chosen "Donetsk Airport," which is one of the largest airports in Ukraine. There is urban ATS that serves the needs of staff and residents of the surrounding area in a high-speed Internet, telephone service. Also there are base stations of mobile operators, they all work on the GSM.
4.1 The network design algorithm
- Network design is going according to the following order:
4.2 Creation of information network of the object
There are three types of potential user groups in accordance to the requirements that they put in front of the operator:
4.3 Calculation of network traffic
The network is designed for passengers and staff of Enterprise "International International Airport Donetsk", it is about 3,500. In reality, only half of them will use services of network. The network is divided into six network nodes, in accordance with the amount of public space at the airport. Table 1 summarizes the technical areas and the number of subscribers.
Table 1. – The technical areas and the number of subscribers
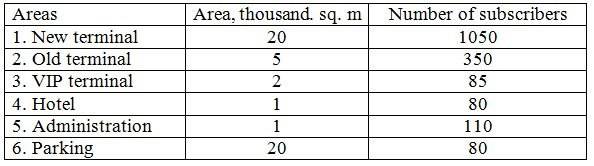
Traffic is calculated separately for each type of service on each node in the network. The formula for calculation is:

where k – network service number;
i – node number;
γ – the expected value of generated traffic by k-service in nodei;
Bср – data rate – the average bandwidth connection, which is sufficient for high-quality traffic of servicek;
Nаб – number of subscribers in node i, which use k-service;
Tс – average duration of a session for k-service;
fвыз – the average number of calls per busy hour for users of node i, which use service k.
Data rate is calculated by:
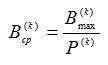
where Bmax – maximum capacity of the communication channel;
P – the ratio between the maximum and average bandwidth required for serice k [3].
In the calculations it was predicted that network traffic is approximately 1.6 Gbit/s.
4.4 The transport network topology
The technology of the transport network must:
As the transport network technology it makes sense to consider Fast Ethernet, Gigabit Ethernet. Ethernet – packet data transmission technology mostly for local computer networks. Depending on the speed of data transmission and a transmission medium, there are several options for technology:
4.5 Network topology
Network segment, for which is simulated network, is selected "International Airport Donetsk" – the total built-up area is about 50,000 square meters, quite small size of the network and, therefore, the main criterion for the choice of topology are the network reliability and its quality characteristics, so the optimal network topology is "hierarchical star" topology. Hierarchical star – kind of a star topology, characterized in that at least part of the "branches" emerging from the main center, branches itself on the second end and performing the role of the hub of the lower level.
The topology of the simulated network can be represented as the structure diagram shown in Figure 1, which shows the relationship of network elements with the LTE network servers and other network elements. In addition, the connecting lines are the transport network technologies for each direction.

Figure 1. – Structural diagram of a network
4.6 The choice of lines
Lines of communication – it is an intermediate apparatus and the physical environment on which information signals are transmitted. In a communication line can form multiple communication channels, such as by frequency or time-division multiplexing. For the designed network will use fiber optic cable because of its acceptable performance. Fiber optic cable – an optical fiber on a silicon or plastic base, enclosed in a material with a low index of refraction of light, which is closed by the outer shell.
4.7 Creation of the structural diagram of a network
In our case, the network, which is designed for small area, but with lots of subscribers, some of which are constantly demanding more bandwidth. Therefore, to address the issue of providing sufficient traffic, consider options for reducing the range of the BS, ie, decrease of cells, we used picacelles – small base stations, which enable to serve limited areas of land with a large cluster of subscribers. As the supporting transportation network only uses the network IP/Ethernet, which is reserved bandwidth required for the passage of traffic generated by the base station. The capacity of a station 100 Mbit/s for recieve and 50 Mbit/s transmission, LTE technology provides flexible bandwidth, so the calculation of the number of for each node to give all possible bandwidths, the results are presented in Table 2:
Table 2. – The number of BS for each node
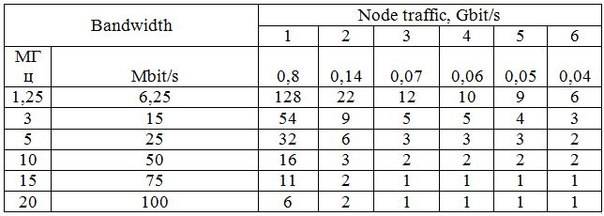
The larger the bandwidth is the better the data transfer rate, and the optimal number of base stations is.
4.8 Creation of the functional diagram of a network
The creation of a functional circuit is a selection of higher-layer protocols that are used to provide services in the designed network:
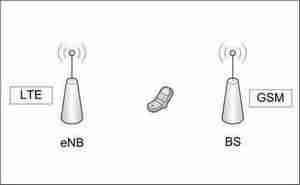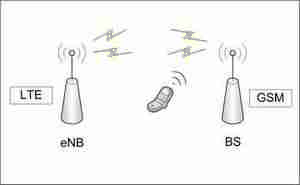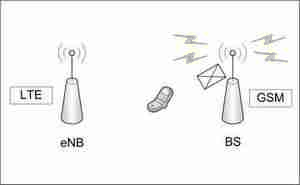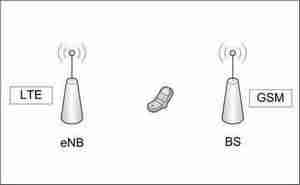
Figure 1. – Visualization of the interaction of BS with the user equipment
(animation: 9 frames, the delay between frames 0.4 s, the number of reproduction cycles 11, size 116 KB, Easy GIF Animator)
Conclusion
Existing mobile networks – circuit-switched network based on the radio access. But with the development of mobile communications in general, and in the provision of new services, the system load increases, and expand the resources of the system is very expensive, and in some places it is physically impossible, so the solution to this problem are in networking technologies to the base 4 generations.
An alternative solution to this problem may be increasing the number of base stations of GSM, but it will led to mutual interference in a limited frequency range, besides the purchase of additional equipment requires a lot of material cost to the operator.
Possible and economically feasible is the use of LTE technology with its capabilities and additional features based on the existing GSM network equipment. The use of this technology will increase the capacity of the communication channel, to the same variety of services that can provide the telecommunications network.
Master's work is devoted to actual scientific problem of the introduction of broadband technology LTE. In the trials were done:
Further studies focused on the following aspects:
Note
To date this master's work is not completed, it will be supplemented and refined. Final completion: December 2012. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his scientific adviser after that date.
