Abstract
Сontent
- Introduction
- 1. Analysis of a design object
- 1.1 Description of the object for which the projected net
- 1.2 The information model of the object
- 2.RF-network
- 2.1Territorial planning placement points BS
- 3. Choice of concepts and technologies of network
- 3.1 Justification of choice of UMTS/HSPA radio access network to build in Amman
- 3.2 Choice of transport network technologies
- 3.3Choice of network topology
- Summary
- Conclusion
Introduction
At the present time in developed countries experiencing a rapid growth of new advances in telecommunications - there are new services (IP-TV, video, video conferencing), the new devices that offer such services. In addition, the observed trend of increasing data rates, improve services, reduce the cost of services and lower prices for subscriber equipment.In such circumstances, he will win the telecommunications operator who can best meet these trends.
It should be noted that mobile subscribers will also increase the demand for new services and higher speeds - people want access to high-speed Internet and IP-TV, while remaining mobile. Mobile operators to solve such problems, we must focus on the transition to the networks of the third or fourth generations, as the second-generation networks with different add-ins will not be able to cope with the task.
The task in the course project is to design a mobile network of third-generation governorates (provinces) in Amman, Jordan. In our region there are carriers, but none of them will not be able to provide subscribers access to new services with the required quality level.
Thus, the aim of the course work is to study the possibility of providing Triple Play services from a mobile cellular communication system of the third generation to Amman Governorate of Jordan.
The aim is achieved by performing the following tasks:
A. Analysis of the study area, population, its preferences, the prognosis of the subscriber, the division of customers into categories.
Two. Compilation of information network model.
Three. Calculation of expected user traffic.
4. RF-radio access network.
Five. The choice of technology and network topology, making the block diagram of the network.
6. Preparation of concept, definition of protocols and speeds.
7. Hardware synthesis of the network.
Eight. Assessment of quality-designed network.
1. Analysis of a design object
1.1 Description of the object for which the projected net
In the administrative division of the country, Jordan is divided into 12 governorates. Amman Governorate is located in the heart of the administrative center of Jordan in Amman. The area of the governorate of 8231 square kilometers, population 2.04 million people. The city is also the capital Amman, Jordan - its cultural, historical, tourist and business center.
In the Amman Governorate of Jordan focused archaeological sites - the ruins of ancient cities, monuments, Roman theaters, museums and more.
Map of the area is presented in Appendix B, the territorial division into districts - in Table 1.1
|
area |
area |
Number of residents |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Аль Абдали |
30 |
127270 |
|
Шафа Бадран |
45 |
63640 |
|
Аль Джбеха |
40 |
72730 |
|
Хербет Апсук |
45 |
54550 |
|
Свалех |
60 |
109090 |
|
Бадер Аль Джадеде |
40 |
45450 |
|
Тла Али |
70 |
49090 |
|
Тарк |
60 |
18180 |
|
Рас Алан |
70 |
218180 |
|
Басман |
20 |
54550 |
|
Марка |
50 |
145450 |
|
Аль Насер |
45 |
118180 |
|
Аль Ярмок |
25 |
72730 |
|
Вади Алсир |
75 |
90910 |
|
Марж Альхамам |
68 |
54550 |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
Захран |
45 |
45450 |
|
Квасмех |
60 |
181820 |
|
Наор |
70 |
127270 |
|
Хосбан |
60 |
27270 |
|
Аль Жезех |
170 |
54550 |
|
Аль Мавакар |
180 |
27270 |
|
Сахаб |
43 |
181820 |
|
Лобан |
90 |
63640 |
|
Аход |
190 |
36360 |
The operators provide access to the Internet via an add-EDGE. But such access speed is not sufficient to provide services to Triple Play, whose popularity is gaining momentum.
Thus, the need to introduce a new mobile communication network of the third generation. This will help to provide new services with the necessary level of quality even if the mobility of people (and even at high speeds).
Thus, the aim of the course project - study the possibility of providing Triple Play services from a mobile cellular communication system of the third generation to Amman Governorate of Jordan.
The aim is achieved by performing the following tasks:
A. Analysis of the study area, population, its preferences, the prognosis of the subscriber, the division of customers into categories.
Two. Compilation of information network model.
Three. Calculation of expected user traffic.
4. RF-radio access network.
Five. The choice of technology and network topology, making the block diagram of the network.
6. Preparation of concept, definition of protocols and speeds.
1.2 The information model of the object
necessary to determine the category of persons to whom you will be given access to the network.
It is advisable to divide them into three categories:
A. The first category - business subscribers. It is the subscribers who work in offices, factories, etc. Their specificity is that they need to guarantee the provision of services because it can be very important for the enterprise. For example, voice, video, high speed Internet access (to view the price lists, presentations, and important programs, news), services, location-based. Business subscribers will account for 30% of the total number of subscribers.
Two. The second category - active subscribers. The specificity of this category - is that the frequency of calls in busy hour is the highest among all categories - a large number of calls, messages, chat sessions with the Internet, watching movies, using the services of online games. Active subscribers, students, youth, social workers. They constitute 45% of the total number of subscribers.
Three. The third category - subscribers with low activity (the remaining 25%). That is, those who do not use the network too often - their job is not connected to the Internet, or talks on the phone. As an example - it can be housewives, elderly people etc. However, the subscribers in this category, high load on the IP-TV services, voice communications. This is due to watching movies, broadcasts, frequent and lengthy calls. It can also be tourists, who need only a voice, Internet access (perhaps even at low speed), services, location-based.
Now we define a range of services to be provided to subscribers of the projected network, and set up the network information model (that is, what category of subscribers to which services are provided).
Thus, the services offered to subscribers:
A. Voice communication
Two. Data transfer
Three. Access to the Internet
4. Video telephony
Five. IP-TV
6. Online Games
7. Services based on location.
Information model of a network that shows what services are available to subscribers of which category is shown in Figure
2. RF-network
2.1 Territorial planning placement points BS
The concept of spatial planning includes analysis of the UMTS network capacity (bandwidth) of base stations, radio resource and service area and, ultimately, the assessment of sites and the hardware base station equipment for a variety of interfaces and core network elements. The task of spatial planning is the placement of radio BS over the territory of the planning area so as to provide 100% coverage and provide access for maintenance of BS.
The average radius of coverage of one base station is 600 meters may vary depending on terrain. Number of BS – 1485. Base stations – three-sector. The average height of BS antenna elevation – 15 m Destinations sectors will be adjusted when operating a network.
Distribution of all base stations in the city area of ??1680 km 2 can not [5], therefore, as an example of the location of BC segment in the city center (figure 2).
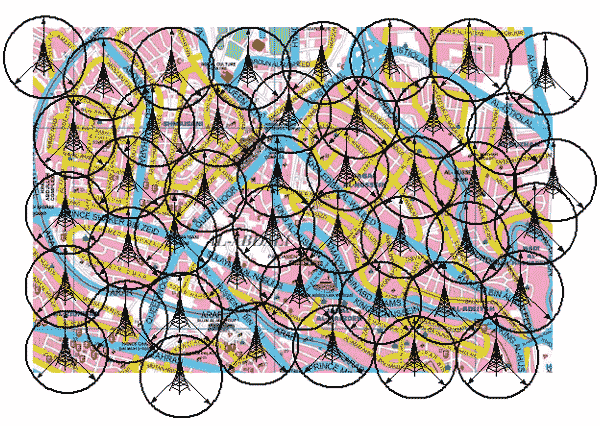
Figure 2 – Example of a UMTS network coverage for the center of Amman
3. Choice of concepts and technologies of network
3.1 Justification of the choice of UMTS/HSPA radio access network to build in Amman
Analysis of the District Planning network shows that it is appropriate to deploy on its territory mobile network UMTS. We give a comparative description of UMTS / HSPA in comparison with the existing GSM network in Amman and other modern technologies of radio generation 3G/4G.
In a GSM network in the evaluation of the energy balance of the radio DL assumption is that the speed of data transmission base station 236.8 kbit / s, coverage should be the same as in the radio UL, which operates at data rates 9.6 kbit/s [6]. Since the DL channel used by the whole power of the base station to communicate with a subscriber station, the size of the base station service area is limited to the channels UL. Thus, the cell radius greater than 200 m speed of data transmission will be unstable and vary from 9.6 to 144 kbit/s, which does not meet the requirements of a modern mobile data network, and access to modern technology in general.
3.2 Choice of transport network technologies
Network operators depending on the needs of its customers profess different approaches to ensure the availability of their services in urban networks. In the European regions, the emphasis is mainly on a regular Ethernet, so that the Ethernet traffic is passed without recourse to an intermediate level of copper or optical media. The need for affordable bandwidth steadily increases, so in urban networks ever more clearly the trend of transition from conventional Ethernet to the so-called optical Ethernet with data rates up to 10 Gbit/s. These networks penetrate the local area in the global network of subsidiaries and associated clients in a variety of city networks of global channel.
The advantages of both approaches are based on their technical background. Ethernet is adapted to the needs of local networks and almost no recourse to the centralized management of data traffic. Such networks can be built using simple and inexpensive components. Today, telecom operators have to use Ethernet in the same way as in regional networks for urban networks. However, based on the parameters of a regular Ethernet to make accurate conclusions about the quality of transmission is unlikely. It is possible for some applications but at a higher level, for example using TCP/IP, which complicates the analysis of errors. Of particular criticality of this situation takes on long transmission lines.
SDH, in contrast, is optimized for data transmission in optical wide area networks, and has mechanisms to monitor and manage data traffic. In addition, due to the synchronous data transfer SDH network work very effectively. Displaying GFP in EoSDH uses this advantage and efficiently operate an asynchronous data traffic in local area networks [9].
The technology allows for standards EoSDH general procedure frame sync (Generic Framing Procedure, GFP), virtual concatenation group (Virtual Concatenation Group, VCG) and the circuit configuration channel capacity (Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme, LCAS). Using these operators modulate Ethernet data from the local client network so that they can be transmitted efficiently through the structure of SDH. GFP results in Ethernet packets of varying lengths in accordance with the requirements of standard shipping containers SDH. VCG provides granular provision of bandwidth on the network SDH. For this method combines a variety of routes in the SDH network into a virtual pencil. The advantage is that with the help of VCG bandwidth SDH networks scales with a smaller step. Finally, LCAS offers one more adapted for Ethernet transmission alternative to traditional protective mechanisms of SDH. She is responsible for ensuring that high availability and SDH remained Ethernet. If one of the joint through the VCG paths fails, the others will continue to perform its tasks [11].
Thus, for the construction of the transport network will be used to further the technology EoSDH transition to Gigabit Ethernet.
3.3 Choice of network topology
After analyzing the possible network topologies, as well as taking into
account the geographical aspects of the design district and the
possibility of switching the location of nodes in the locations of
existing equipment GSM, we conclude that for scalability and
performance, the most reasonable is a ring
topology on the
transport layer nucleus (RNC, MGW, MGC, SGSN) and ring connections for
access between levels trancportnom Node B.
The advantage of this topology is that, in comparison with topologies it has better fault tolerance, since it includes all the best qualities of other topologies, and provides highly reliable data transmission.
Thus, this project will be organized by the backbone network on the basis of the ring, which will combine the core network router nodes (RNC, MGW, MGC, SGSN). Transport network access will be provided as a ring topology to connect the Node-B. This will keep the services of the subscribers in case of emergency. Node B will be included in a large ring road.
The topology for the network segment of the central part of the city in relation to the Amman map is shown in figure 3.
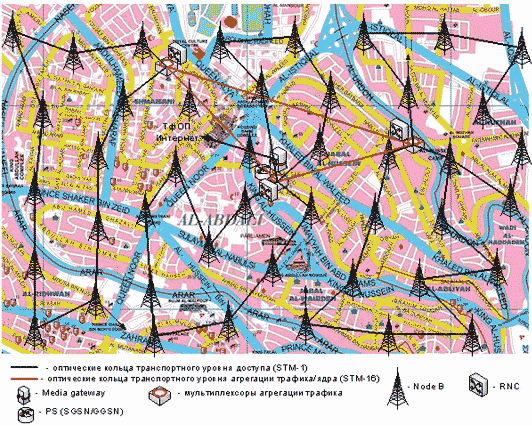
Figure 3 – Network topology map of the central district of city
Topology allows the connection of a large number of stations and the characteristic, usually for large networks, and maintains a high level of scalability and manageability.
Summary
In the present work was carried out design of the UMTS network in Amman – Jordan's capital. Development of a segment of a UMTS network in Amman is an urgent problem, the services provided by the network will be three generations vosstrebovan. According to market research of potential customers for the next 5–10 years is 20% of the population of the city, that is, 500 000 inhabitants.
Based on the calculations, the average load of a network subscriber using a single radio access services is: for DL = 0.318 Mbit/s, for UL = 0.058 Mbit/s. At the same time share a single channel DL can be distributed between the three network users. UL channel can take up to 6 users [12].
There have been justification for the selection of UMTS/HSPA radio access network design in Amman. This technology provides the full requirements for network services and make it easy to deploy new broadband services.
Based on fact that in Amman there is a well-developed network of SDH, is to reduce the cost of building the network would be rational to use the technology EoSDH (in optics), with the gradual replacement of part of the network to the optical Gigabit Ethernet.
In a course of the work have been developed and described the structural and functional network diagrams, protocols and interfaces, the interaction sites.
Also in the work was carried out selection of network equipment at all levels. Analysis of existing solutions for 3G networks showed that optimalnyi in all respects is a provider of company Ericsson.
Qualitative assessment of allowable loss of the radio BS-MS for the different services and different network conditions at the location of subscribers showed that at the boundary of the loss of hundreds of permissible under the TK is not more than 160 dB are observed for all cases considered. This means that not all of the coverage network subscribers will be provided with the necessary signal level, which means a high level of service quality.
Conclusion
- Шиллер Й. Мобильные коммуникации.: Пер. с англ. – М. :Издательский дом "Вильямс", 2002. – 384 с.
- Маковеева М.М., Шинаков Ю.С. Системы связи с подвижными объектами: Учебное пособие для вузов. – Г.: Радио и свиязь, 2002. – 440 с.
- Андрианов В., Соколов А. Средства мобильной связи. – СПб.: BHV-Петербург, 2001. – 256 c.
- Карташевский В. Г., Семенов С. Н. Сети подвижной связи. – М.: Эко-трендз, 2001. – 299 с.
- Невдяев Л. М. Мобильная связь 3-го поколения. – М.: Связь и бизнес, 2000. - 208 с.
- Бабков В.Ю., Вознюк М.А., Михайлов П.А. Сети мобильной связи. Частотно-территориальное планирование. СПбГУТ, СПб, 2000, 196 с.
- Sipila, K., Laiho-Steffens, J., Jasberg, M. and Wacker, A., «Modelling the Impact of the Fast Power Control on the CDMA Uplink», Proceedings of VTC'99. Houston, Texas, May 1999, pp. 1266–1270.
- Ojanpera, T. and Prasad, R., Wideband CDMA for Third Generation Mobile Communications, Artech House, 1998.
- Lee, J. and Miller, L., CDMA Systems Engineering Handbook, Artech House, 1998.
- 3GPP Technical Specification 25.101, UE Radio Transmission and Reception (FDD).
- 3GPP Technical Report 25.942, RF System Scenarios.
- 3GPP TSG RAN WG4 Tdoc 99/329, Impact of OHG Harmonisation Recommendation on UTRA/FDD, June 1999.

