The study of the dynamics of the system control the technical condition of equipment
Авторы:
В. А. Резников, Е. М. Сорокина
Перевод: Сорокина Е.М.
Описание: It is suggested to examine the technical systems of the state, as systems of automatic control, by the formed chart of service of technical service and repair, as a managing device.
Источник: Журнал "Искусственый интеллект"
УДК
658.3
V.A. Reznikov, K. M. Sorokina
Research of dynamics of control system by the technical state of equipment
Statement of the Problem
The effectiveness of the equipment in
the respective
estimated using objective or subjective indicators (called performance
indicators [1]), which are observed either directly by staff or special
technical means. The defects that occur in equipment during its
operation, lead
to changes in the parameters of efficiency, and as a consequence, the
deviation
from the values of
performance indicators established by the normative and technical
documentation. Depending on the magnitude of these deviations are
recorded
failure of the object or its pre-crash (predotkaznoe) technical
condition, and
thus determined by the work already accomplished to eliminate the
failure or
the various preventive maintenance and repairs to prevent the
occurrence of
failures when the equipment is intended. All these works are carried
out
service maintenance and repair service (TOR). And, as in the first,
that in the
second case the problem is actually the TOP service is to eliminate
these
variations, that is, the "return" performance at the limits of the
established tolerances for them.
Consequently, the service can be
regarded as the TOP
management system technical condition of equipment (SUTS), whose
mission is, by
definition [2], is to stabilize the performance parameters set at the
level
prescribed by the normative and technical documentation for the entire
period
of use of the equipment as intended by purposeful human action (a group
of
people) and instruments of labor, that is, by the government. Moreover,
a
feature of this control system is that there are intra-driven variable
properties
of machines and mechanisms, which maintain the required level ensures
efficient
use of equipment for other purposes.
At the same time, considering the
equipment as a
dynamic system (a dynamic object management), in [3] indicated that the
failure
object to transition from one state to another technical accompanied by
a
transient whose duration depends on the type of violation and the
dynamic
properties of the object. It is clear that the dynamic nature of the
process is
and disaster recovery. Thus, there is reason to study the control
system
technical condition of equipment, such as the stabilization system,
using the
methods adopted in control theory.
This paper focuses on the formation of
the block
diagrams of control of the technical condition of the equipment as a
system of
automatic stabilization performance at a given level.
The structure of the facility maintenance
In accordance with the approach we
assume that the
object of maintenance is generally described by the transfer function
of the form:
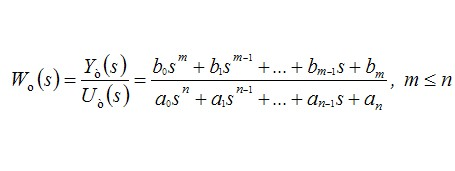 (1)
(1)
where Yt (s) - Output (controlled)
process variable
object, UT (s) - the control action, provided the technology of the
object.
Defects of the object, by definition [4], are the outputs of its own (structural) parameters beyond tolerances established for them. In the framework of the model (1), this means changing the coefficients b0, ..., bm, and a0, ..., an. When a certain character of the change of control action UT (s) specified changes in the coefficients of the model (1), of course, warrant a change as most Yt output variable (s), and its characteristics (eg quality of the transition process), ie, in the end , performance of the object to its destination.
At the same time, we know that the
dynamic object
described by the transfer function of the general form (1) can be
represented
as a corresponding block diagram. For example, suppose an object is
described
by the transfer function
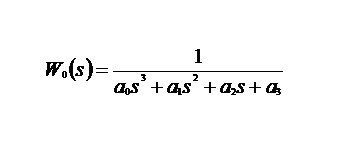 (2)
(2)As a result, the necessary transformations, we obtain that this object can be represented as the block diagram shown in Figure 1. Such a structural representation of the mathematical model (2) suggests that in the restored object parameters a0, a1, a2 and a3 "represent" the appropriate functional-structural elements A 0, A 1, A-2 and A-3. In this case, the output values of these parameters outside the specified tolerances on them (ie, defect) can be equated with the refusal of the corresponding functional-structural component. For example, the parameter a3 can be formulated as the following defect: "Refusal of A-3."
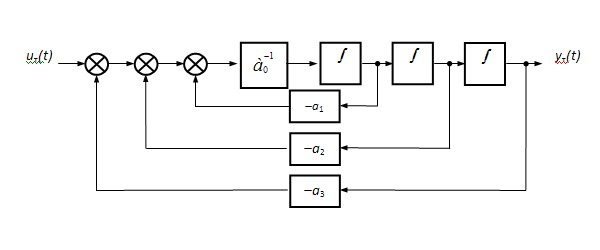
Such a structural representation of object maintenance (control object, the object of stabilizing the technical conditions) makes it possible to carry out further transformations, which consist of the following.
Each i-th parameter of the object (1)
can be written
as:
 (3)
(3)
where - the
nominal value of the i-th parameter (working-state of the Ai); -
changes in the
i-th parameter, due to the fault element of Ai.
This, in turn, allows us to represent the object of control, in which there are single defects in the form of the block diagram shown in Figure 2, and - the transfer functions of the object at the nominal parameter values.

Figure 2 - Modified block diagram of the control object
The structure of the control device
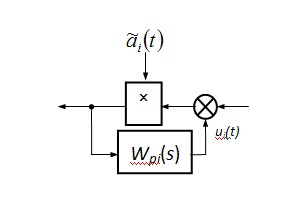
Figure 3 - Block diagram of the
stabilization system
in case of failure of i-th element
Every single object with parametric perturbations can be represented as a set of objects. For example, if an object is described by the model (1), for m = 0 we have N = (0, 1, ..., n) objects, which are block diagrams of the form shown in Figure 2. At the same time, the principle of adaptation, in fact, lies in the fact that as a result of self-tuning control parameters of the base is formed by the set of non-adaptive controllers, each of which is intended to stabilize the quality "of his» i-th object (see Figure 3).
On the other hand the service of TOR as some organizational and structural unit of the enterprise, can be represented in a simplified form: Head + repair personnel. The task manager is to determine the technical state of the object and the direction of "appropriate" repairman to eliminate the causes of technical change in the state. The task of each repairman is in immediate removal causes changes in the technical state of the object. Consequently, the language of the concepts adopted in control theory, the service can be regarded as the TOP control unit consisting of a logical block (head) and a set of regulators (repairers), that is, the control device formed on the basis of structural adaptation [8] and has structure shown in Figure 4, where indicated: LB - logical block; S (t) - the set of input variables that contain information about the technical state of the object of control, 1 - identifier, designed to determine the reasons for the refusal of the object (object identity of the failed element), 2 - decision-making unit, 3 - a modifier that produces a control signal switching power supply unit; Pk - k-th control; uik (t) - management of the technical state of the i-th element of the object formed by the k-th controller.
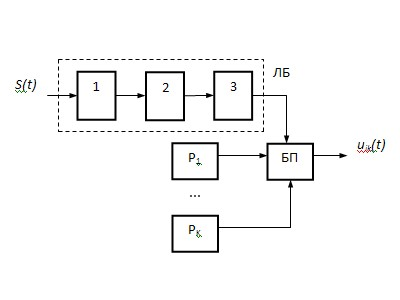
It should be noted that in most
practical cases, the
power of K less than the power of N. Moreover, in practice TOP Service
manages
the technical condition of not one but several objects, and therefore
this
relation between the capacity of the sets K and N is even more so.
However, it
should take into account a person's ability to adapt to the dynamics of
the
object as well as to the form of perceived their input signals [9].
Consequently, service in the TOR adopted in control theory concepts and
definitions can be considered as a control device consisting of a set
of
adaptive controllers.
Conclusion
The relevant regulations define as the
primary task of
the service TOP task management technical condition of equipment,
rather, the
task of stabilizing the parameters of the technical state at a given
(desired)
level. That, and the dynamic processes of loss and recovery of the
equipment
create conditions for the study SUTS using the methods adopted in
control
theory.
Proposed in this paper, the structural
scheme SUTS as
automatic control systems make it possible to analyze the nature and
extent of
the influence of experience, qualifications, etc. maintenance personnel
on the
efficiency of maintenance by using the known methods of analyzing the
stability
and quality self-propelled guns.
This aspect of the research will, in our
opinion, to
get the results that improve the efficiency of the modern health
service and
repair equipment.
Literature
1. The reliability and efficiency of the
technique: A
Guide to the 10-book. / Kn. 8: Maintenance and repair / Ed. VI
Kuznetsov, and
EJ Barzilovicha. - Moscow: Mashinostroenie, 1990. - 320.
2. GOST 18322-78. System maintenance
and repair of
equipment. Terms and definitions.
3. Sklyarevich AN Linear systems
with possible
violations. - Moscow: Nauka, 1975. - 352.
4. DSTU 2389-94. Technical diagnostics
and control of
technical condition. Terms and definitions.
5. Solodovnikov VV Biryukov, VF, VI
Tumarkin The
principle of control theory. - Moscow: Nauka, 1977. - 344 p.
6. KV Frolov Reduction of the
oscillation amplitude of
the resonance systems by controlled variation of the parameters / / of
machines. - 1965. - № 3. - S. 25-30.
7. Aleksandrov, AG Optimal and adaptive
systems. - M.:
High School, 1989. - 263 p.
8. Schulze, KP, K. Reber Engineering
analysis of
adaptive systems. - Springer-Verlag, 1992. - 280 p.