Abstract
TABLE OF CONTENTS
- Introduction
- 1. Goal and tasks of the research
- 2. Actuality of the topic
- 3. Scientific novelty
- 4. Review of Research and Development
- 5. Development directions for the rational use of technogenically damaged lands
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
The natural basis of existence of society is the natural environment, i.e. collection of objects and conditions of nature, in which any activity of the subject is occurs [1].
Since ancient times, of existence mankind has tried to balance as its relationship with the environment, so that nature as possible longer provided him with a comfortable existence, but do not always succeed [2]. Nature is the foundation of all of human activity, the source of all the resources of its economy, science for a long time did not notice the issue of the impact of civilization on nature. First raised this issue V.I. Vernadsky. He proved that a power of influence on the biosphere of man-made processes to the beginning of the twentieth century. became comparable with geological and other natural processes [3].
The development of the mining industry around the world is going to 1,4-1,7 times faster compared with other industries. The volume of world mineral production will be doubled roughly every 15-18 years.
With such large amounts of mineral production problem rational nature management careful attitude to the wealth of mineral resources and complex use gets global significance and becomes more acute.
1. Goal and tasks of the research
Objective: To develop and prove directions for the recovery technogenically disturbed lands (Kiev district the city of Donetsk) and involving them in use on the basis of their assessment of ecological status.
To achieve the formulated goal we need to solve the following tasks:
- To substantiate the relevance of the rational use of technogenically disturbed lands of the Kiev district of Donetsk.
- Analyze the research in the field of environmental protection and rational use of land resources.
- Rate the ecological situation on the technogenically disturbed areas.
- To develop and validate directions recovery of technogenically disturbed lands this district and engage them in use.
The object of this research is the Kiev district of Donetsk. District is located in the northern part of the city. It is called the main gate of Donetsk, as there is Donetsk airport belonging to the category of international and accepts all classes of airplanes, as well as the train station. Near Airport – Putilovskiy bus station, the departure point in the long-haul flights passenger buses [5].
Subject of investigation: violations of useful properties of the soils of the Kiev district of Donetsk as a result of industrial activity.
2. Actuality of the topic
Relevance of this research lies in the fact that the Kiev district of Donetsk city occupies an area of 33 km², and the population of the district reaches nearly 150,000 people. It is the most densely populated district of the city [6], the industrial potential of which is diversified industry with prevalence hard – coal, engineering and metallurgy. There are more than 20 large and medium-sized industrial enterprises in the district.
In the territory of Donetsk is located according to different estimates between 120 and 138 waste dumps, which occupies the territory of 1000,71-1104,20 hectares. The number of valid waste dumps – 32, burning of them – 28. The total volume of the rock is about 336-337 million m³.
So when considering questions of rational land use the Donetsk region [7] focuses attention on the fact that a large number of damaged lands formed as a result of irrational use of land enterprises, especially because of pollution rock mining. Due to the fact that a large amount of land in the Donetsk region occupied by waste dumps located near population centers, cities, worsening living conditions, both humans and all other living organisms.
A systematic approach solving this problem will allow to develop and substantiate directions of the restoration of technogenically disturbed lands Kiev district of Donetsk and involving them in use on the basis of assessment their ecological status.
3. Scientific novelty
Scientific novelty – the development and a substantiation directions to restore technogenically damaged lands Kiev district of Donetsk and involving them in use on the basis of assessment their ecological status.
The scientific novelty discloses in results of the following research:
- These researches will allow to consider objects as elements of
Man – an enterprise – the natural environment
. - I have proposed criteria for choosing elements of the system for later recovery and use.
- Directions to recovery technogenically damaged lands Kiev region of Donetsk were developed.
- Ecological, economic and social results were substantiated with using a systematic approach to the functioning of the Kiev district.
4. Review of Research and Development
Many works of Donetsk's scientists and researchers of other coal-producing regions are devoted to the problem of using waste heaps. In particular, M.P. Zborschik, V.V. Osokin and others [8], V.I. Bondarenko, G.G. Pivnyak, A.N. Zorin [9], M.D. Pharmacist, N.G. Matveev [10], N.S. Surgai and V.N. Buslik [11], M.F. Smirniy [12] offer different variants of recultivation and using natural dumps.
The analysis of works and other publications of this authors indicates that many specialists consider that recultivation of waste heaps is mandatory procedure, as they are a source of chemical and radiological contamination of soil, dust and gas pollution and render hazardous effects on the environment [13].
This shows that the rational use of natural resources on a large scale – it is pretty a complicated science. And do it should experienced professionals. There are such scientists and environmentalists In Dnepropetrovsk and united in distinct institution. It is the Institute of Problems Nature Management and Ecology of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, which was established in 1991. To the main areas of research for the Institute include the following:
- Development and substantiation methodology for selecting a strategy for sustainable development of technogenically-loaded regions of Ukraine;
- Development of scientific foundations of regional environmental monitoring system;
- Assessment and forecast environmental impacts of the use of technology.
All the time the Institute is headed by renowned scientist, Ph.D., professor, corresponding member of the National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, laureate of the Prize A.N. Dinnik National Academy of Sciences of Ukraine, laureate of the State Prize of Ukraine in Science and Technology, Honored Scientist of Ukraine Shapar Arkady G. [14]. He was the first who scientifically proved the influence of modern mining on the dynamics of the geological environment and the environment in general [15].
It should also be mentioned great contribution of Ukrainian State Research and Project Designing institute of Mining Geology, Geomechanics and Mine Surveying (UkrSRPD NAS of Ukraine).
Currently UkrSRPD performs research for the Ministry of Coal Industry of Ukraine, the Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine, the Ministry of Agrarian Policy of Ukraine and other agencies, takes part in international projects with Russia, France and other countries near and far abroad [16].
A systematic approach to solving the problem will allow to develop directions to restore technogenically damaged lands Kiev district of Donetsk and involving them in use on the basis the assessment of their ecological status.
5. Development directions for the rational use of technogenically damaged lands
Rational nature management demands strengthening links between the scientific and technical progress, and environmental protection, in particular, the implementation of measures aimed at reducing and eliminating the negative human impact on the environment, conservation, improvement and rational use of natural resources, and this means that the development of national management should take more environmental character [19].
The territory of Donetsk has more than 200 zones of pollution and cluttering lands, which cover an area of 50 km² (up to 3% of the total area of the city). As a part of the examined soil in and around enterprises found 26 dangerous chemicals, including mercury, lead, zinc, germanium, as well as nitrates, nitrites, chlorides. The most contaminated soils industrial areas of the city and the surrounding living areas and farmland [20].
Technogenic intensification of production contributes to the pollution and dehumification, secondary salinization, soil erosion [21]. Main part polluting substances enters the soil with atmospheric precipitation and because placing waste disposal industrial enterprises and life of the population [20].
On the territory of the Kiev district there are 29 waste dumps with a total area 0,45 km² with a volume of rock 17308 m³ [22], of which:
- 7 waste dumps – do not burning and do not greened (about 7.9*106 m);
- 8 waste dumps – do not burning, partially greened;
- the other 14 are acting and burning.
Characterization of the state of waste dumps is presented in Picture 1.
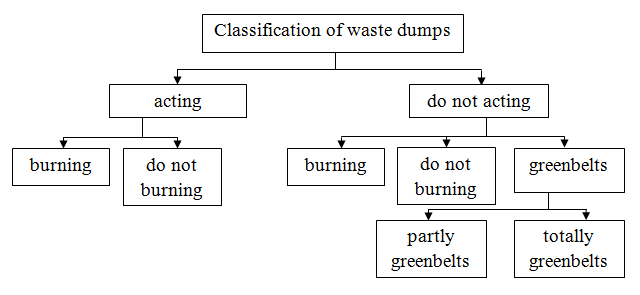
Picture 1 – Status classification of waste dumps.
Lands which were occupied by waste dumps can be re-cultivated through the development and export of rocks from the occupied lands, filling dumps fertile soil surfaces and planting grass on them or planting trees and shrubs, as well as bio-remediation of surface dumps at the expense of planting trees and shrubs to the soil
waste dump, which is formed by the decomposition of rocks by water, wind, temperature, etc. [18]
Were applied ecological measures on the use of do not acting do not burning and do not greenery waste dumps as technogenic mineral deposits or as a raw material for industrial production.
Do not acting, non-burning and partially greened waste dumps should be further greening and use as an ecological network of the city. Totally greened waste dumps can be used to create zones of tourism or recreational areas.

Picture 2 – Evolution of the form of waste dump
(animation: 4 frames, 5 cycles of repeating, 48 kilobytes)
The rest of the waste dumps should be putting out according to KD 12.09.0801-99 Manual for the Prevention of spontaneous combustion, extinguishing, demolition and reclamation waste dumps of coal mines and preparation plants
.
Meanwhile, as the results of numerous research and development, as well as the experience of leading enterprises and individual regions of the country, most of the sectors of waste mineral complex can be successfully used for various sectors of the national economy. For example, for the production of building materials are suitable 67% of the overburden, including for the production of crushed stone – 30%, cement – 24%, ceramic materials – 16% and silicate materials – 10% [17].
Conclusion
Currently, human civilization has become the most important factor of influence on the nature: the laws of society and nature are inextricably intertwined and interact. Humanity as a whole and its private individuals faced the need to transition to a new way of thinking – the perception of the planet as a single entity [4].
The main objective of reinstatement of the environment disturbed by mining activities is the inclusion of disturbed lands in the economic or cultural use by creating an ecologically balanced system which represents the economic and aesthetic value [1].
As a result, were performed the following tasks:
- The urgency of the rational use of technogenically disturbed lands of the Kiev district of Donetsk was substantiated.
- Researches in the area of environmental protection and rational use of land resources were analyzed.
- Directions to restore technogenically damaged lands the district and engage them in use were developed.
The rational use and restoration of technogenically damaged lands Kiev district of Donetsk will eventually lead to:
- Solve environmental problems:
- Solve social and economic problems:
1) reduction of air pollution with toxic gases, dust, etc.;
2) reducing the concentration of pollutants to the background;
3) reduction of pollution by sewage from the waste heaps of water objects of the district;
4) an increase of "green" territories, elimination the deficit of public green space in the city;
5) conservation and ecologically balanced use of natural resources;
6) exemption of large areas of land which were occupied by waste dumps;
7) improvement of useful soils properties.
1) the emergence of jobs in the city;
2) improve the health of the population;
3) improve the aesthetic state of the city;
4) preventing cluttering of land in the city that could be used for other purposes;
5) the establishment of zones for recreation and tourism.
Experience shows that the vast majority of waste mineral complex can be used with a significant economic effect [23]. In particular, in some enterprises of coal industry the specific weight of wastes which are used, reaches 80-95%.
References
- Горное дело и окружающая среда: Учебник. – М.: Логос, 2001. – 272 с.: ил.
- Некос В.Ю., Максименко Н.В., Владимирова О.Г, Шевченко А.Ю. Нормування антропогенного навантаження на навколишнє природне середовище: Підручник для студентів екологічних спеціальностей вищих навчальних закладів. – Вид. 2-ге доп. і перероб. – Х.: ХНУ імені В.Н. Каразіна, 2007. – 288 с.
- Гирусов Э.В. и др. Экология и экономика природопользования: Учебник для вузов/Под ред. проф. Э.В. Гирусова; Предисловие д-ра экон. Наук Председателя Госкомэкологии РФ В.И. Данилова-Динальяна. – М.: Закон и право, ЮНИТИ, 1998. – 455 с.
- Арский Ю.М., Архипов Н.А., Аюров В.Д., Бондарев И.В., Гаркавенко Н.И., Коваль В.Т., Куприянова Н.Ю., Панфилов Е.И., Петров И.В., Попов С.М., Таскаев А.В., Третьяков О.Н., Трубецкой А.К., Умнов В.А., Харченко В.А. Рациональное природопользование в горной промышленности. Изд. 2-е. Под ред. проф. Харченко В.А. – М.: Издательство Московского государственного горного университета. – 1998, 444 с.
- Донецкий форум. Районы Донецка [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.doneckforum.com....
- Новости Донецка. Киевский район [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://autoexpo.dn.ua...
- Штагер О. А. Проблеми раціонального використання земельних ресурсів Донецької області. /Штагер О. А. // Вісті Донецького гірничого інституту. – № 1, 2009.
- Зборщик М.П., Осокин В.В., Рудь А.М., Варакин В.В., Вознесенский В.В. Патенты России № 01432248. Способ устранения пожаро- и взрывоопасности породных отвалов. – Бюллетень № 4 от 23.10.1988.
- Бондаренко В.И. Закономерность омоноличивания рыхлых водонасыщенных пород под воздействием электрического тока / В.И. Бондаренко, Г.Г. Пивняк, А.Н. Зорин. – Диплом № 12 Российской академии естественных наук [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.raen.info...
- Аптекарь М.Д. Возможность применения мирового опыта в переработке породы отвалов угледобывающей промышленности в угольных регионах Донбасса / М.Д. Аптекарь, Н.Г. Матвеева // Сборник материалов Международной научно-практической конференции "Экономические, экологические и социальные проблемы угольных регионов СНГ". – Краснодон: Краснодонский факультет инженерии и менеджмента Восточно-украинского национального университета им. В.Даля, 2007.
- Сургай Н.С. Рекультивация породных отвалов закрывающихся шахт Львовско-Волынского угольного басейна / Н.С. Сургай, В.Н. Буслик // Уголь Украины. – 2000. – №6. – С. 27-29.
- Смирный М.Ф. Экологическая безопасность терриконовых ландшафтов Донбасса: монография / М.Ф. Смирный. – Луганск: Изд-во ВНУ им. В.Даля, 2006. – 232с.
- Попова И. Горящие терриконы – мина замедленного действия / И. Попова // Донецкий кряж. – 2004. – № 948. – 26 марта.
- Інститут проблем природокористування та екології [Электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.treasury.gov.ua...
- Приднепровский научный центр. Шапар Аркадій Григорович. [Електронний ресурс] – Режим доступу: https://intranet.nas.gov.ua...
- Украинский государственный научно-исследовательский и проектно-конструкторский институт горной геологии, геомеханики и маркшейдерского дела (УкрНИМИ НАН Украины) [Електронний ресурс] – Режим доступу: http://ukrnimi.donetsk.ua/
- Лебединский Ю. П., Склянкин Ю. В., Попов П. И. Ресурсосбережение и екология. – К.: Политиздат Украины, 1990. – 223 с.
- Меркулов В.А. Охрана природы на угольных шахтах. М., Недра, 1981, 184 с.
- Курило В.І. Методичний посібник
Охорона навколишнього середовища та раціональне використання природних ресурсів
. Київ, 2010. – 176с. - Программа охраны окружающей природной среды и обеспечение экологической безопасности города Донецка до 2015года. № 14/32 от
02
ноября 2007 г. - Природопользование: Учебник. Под редакцией проф. Э.А. Арустамова. 2-е изд., перераб. и доп. – М.: Издательский Дом
Дашков и Ко
, 2000. – 284 с. - Я. Олійник, О. Кононенко, А. Мельничук. Напрями відновлення порушенних територій унаслідок надмірного техногенного впливу. // Географія. 54/2007.
Временное руководство по определению объема и номенклатуре исходных данных для составления мероприятий по утилизации вскрышных и вмещающих пород
. П.М. Джунько, М.Я. Шпирт, Ю.Н. Жаров, Т.А. Михалева. Всесоюзный научно-исследовательский и проектно-конструкторский институт охраны окружающей природной среды в угольной промышленности (ВНИИОСуголь). 1983. Стр.11-26.
