Abstract
Сontents
Introduction
In today's world, drones can be used in areas such as detection of ground and flying objects can be applied in various areas of life, such as aerial photography (geodesy, cartography), meteorology, protection of critical facilities, fire detection, in the military industry (video monitoring, detecting terrestrial aerial objects). The urgency of developing such devices supported by fast growing market and the scope of tasks.[1]
1. The general problem
When creating drones solved a number of challenges:
1. Determining the orientation (three-axis angles relative to the ground) and the stabilization of the results;
2. Determination of the height and the stabilization of the application;
3. Determination of the origin and the flight from the given points;
4. Flight of trikopter a predetermined rate.
Trikopter - is remotely controlled or autonomous unmanned three-rotor flying mashines with three screws (рис. 1).[2]
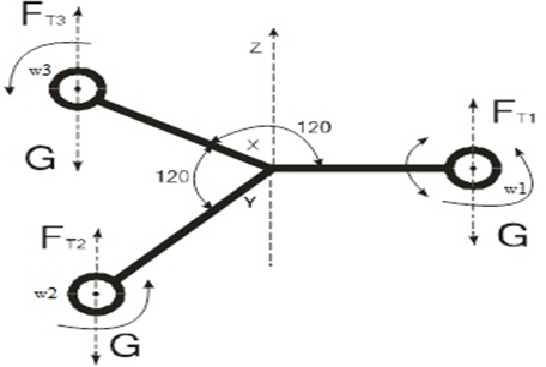
Figure 1 –model of trikopter
2. Review of existing solutions
Trikopter's management refers to the management class multirotor systems. Trikopter's control block diagram is shown in Figure 2
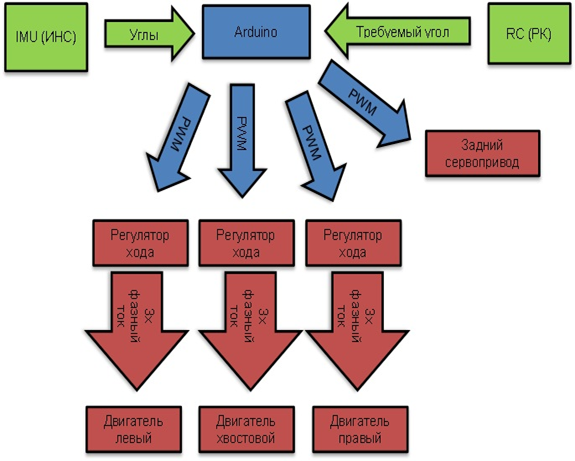
Figure 2 – Block diagram of the control trikopter[4]
The elements of this structure diagram:
RK - the hand controller. To set the mode of operation of the facility used by a radio transmitter. Multicopter mounted on the receiver receives the signals sent from the control unit (transmitter) by the operator, and converts them into electrical signals which commutes microcontroller sending control signals beskollektrnym engines. Mikrokopterom used to control the summed signal (called PPM - Pulse-position modulation). Standard, commercially available receivers and transmitters are designed to control the actuators flying model airplanes and helicopters and other radio-controlled models. Control they are the so-called signal PWM (Pulse-width modulation) Each transmitter has a number of channels (7, 9, 12), which outputs correspond to the actuators receiver. At the same mikrokoptere to the main board (FlightCtrl) fits only one (except GND and 5V) control wire that carries the added signal PPM, comprised of the data on all the signals transmitted from the transmitter.
Arduino - the main board. Is a central and indispensable part of any multirotornogo aircraft. This board consists of a main processor (at version 2.0 microcontroller Atmega644P, at version 2.1. - Microcontroller Atmega1284P) and of the sensors that are needed to ensure sustained flight. [6 ]
INS - inertial navigation system - a set of sensors that provide the desired mode of the object. Of all the sensors, positioning motors are the most important. The software uses them to determine the position of the platform in the air and give the command to compensate for changing the position of the external agents. For each axis (x, y, and z) needs one sensor. Typically, these sensors are called gyroscope or Gyros, and they measure inclination in degrees per second. Another sensor - accelerometer. It measures the acceleration of the device in all three axes. The vertical acceleration sensor is also able to measure the angle of inclination relative to mikrokoptera surface. They are called accelerometers or Accellerometer (ACC). Mikrokopter can fly without this sensor, but with him mikrokopter will always try to take a position parallel to the ground. To measure the altitude of an object on the main board is set height sensor (MPX4115A). When activated the unit gains the ability to fly all the time at the same height.[7]
Rear actuator - servopovorotny mechanism which is used to change the angle of the plane of rotation of the tail engine. Most servos use three wires to work. Wire for power, typically 4.8V or 6V, common (ground) and signal wire. The control signal conveys information about the desired position of the output shaft. The shaft is connected to a potentiometer, which defines its position. The controller in the servo on the resistance of the potentiometer and the value of the control signal determines which way you want to rotate the engine to get the right position of the output shaft. The higher the voltage servo, the faster it works and develops more torque. Actuators may have an angle of rotation of the shaft 60, 90, 180 degrees. The angle of rotation is limited electronically and mechanically. There actuators without limitation, i.e. rotating through 360 degrees. If you have a servo drive with an operating range of 60 degrees, then you can extend it only changing the design of the servos. Sometimes it is possible to increase the range of specially distorting the control signal. But this is non-standard and unreliable way. [9]
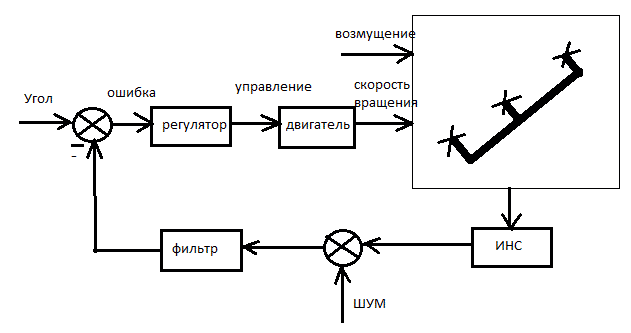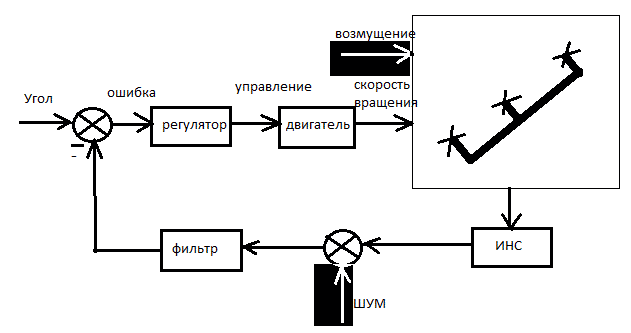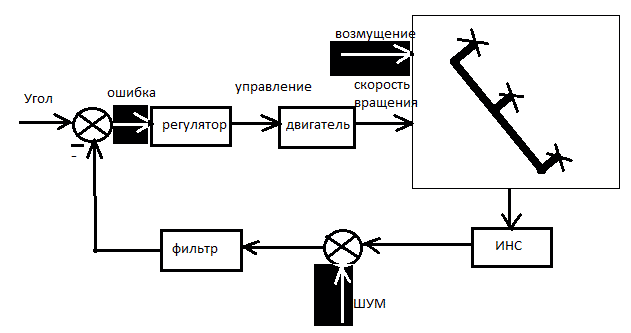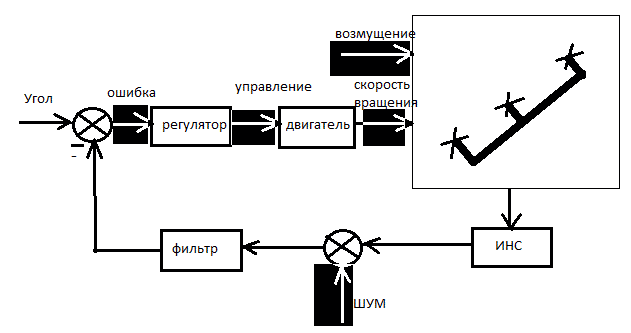
Figure 3 – Chart stabilization angle of trikopter
(animation: 4 frames, 10 cycles of repetition, 12 kilobytes)
Conclusion
The study examined the existing methods of the unmanned aircraft. The basic problem the solution of which will lead to the goal.
References
- Автоматизація технологічних об’єктів та процесів. Пошук молодих. Збірник наукових праць XIII науково-технічної конференції аспірантів та студентів в м. Донецьку 14-17 травня 2013 р. – Донецьк, ДонНТУ, 2013. – 441 с
- Использование инерциальной навигационной системы (ИНС) с несколькими датчиками на примере задачи стабилизации высоты квадрокоптера [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://habrahabr.ru/post/137595/
- Стабилизация полета трикоптера [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://ea.donntu.ru:8080/jspui/bitstream/123456789/20644/1/%D0%91%D0%B5%D0%B7%D1%80%D1%83%D0%BA%20%D0%A5%D0%BE %D1%80%D1%85%D0%BE%D0%B4%D0%B8%D0%BD%20%D0%A1%D1%82%D0%B0%D0%B1%D0%B8%D0%BB%D0%B8%D0%B7%D0%B0%D1%86%D0%B8%D1 %8F%20%D0%BF%D0%BE%D0%BB%D0%B5%D1%82%D0%B0.pdf
- Проект трикоптер [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://tm.spbstu.ru/%D0%9F%D1%80%D0%BE%D0%B5%D0%BA%D1%82_%22%D0%A2%D1%80%D0%B8%D0%BA%D0%BE%D0%BF%D1%82%D0%B5%D1%80%22
- Приемник-передатчик [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://multicopter.ru/technical/radio
- Основная плата [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://multicopter.ru/technical/mainboard
- Плата навигации [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://multicopter.ru/technical/platanavi
- Бесколлекторные двигатели [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://multicopter.ru/technical/bl-motors
- Типы сервоприводов [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://www.amg-rc.ru/node/50
- Контроллеры бесколлекторных двигателей [Электронный ресурс].– Режим доступа: http://multicopter.ru/technical/controllers
