
Хамидуллина Екатерина Дмитриевна
Факультет компьютерных наук и технологий
Кафедра компьютерных систем мониторинга
Специальность «Компьютерный эколого-экономический мониторинг»
Разработка политики информационной безопасности предприятия с учетом оценки потерь, связанных с угрозами информационных систем
Научный руководитель: к.т.н., доц. Губенко Наталья Евгеньевна
Evaluation and forecasting of losses associated with information security threats using analogy method
Khamidullina K., Gubenko N.
Donetsk National Technical University,
hamidullina_k91@mail.ru
Источник: Источник статьи 3
Abstract
Khamidullina K., Gubenko N. «Evaluation and forecasting of losses associated with information security threats using analogy method» One of the goals of this paper is to understand the principles of information security. The main risk analysis methods are discussed, the model analysis for evaluation of losses is explored and an example of forecasting of losses by analogy method is proposed. The results can be used in companies that need protection from threats and that are supposed to estimate the losses in case of emergency.
Keywords: Information security, threats, risk analysis, model, losses
Introduction
Nowadays, the question of information security is an essential part of business management.
Despite the fact that the terms information security, computer security and information assurance are interrelated and share the common goals of protecting the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information, there are some differences between them.
Thus, information security depends on the form the data may take: electronic, print or others. Computer security ensures the availability and correct operation of a computer system. It can not work with the information stored or processed by the computer. Information assurance focuses on the reasons for assurance that information is protected and is thus reasoning about information security.
The field of information security has grown and evolved significantly in recent years. It is a very vital fraction in the security and computer science studies [1].
Top 10 information security threats
There are a lot of threats that can cause great losses to any company. The list of the most common of them is presented below [4]:
- malware;
- malicious insiders;
- exploited vulnerabilities;
- careless employees;
- mobile devices;
- social networking;
- social engineering;
- zero–day exploits;
- cloud computing security threats;
- cyber espionage.
There is another version of classification of information security (fig. 1) threats presented by Verizon [5].
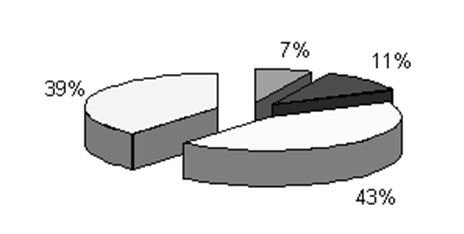
Figure 1. – Information security threats
According to it on the first place there are only external threats (43%), on the second place – multiple sources threats (39%), on the third place – threats caused by internal vulnerabilities (11%) and on the fourth place – threats caused by insiders and partners (7%).
Quantitative Risk Analysis
This method of risk analysis uses two fundamental elements: the probability of an event and the likely loss in case of its occurrence.
Annual Loss Expectancy (ALE) is calculated by simple multiplication of the potential loss by the probability.
Thus, it is theoretically possible to estimate the degree of risk events (ALE) and to make decisions based on that.
On the other hand, unreliability and inaccuracy of the data make this method complicated to deal with. Moreover, controls and countermeasures often tackle a number of potential events and the events themselves are frequently interrelated.
Qualitative Risk Analysis
In contrast to the previous method qualitative risk analysis does not require the probability of an event and the possible loss in case of its occurrence. Instead of this it uses a number of interrelated elements:
- threats (something that can attack the system);
- vulnerabilities («Achilles' heel» of the system. For example, for fire a vulnerability would be the presence of inflammable materials);
- controls (countermeasures),
- and four types of controls [7]:
- deterrent controls reduce the likelihood of a deliberate attack;
- preventative controls make an attack unsuccessful or reduce its impact;
- corrective controls reduce the effect of an attack;
- detective controls discover attacks and trigger preventative or corrective controls.
These elements can be illustrated by a simple relational model (fig. 2).
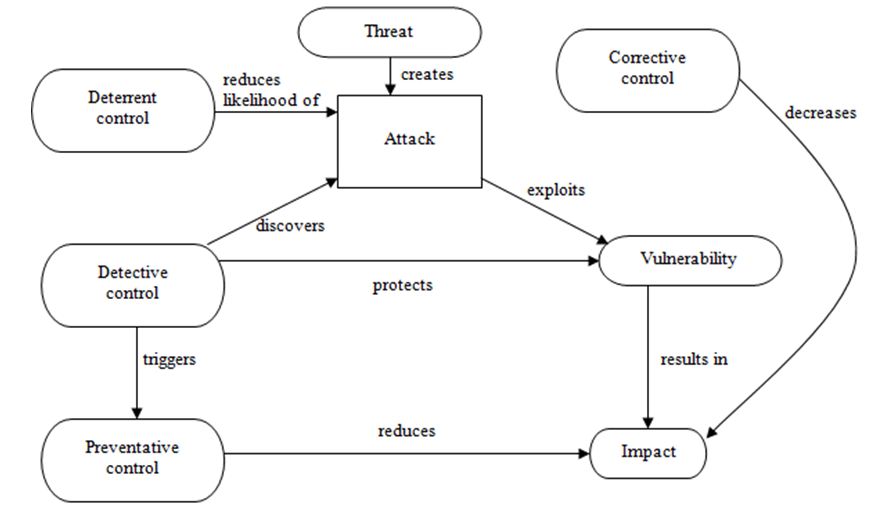
Figure 2. – Relational model of qualitative risk analysis
Model analysis for evaluation of losses by Grezdov G.
Development of an estimation model of losses is an important task. It brings together management goals of the profit increase of the enterprise with the aim of Information Security (IS) to reduce losses associated with problems of the main features of information protection (availability, integrity, confidentiality).
The threat of availability – is the limitation in access to the resources or its absence, that can occur in cases of intentional or accidental actions. If access to the resource is available, but it takes a great amount of time, they say that the resource is exhausted.
The formula for calculating the losses from the threats of availability is following

where Lul – losses from delayed services in the information access; Lr – losses associated with the recovery of operability; Ld – losses associated with the downtime of the system node (SN); Lli – losses associated with the loss of income [1]. Losses from delayed service in access can be fixed in the operating agreement and represent penalty and indemnifications.
Losses associated with the recovery of operability are calculated by the formula:
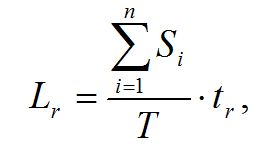
where Si – employee’s salary per month, who recover the operability of the attacked system node (ASN); N – number of employees, restoring the ASN; tr – operability recovering time; T – the number of working hours of the system node in a month.
Losses associated with downtime of ASN are calculated as
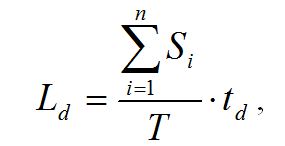
where Si – ASN employee’s salary per month; N – number of ASN employees; td – ASN downtime, T – the number of working hours of the system node in a month.
Losses associated with the loss of income are defined as
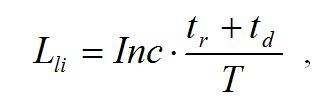
where Inc – the annual income from the use of ASN; tr – ASN recovery time; td – ASN downtime, T – working period of the system within a year.
The concept of «integrity» means that the data are complete and unchangeable. Data may be changed intentionally and unintentionally. For integrity threats losses can be calculated by the formula:

where Lum – losses from unauthorized modification of information and depend on the significance of information, which integrity is broken; Lr – losses associated with the recovery of the operability; Ld – associated with the downtime of the system node and Lli – losses associated with the loss of potential income.
The amount of losses associated with recovery of operability is described by the expression:
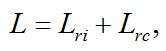
where Lri – losses associated with data recovery and Lrc – losses associated with the replacement of damaged components, those are fixed material costs.
Losses associated with data recovery can be evaluated as follows:
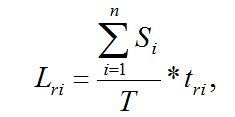
where Si – ASN employee’s salary per month; N – the number of employees on the ASN; tri – the time required to recover information on the attacked ASN, T – the number of working hours of the system node in a month.
Losses associated with the loss of potential income are found by the formula:
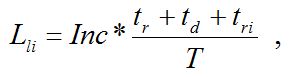
where Inc – annual ASN income; td – ASN downtime; tr – ASN recovery time; tri – recovery time on the attacked ASN, T – system working period within a year.
Confidentiality of information is the need to prevent leakage (disclosure) of any information. Herewith while divulging of information, its owner will have losses that may be related to the financial aspect of the problem, loss of reputation, competitiveness, etc. Therefore, confidential information includes the right to use it only by a limited number of people, for others it remains a mystery.
Therefore, for the calculation of losses the most convenient method is the method of the experts’ estimates. The essence of the method lays in the analyzing the losses, based on the importance of the information, by a group of experts in the field.
Company’s informational risk insurance is a method of protection of information in the financial and economic support of information security systems. It is based on the issuance of guarantees by the insurance companies for the subjects of informational relations to fill in the property damage in case of the implementation of informational security threats.
Using the company’s informational risk insurance the resulting losses (L*) are calculated as follows:

where L – the total losses due to the violation of several categories of information; Ins – the total profit of the risk insurance.
In addition, monetary inflation affects total annual information loss. Inflation encourages lazy employees who look for easy money in committing computer crimes, including the sale of confidential information.
The calculation of the rate of inflation is based on the following data: socio–economic development forecast, which is annually given by the Government in parliamentary structures and published in the media; the project of the state’s and regional’s budgets for the coming year, where inflation, which is accounted for in the budget calculations, is rating; the calculation of the National Bank of the possible inflation; forecast data on the dollar exchange rate for countries which economy depends on this index; estimates of experts (research organizations, etc.).
Thus, as shown by the analysis, to the existing models and methods of estimation it is appropriate to add informational risk insurance and estimates of the rates of inflation [10, 13].
Forecasting of losses
It is a well–known fact that prognostication (or forecasting) is an important part of every business. It is essential to understand that threats are very difficult to detect before they appear. To be prepared to threads it is also essential to be up–to–date with last news connected with technologies and to use forecasting by analogy. Forecast by analogy is a forecasting method that assumes that two different kinds of phenomena share the same model of behavior [12].
It means that IT managers can study similar situation that happened before or with another company and try to predict the next step of a thread.
In order to watch the frequency of threats and methods that were used by IT managers to avoid problems or to improve the system it has to be developed the data base with the essential information of the company.
An example of such data base is shown on the figure 3.
It is essential to remember all the methods that were used to avoid the threats and the vulnerabilities of these methods. That is why table «Methods« is an important part of the base.
Conscientious managers always try to find new methods of dealing with threats. They can be noted in the table «New method».
Forecast by analogy means that manager has to find out the same information in the past. So, development of the table «Forecasting» can help to estimate the situation and to compare it to the same in the past.
The table «Developer» can help us to find out information about developer of the method of dealing with threats and where this method can be used.
In order to predict future losses IT managers have to know costs of the same losses in the past. They also have to take into consideration the inflation and the last appearance of the threat.
Development of the data base is a vital part of forecasting by analogy. It is much easier to watch the threats and aftermaths by using the well–structured data base.

Figure 3. – Structure of the data base
Conclusion
The Internet and information systems have enabled businesses to reduce costs, attain greater market reach and develop closer business partnerships along with improved customer relationships. However, using the Internet has led to new risks and concerns.
It is essential to understand that every business has to be protected. And for doing it properly it is vital to know the problems which can occur. In this paper it is listed top 10 threats that seem to be a big problem to businesses.
Moreover, there is a possibility to evaluate the losses that are caused by the threats. There are some approaches and certain correlations that can help to estimate the losses from several types of risks.
It is also important to mention that level of security may be improved with the help of prognostication for future threads. It is essential to use several types of forecasting in order to get the better model. And this may help managers to avoid greater losses.
So, it can be concluded that the importance of risk analysis is undeniable.
References
- Wikipedia [Electronic resource]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_security (05.08.2012).
- Techopedia [Electronic resource]: http://www.techopedia.com/definition/24838/information-security-policy (05.08.2012).
- Wikipedia [Electronic resource]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Threat_(computer) (07.08.2012).
- Help Net Security [Electronic resource]: http://www.net-security.org/secworld.php?id=8709 (03.08.2012).
- 2009 Data Breach Investigations Report [Electronic resource]: http://www.verizonenterprise.com/resources/security/reports/2009_databreach_rp.pdf?__ct_return=1 (02.09.2012).
- The security risk analysis directory [Electronic resource]: http://www.security-risk-analysis.com (07.08.2012).
- The security risk analysis directory [Electronic resource]: http://www.security-risk-analysis.com/introduction.htm (05.08.2012).
- B.D. Jenkins, Security Risk Analysis and Management, - Countermeasures Inc., 1998.
- Zeki Yazar, A qualitative risk analysis and management tool – CRAMM, – SANS Institute InfoSec Reading Room.
- E.D. Nikulenko, N.E. Gubenko, Model analysis for evaluation of losses, connected with realization of threats and insurance of informational risks.
- Wikipedia [Electronic resource]: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Forecasting (04.08.2012).
- McAfee report. Threat prediction [Electronic resource]: http://www.mcafee.com/us/resources/reports/rp-threat-predictions-2012.pdf (12.08.2012).
- Грездов, Г.Г. Способ решения задачи формирования комплексной системы защиты информации для автоматизированных систем 1 и 2 класса [Текст] – Киев : ЧП Нестреровой, 2005. – C.66.