Abstract
The Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3.Land expropriation
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Land expropriation always has been an extremely important issue and remains so today, because closely related to the rapid development and changes in land use. For persons at risk of losing property, eminent domain is a factor of instability. Land expropriation for the purposes of exploration and development can bring benefits to society, but it can be devastating to the people who enforce climbs site. Only if the government carries out the procedure satisfactorily, the citizens are in a situation similar to that in which they were before the alienation, and the company gets envisaged benefits
1. Theme urgency
The issue of alienation of land for public purposes and for reasons of social necessity (the "land acquisition") is relevant in connection with the continuous development of cities, expanding their boundaries, the need to build new infrastructure for the implementation of which requires significant areas that may already be in owned by citizens. The most controversial issue is the calculation of the amount of compensation for confiscated property that threatens the rights of citizens and the competence of state and leads to the issue in court.
That numerous lawsuits and long-term litigation point to insufficient resolution of this issue in the legislation that creates the interest of researchers in this issue and emphasizes its importance.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
The aim is to identify the main problems in the process of land expropriation, develop project how to improve it.
Main tasks of the research:
- Collect and analyze materials on cases of expropriation of land with potential for classification and identification of the most problematic areas in the process of expropriation
- Develop a project to improve the procedure of land acquisition and the concept of determining the amount of compensation for confiscated land
The idea of work: simplifying and improving procedures for land acquisition
The object of study is the law on the land expropriation from the public needs and motives of public necessity and the decision on seizure of land
The subject of the study - the problems arising in the process of land expropriation
3.Land expropriation
Expropriation - it's the government's authority to acquire the ownership of private land without the consent of the owners or users in order to meet the needs of society. This authority is often necessary for socio-economic development and environmental protection. The most common targets for expropriation of the following subjects:
All modern states have this power in one form or another. But regardless of the name (variable "compulsory acquisition", "expropriation", "seizure of land", or "reservation of land for public use") and the form of the realization process of alienation has the general structure (Fig. 1).
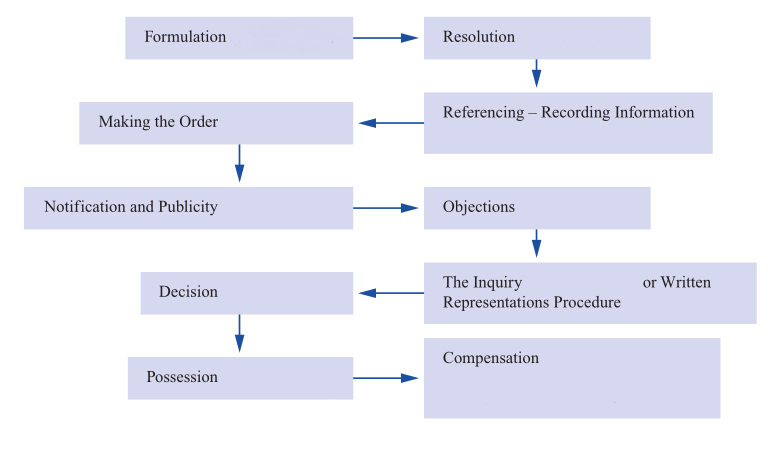
Figure 1 – Procedure of land expropriation
At the planning stage to identify possible options for the location of land required to meet the needs of society, involving all stakeholders. Determine the exact location and area of land to be expropriation.
After selecting the location of the site is necessary to promulgate messages to inform landowners and land users, the government's intention to withdraw their land forcibly. Post outlines the purpose of expropriation, the procedure, important dates, the procedural rights of the persons concerned.
Evaluation and reporting requirements included the supply of land owners and users of their claims for compensation. Being assessed land authority (institution), which disposes of the land, or other government agency. Authority (institution), which alienates the land, considering the requirements and offers the amount that the organization considers adequate compensation.
In case of agreement on the terms of the alienation of the Government shall pay compensation to the victims or provide them with other land, after which it shall take title to the land and begin immediate possession of the plots alienated for the stated purpose.
If an agreement between the landowner and the government is not found, they have the opportunity to challenge the compulsory acquisition, including solutions for the alienation, the alienation of the procedure and the amount of the proposed compensation.
Restitution creates an opportunity to return to the land that had been forcibly taken, the former owners (users) when the need for such sites anymore.
Gaps in the law, some of the unresolved issues in it leads to a lot of problems in the implementation of procedures for disposal. The most common problems are:
On the basis of these problems can be concluded that at this stage of development and the Study of the compulsory acquisition of land it is imperfect and requires legal reform, during which will take into account the basic principles that will help make the procedure more efficient disposal.
These principles include the following:
- Protecting and ensuring due process and procedures. Norm, it is reasonable to limit the government's authority to use eminent domain, strengthen citizens' confidence in the judicial system, provide them with a real opportunity to protect their rights and maintain a sense of security of tenure at the proper level. Rules should provide for prior consultation, planning with the involvement of communities and citizens, accessible complaint mechanisms, as well as to limit the self-will and sole discretion of officials.
- Good governance. Establishments carrying out compulsory acquisition should be accountable to the faithful implementation of the requirements of the law. Violation of laws by local officials undermines the legitimacy of compulsory acquisition. Good governance reduces the abuse of power and opportunities for corruption
- Adequate (equivalent) compensation. Affected persons must be compensated, which is nothing more nor less than the damages and losses they have suffered as a result of expropriation of their land. Laws should ensure that the affected owners (users) receive adequate (equivalent to) the payment in cash or by providing alternative land. The legislation should set clear and logical basis for the evaluation to achieve this outcome[1].
Thus, it can be noted that the effective and fair eminent domain can not exist without good governance and the rule of law
Conclusion
Legislation of all countries in relation to the matter must comply with the principles of the protection and promotion of human rights. It can be concluded that, despite the existence of differences in national legislation no harm would be the appropriate international code to regulate the procedure of withdrawal of general issues, evaluation methods of compensation, which could harmonize certain critical aspects of the practice to globalization standards
References
- S. Keith, P. McAuslan, P. Knight, J. Lindsay "Примусове відчуження земельних ділянок та компенсація" — ФАО ООН Дослідження землекористування, випуск 10, Рим 2008 Земельний Кодекс України [електронний ресурс]. — Режим доступу: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/2768-14
- Л.Терлецька — "Викуп державою земельних ділянок для суспільніх потреб — підстава відшкодування збитків в Україні", Юридичній вісник, 2009/3
- Цивільний Кодекс України [електронний ресурс]. — Режим доступу:http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/435-15
- Земельний Кодекс України [електронний ресурс]. — Режим доступу: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/2768-14.
- Закон України "Про відчуження земельних ділянок, інших об'єктів нерухомого майна, що на них розміщені, які перебувають у приватній власності, для суспільних потреб чи з мотивів суспільної необхідності", від 17.11.2009 № 1559-VI [електронний ресурс]. — Режим доступу: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/1559-17
- A. Кальченко "Про відчуження земельних ділянок для суспільних потреб чи з мотивів суспільної необхідності", Землевпорядній вісник №1, 2010р
- I.Kakulu, K.Viitanen, "Проблеми примусового викупу земельних ділянок: глобальний контекст" — FIG Article of the Month in February 2009
- Т. Саати «ПРИНЯТИЕ РЕШЕНИЙ. Метод анализа иерархий» [електронний ресурс]. — Режим доступу: http://www.pqm-online.com/assets/files/lib/saaty.pdf
