• design execution (sectional, modular, instrument, laboratory); • mean discharge chamber (tubular , plate, special); • method of cooling the discharge chamber (air, water, special); • displacement method (container, fixed, mobile, portable); • ozone performance (high capacity (more than 100 kg/hour), the average power (5 to 100 kg/hour), low power (up to 5 kg/hr)) [3].
ABSTRACT
СONTENT
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance, purpose and objectives of the study and planned results
- 2. General information about ozone
- 3. Application of the ozone generator
- 4. Possibilities of application of ozonation for off-gas cleaning
- 5. Carrying out the experiment
- Conclusion
- References
INTRODUCTION
Atmospheric air is the most important life-supporting natural environment and is a mixture of gases and aerosols of atmospheric boundary layer, which was developed in the course of evolution of the Earth, and human activities located outside of residential, industrial and other buildings. Ecological studies clearly indicate that the contamination of the surface atmosphere is the most powerful, permanent factor effects on human food chain and the environment. Atmospheric air has unlimited capacity and plays the role of the most mobile, chemically aggressive and pervasive agent interaction near the surface components of the biosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere.
Thus, it is obvious that it is necessary to take urgent measures to prevent the emission of pollutants into the air, including improvements in
off-gas cleaning technology.
1. RELEVANCE, PURPOSE AND OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY AND PLANNED RESULTS
Aim is to study the process of off-gas cleaning by ozonation to reduce emissions of harmful substances into the atmosphere, taking into account environmental safety.
The idea of work based on the ability to exercise oxidative properties of ozone with organic and inorganic substances in a liquid, gaseous and solid phases.
Research objectives:
1. Analyze the literature on the research subject.
2. To design and fabricate the device.
3. Determine the effectiveness of the device.
4. Conclude the feasibility of application of the ozone generator for off-gas cleaning.
2. GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT OZONE
Ozone (O3) — the second relatively stable (metastable) simple molecular compound, which is formed together with the oxygen O2 forms.
There are seven simple oxygen species, including complexes O4 and O6. Basic physical and chemical properties of ozone are shown in table 2.1.
Table 2.1 — Physical and chemical properties of ozone
| № | The physical and chemical properties of ozone | Physico-chemical characteristics |
| 1 | Boiling point | -111,9 °С: dark blue volatile liquid |
| 2 | Melting point | -192,5 °С |
| 3 | Molecular weight ozone | 48 g/mol |
| 4 | Ozone density at 0 °C | 2,144 kg/м3 |
| 5 | Ozone density at 20 °C | 1,997 kg/м3 |
| 6 | The solubility in water under normal conditions | 45 % |
| 7 | Solubility in water mass | 0,0394 % |
| 8 | Lower explosive limit | 9 % |
| 9 | Toxicity (causes respiratory irritation, coughing, vomiting, dizziness, fatigue) | 0,002...0,02 mg/l |
| 10 | MPC w.a. | 0,1 mg/м3 |
| 11 | MPC air | 0,15 mg/м3 |
A particular advantage of ozone is that it represents the most environmentally friendly oxidant, fungicide, disinfectant and deodorizer.
The role of ozone today is so significant that the International Antidioksin Association (IAA) has proposed to assess the degree of civilization and industrialized states in the number of produced and consumed them ozone [1].
3. APPLICATION OF THE OZONATOR
The tube for ozone was invented and first used by Siemens
for
the creation of the system for the purification of drinking water in 1857 [2].
Ozonator (ozone generator) is a device that produces ozone from oxygen in the air.
Ozone generators varies by:
Widespread use of ozone generators found in water purification and disinfection. Water ozonator is indispensable equipment in the deteriorating environmental situation [4].
Currently water ozonator is increasingly used in industrial water treatment and other fields of human activity (decontamination wastewater disinfection of water in swimming pools, water disinfection in the food industry, etc.) [5].
4. POSSIBILITIES OF APPLICATION OF OZONATION FOR PURIFICATION OF OFF-GASES
The main sources of pollution of industrial zone enterprises are exhaust gases and ventilation emissions, which are very diverse in composition and concentrations ozone and electrical discharge were proposed as a universal remedy [6].
The cleaning efficiency of chemical contaminants may be up to 99.9 %, depending on the concentration of pollutants and capacity ozonizer [7].
Ozonator may be used for the oxidation of organic substances (solvents, phenol, formaldehyde, toluene, xylene), sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulphide, mercury, as well as inactivation of bacteria. Wherein hydrocarbons are oxidized into harmless components — carbon dioxide and water vapor:
Electricity consumption per 1 g of ozone concentration is determined from the formula (4.2):
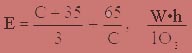
where D — disintegration of electricity;
C — concentration of ozone, g/m3.
At the optimal concentration of 14 g/m3 required power consumption by the formula will be: E = 21 kW-hour/kg ozone
The notion of efficiency ozone treatment plants usually understand specific energy consumption:

Scheme of ozonation of working area on the principle of a glow discharge is shown in picture 4.1 [8].

1 — moisturedustabsorber; 2 — compressor;
3 — ozonator; 4 — working chamber;
5 — cooler; 6 — high voltage transformer
Picture 4.1 — Scheme of the ozonation of the working area
Scheme of the ozonation of gas-flow is shown in picture 4.2 [9].
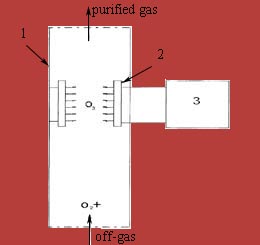
1 — plot of gas-pipe, 2 — quartz lamps,
3 — battery for quartz lamps
Picture 4.2 — Scheme of the ozonation of gas-flow
5. THE EXPERIMENT
The ozone generator was made using the scheme (picture 5.1).
Manufactured ozonator is shown in picture 5.1.

1 — mounting board; 2 — resistor; 3 — induction coil;
4 — element, which is forming ozone; 5 — fan
Picture 5.1 – Scheme of the ozonator
(animation: 3 frames, 20 cycles of repetition, 179 kilobytes)
Ozonator was experimentally tested in a production conditions at the enterprise Donetsk Training and Production Association Electroapparat
of Ukrainian Society for the Blind. The device was installed in the suction system from the emission source Hydraulic presses
.
The emissions of phenol are observed in the off- gas emissions from this source. Samplings were carried out in two places: before and after the ozonator.
Five samples before purification and after five samples were analyzed to determine the phenol concentration. The measurement is carried out by the method The
method for measuring the mass concentration of phenol in the organized industrial emissions of stationary sources of air pollution
, approved by the State Environmental
Inspectorate of Ukraine.
This method is designed to determine the mass concentration of phenol in the organized industrial emissions of stationary sources of air pollution in the range from 0.5 to 200 mg/m3 at a temperature up to 250 °C.
The measurement of phenol was carried out by the photometric method.
The method is based on the reaction of phenol with p-nitroaniline in a solution of sodium carbonate. The compound is forming, which colors solution to red [10].
The results of the measurements are shown in table 5.1.
Table 5.1 — Results of measurements
| Gas at the entrance | Gas at the outlet | Pollutant | |||
| Volumetric flow rate, m3/с | Temperature, °С | Volumetric flow rate, m3/с | Temperature, °С | Code | Name |
| 2,05 | 18 | 2,09 | 14 | 1071 | Phenol |
| The average concentration of the substance at the entrance, mg/m3 | The average concentration of the substance at the outlet, mg/m3 | Cleaning efficiency, % | |||
| 2,6 | 2,1 | 20,8 | |||
Based on the obtained data the efficiency of the ozonator was calculated and it was 20.8 %.
CONCLUSIONS
In this work the literature review was carried out, we consider general information and main characteristics of ozone. We found that ozone is one of the strongest oxidants, which gives reason to use it to oxidize substances. Also we considered the application of ozone generators at this stage.
Ozonator was made, which was tested in thee Donetsk Training and Production Association Electroapparat
Ukrainian Society for the Blind. Efficiency is 20.8 %.
Low efficiency can be explained by insufficient capacity of the device. That is further design improvement is required to increase the capacity and efficiency of the ozonator.
Thus, ozonation is a promising method for purification of gas emissions. The work gives rise to the advisability conduct further research and practical laboratory work on the use of the ozonator for neutralization of industrial emissions of a number of pollutants.
REFERENCES
- Лунин, В.В. Физическая химия озона / В.В. Лунин, М.П. Попович, С.Н. Ткаченко. — М.: Издательство МГУ, 1998. — 480 с.
- Применение озонаторов в народном хозяйстве [Электронный ресурс] — Режим доступа: http://ecospb20041.narod.ru/application.htm.
- Воронов, Ю.В. Водоотведение и очистка сточных вод: Учебник для вузов / Ю.В. Воронов, С.В. Яковлев. — М.: Издательство Ассоциации строительных вузов, 2006. — 704 с.
- Василенко, Л.В. Методы очистки промышленных сточных вод: учеб. Пособие / Л.В. Василенко, А.Ф. Никифоров, Т.В. Лобухина — Екатеринбург: Урал. гос. лесотехн. университет, 2009. — 174 с.
- Кожиков, В.Ф. Озонирование воды / В.Ф. Кожиков, И.В. Кожиков. — М: Издательство МГУ, 1974. — 325 с.
- Пригожин, В.И. Теоретические экспериментальные исследования создания высокоэффективного озонаторного оборудования / В.И. Пригожин, М.В. Бударин // «Альтернативная энергетика и экология» международный научный журнал. — 2004. — №10. — с. 16–20.
- Минаева Н.А. Обезвреживание газових выбросов методом озонирования / Н.А. Минаева, Ю.Н. Ганнова // Охорона навколишнього середовища та раціональне використання природних ресурсів / Збірка доповідей XXIII Всеукраінської наукової конференції аспірантів та студентів. Т. 1 — Донецьк: ДонНТУ, 2013 — с. 18–19.
- Самойлович В.Г. Современные тенденции в конструировании промышленных озонаторов / В.Г. Самойлович, В.В. Панин, Л.Н. Крылова // Тезисы докл. всерос. конф., посвящ. озону и другим экологически чистым окислителям, науке и технологиям — Москва, 2005 — с. 56–58.
- Пичугин Ю.П. Структура барьерного разряда и синтез озона / Ю. П. Пичугин // Тезисы докл. всерос. конф., посвящ. озону и другим экологически чистым окислителям, науке и технологиям — Москва, 2005 — с. 68–70.
- Методика виконання вимірювань масової концентрації фенолу в організованих викидах промислових стаціонарних джерел забруднення атмосферного повітря. МВХ 08. 315-2001. — Х.: НДПІ «Енергосталь», 2001. — 12 с.


