Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Concepts Computer-aided designand CALS-technologies
- 2. Aktualnost threads
- 3. Purpose and objectives
- 4. Analysis of existing types of enterprises
- Preliminary findings
- Literature
Introduction
Scientific and technical progress is manifested in the fact that in our life there with the best product specifications. Designing such products - the main task of designers and engineers of the engineering corps enterprises.
Creating new products consists of several stages, ranging from finding physical effects providing a principled implementation plan and the formation of intent to the calculation and justification, creation of a prototype and technology development of industrial manufacturing.
Finding solutions to the problem – the most difficult and intellectual stage. At the moment it requires a data bank and knowledge engineers use information stored in it to find technical solutions. Increase developer productivity, new products, reducing design time, improve the quality of development projects – the most important problems whose solution determines the level of accelerating scientific and technological progress of society. Development of computer-aided design (Computer-aided design) is based on a strong scientific and technical base. This – modern computer technology, new ways of presenting and processing information, the creation of new numerical methods for solving engineering problems and optimization. Computer-aided design systems allow based on the latest basic science work and to improve the design methodology, stimulate the development of the mathematical theory of the design of complex systems and facilities.
1. Concepts Computer-aided design and CALS-technologies
Under Design Automation understand systematic use of computers in the design process with scientifically sound distribution of functions between the designer and the computer and science -based selection methods for solving machine.
The purpose of design automation – to improve design quality, reduce material costs at him reduce design time and eliminate the growing number of engineering and technical personnel involved in design and construction.
Scientifically based allocation of functions between humans and computers means that people should solve the problem, wearing a creative nature, and computers-tasks that are amenable algorithmization [6].
In accordance with GOST 23501.101-87, Computer-aided design – an organizational and technical system, part of the structure of the project organization and carrying out complex design using computer-aided design.
Computer-aided design – system that combines hardware, mathematical and software options and features which are selected with maximum consideration peculiarities problems of engineering design and construction. In Computer-aided design provides easy to use programs through the use of funds operative communication with a computer engineer, special problem-oriented languages and the availability of reference base.
Structural component and subsystem components are Computer-aided design, having all the properties of systems and created as stand-alone system. It highlighted some of the featured Computer-aided design, ensuring the implementation of some project tasks completed to obtain appropriate design solutions and project documents.
In accordance with GOST 23501.108-85 Computer-aided design classified by [8]:
- Тip/raznovidnost and complexity of the design object;
- The level and complexity of design automation;
- Nature and quantity of documents produced;
- The number of levels in the logistics.
Currently one of the most successful models of modern business in the world is the use of CALS-technologies.
The acronym CALS (Continuous Acquisition and Life-Cycle Support) is the continuous integrated provision of information lifecycle product data, related processes and the environment mainly in electronic form. First of all, CALS – business strategy of integration of information processes between the participants of the product lifecycle (customers, developers, manufacturers, suppliers, maintenance, servicing and repair facilities, recycling facilities) in order to provide them with the necessary business of product data and related processes and environment. Despite the presence of the word in the title of Support CALS – this is software and not support. And for systems integrated logistics support life cycle of products, and products for the creators of the transition to electronic design CALS becomes an integral part of the system-software works [4].
In the context of modern successful business appointment CALS-technologies is providing the necessary information at the right time in the right way, at a particular location to any user at all stages of the product lifecycle.
One of the important tasks of creation and successful implementation of CALS-technologies is to provide uniform descriptions and semantic interpretation of the data regardless of the place and time of their receipt of a total system having up to global scale. Thus the structure of the design, technological and operational documentation, conceptual apparatus and data representation languages should be standardized [10].
The essence of the concept of CALS business consists in applying information technology and support at all stages of the life cycle of products, based on the use of IMS, which provides a consistent way to manage processes and interaction of all participants in this cycle: production customers, suppliers (manufacturers) products, operations and maintenance personnel. In IMS information is created, transformed, stored and transferred from one party to another life cycle using software applications, which include system CAD/CAE/CAM, PDM, MRP/ER, SCM. Here the product life cycle is represented as a line of marketing research and to disposal facility.
Since the implementation of CALS-technology involves the use of IT including computer hardware and software, all software used in the CALS-technologies can be divided into two large groups:
1. The software products used to create and transform product information, production environment and production processes, the use of which does not depend on the implementation of CALS-technologies;
2 . Software products, the use of which is directly related to CALS-technologies and relevant standards.
The first group includes software products, traditionally used by various industries and designed to automate a variety of information and manufacturing processes and procedures. To this group belong the following software and systems:
- preparation of the text and tabular documentation for various purposes (word processing, spreadsheets, etc. – office systems);
- automation engineering calculations and schematic design (CAE-systems);
- automation of design and manufacturing work design (design) documentation (CAD-system);
- automation of technological preparation of manufacture (CAM-system);
- аutomation of production planning and control of manufacturing processes of products, inventory, production resources, transportation, etc. (system MRP/ERP);
- identification and authentication information (means EDS).
The second group includes software and systems:
- Product Data Management and configuration (system PDM – Product Data Management);
- Project Management (Project Management);
- flow control tasks when creating and editing technical documentation systems (WF – Work Flow);
- providing information support for post-production stages of product life cycle;
- functional simulation, analysis and business process reengineering [2].
As can be seen from CALS-technology – a modern business model of production, which is based on the foundation of CAD/CAM/CAE/PLM systems.
CAD/CAM/CAE-systems occupy a special position among other applications, as industrial technologies are aimed directly at the most important areas of material production. Currently, it is generally agreed inability manufacturing complex high-tech products (ships, planes, tanks, various types of industrial equipment, etc.) without the use of CAD/CAM/CAE-systems. Over recent years CAD/CAM/CAE-systems have evolved from relatively simple drawing applications to integrated software systems that provide unified support the development lifecycle, from conceptual design through technological preparation of production, testing and maintenance. Modern CAD/CAM/CAE-systems not only provide an opportunity to reduce the period of the introduction of new products, but also have a significant impact on the production technology, allowing to improve the quality and reliability of production (increasing thus its competitiveness). In particular, computer simulations of complex products designer can fix the inconsistency and saves on the cost of manufacturing a physical prototype [5].
CAD-system (somputer computer-aided design design support) designed to solve design problems and design engineering documentation (more accustomed they are called computer-aided design Computer-aided design). As a rule, modern CAD-system includes modules for modeling three-dimensional solid structure (parts) and design drawings and text design documentation (specifications, statements, etc.). Leading three-dimensional CAD-systems can implement the idea of through the cycle of preparation and production of complex industrial products.
CAM-system (computer-aided manufacturing computer support manufacturing) are intended for the design of treatment products on the machines with numerical control and the issuance of programs for these machines (milling, drilling, erosion, punching, turning, grinding, etc.). CAM-systems are called systems of technological preparation of production. Currently, they are virtually the only way for the manufacture of parts and complex - contraction cycle of production. In CAM-systems using three-dimensional model of the items created in the CAD-system.
CAE-system (computer-aided engineering support for engineering calculations) represent a large class of systems, each of which allows us to solve certain computational task (task group), from the strength calculations, analysis and modeling of thermal processes to calculations of hydraulic systems and machines, calculations casting processes. In CAE systems also used a three-dimensional model of the product, created in the CAD-system. CAE-systems are called systems engineering analysis [1].
PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) is a methodology for the application of modern information technology to improve industrial competitiveness, with an emphasis on product data management. PLM application is based on the use of integrated models of product data and business processes. PLM requires new ways of working with information concerning the product, allowing it to be closely linked processes, providing simultaneous access to data of different categories of employees, allowing to fully implement the principles of concurrent engineering products [9].
The life cycle of industrial products (product life cycle) includes a number of stages, from inception of the idea of a new product to its disposal at the end of use. Main stages of the life cycle of industrial products are shown. These include the design stages, technological preparation of production, the actual production, sales, use, and finally disposal (in the number of stages in the life cycle may also include marketing, procurement of materials and components, the provision of services, packaging and storage, installation and commissioning).
Consider the content of the main stages of product life cycle product engineering.
In the design phase project procedures are performed – the formation of fundamental solutions, the development of geometric models and drawings, calculations, process modeling, optimization, etc.
In the preparation stage of production developed routing and operating parts manufacturing technology implemented in programs for CNC machines; assembly and installation of technology products; control technology and testing.
Carried out at the production stage: the calendar and operational planning; purchase of materials and components with their input control; machining and other treatments are required; control processing results; assembly; test and final test.
Оn the post-production stages performed preservation, packaging, transportation; installation of the consumer; operation, maintenance and repair; recycle.
At all stages of the life cycle has its own target setting. The participants of the life cycle tend to achieve their goals with maximum efficiency. During the design, production and CCI need to fulfill the requirements for product performance for a given degree of reliability of the product and minimize the time and costs that you need to succeed in a competitive market economy. Concept of efficiency includes not only reduce production costs and shortening design and manufacturing, but also to ensure convenience and reduce development costs for future operation of the products. Of particular importance are the requirements for ease of use, sophisticated technology, for example, in industries such as aircraft or automobiles.
Achievement of objectives in modern factories producing complex technical products, it is impossible without extensive use of automated systems (AS), based on the use of computers and for creating, processing and use of all necessary information about the properties of products and accompanying processes. Specificity problems solved at different stages of product life cycle determines the diversity of speakers used [3].
2. Aktualnost threads
Currently, the majority of enterprises in Ukraine move on rails effective automation of its production. Today it is hard to imagine a company engaged in the design of high-tech, high-tech equipment, wherever the designer doing his job the old fashioned way, at the board drawing board.
Until recently, the concept of automation in Ukraine working designer based on the principles of geometric modeling and computer graphics. At the same time, the system of computerization work of designers, engineers, technologists-programmers, engineers-managers and production masters developed autonomously and engineering knowledge – the basis of design, remained outside the computer. However, this situation does not meet modern requirements for automation. Now in Ukraine requires a comprehensive approach to the technical preparation of production at all stages of the life cycle of products, which can be solved CALS tools. Traditional Computer-aided designtheir geometric and not core information can not be the basis for the creation of such systems. Today every product during its life cycle must be submitted in a computer environment as a hierarchy of information models, make up the whole and with subordination.
In industrial production in Ukraine there is tough competition. To survive in these difficult circumstances businesses have as quickly as possible to produce new products, reduce their costs and improve quality. In this they are assisted by modern Computer-aided design tools, allowing ease the entire product development cycle - from concept to prototyping and launch it into production. So now without Computer-aided design does not do any design or industrial enterprise. And although the share of these systems account for only about 3 % of the market, they are very important because they help create products, without which it is impossible to our daily lives: cars, airplanes, household appliances, industrial equipment.
Currently one of the most powerful Computer-aided design systems are – Dassault Systemes (which promotes it with IBM), ASCON (Russia) and AutoDesc (USA). The main feature of Computer-aided design, these producers – extensive functionality, high performance and stability. Important role in the formation of the middle class Computer-aided design played two solid parametric modeling kernel ACIS and Parasolid, which appeared in the early 90s and is now used in many leadingComputer-aided design .
Today in Ukraine leading companies in the field of Computer-aided designapplicability average level of complexity – is Autodesk and ASCON software products and AutoCAD КОМПАС, respectively [7].
3. Purpose and objectives
The aim of this work is: more efficient use of CAD/CAM/PLM by selecting the rational structure of systems for different types of businesses.
The main objectives of research:
- Analysis of the existing types of manufacturing plants and their classification;
- Analysis of the Performance of Computer-aided designand PLM-systems;
- Experimental studies.
4 . Analysis of existing types of enterprises
Currently, there are more than 200 different levels of Computer-aided design and different manufacturers. In this regard, before many businesses appear difficult task of choosing one or another Computer-aided design. Selection criteria for Computer-aided design companies are features and specifications of Computer-aided design and restriction – total cost of ownership.
Another essential task of enterprises in the technical preparation of production is the storage of electronic documents for projects: working and assembly drawings, specifications, calculations, manufacturing processes and product assembly. Such electronic storage should possess characteristics: quick search documentation on attributes, reliable and orderly storage of electronic documents, electronic approval and the possibility of change, the availability of digital signatures. These properties will not only keep current information about the object, but also to manage the lifecycle of the object (from its inception to disposal).
Therefore I propose to all industrial enterprises in our country divided into two large groups: industrial enterprises and design organizations. But since they are all different, not to say that all businesses will approach the same CAD/CAM/PLM system, and thus may divide enterprises into three stages (large, medium, small) based on the numbers in the design and technological departments.
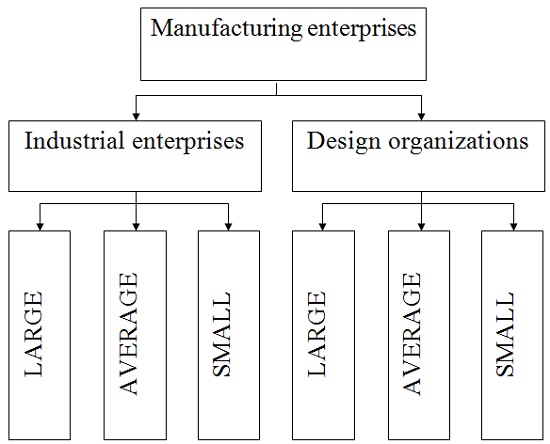
Scheme 1 – Classification of industrial enterprises
We analyze the necessary functions CAD/CAM/PLM systems:
- Large-optimization of existing processes;
- Medium-efficiency for a reasonable price and short lead time;
- Small-lowest price of the product, at least the paid services.
Рreliminary findings
Ukrainian enterprises varied both in the number of employees, and by activity. Therefore, you can not make recommendations on the selection of similar Computer-aided design. To confirm the results of preliminary theoretical studies are planned:
- Experimental studies to determine the needs of enterprises and their classification;
- Additional theoretical research on the analysis of rational structures of CAD/CAM/PLM systems for various types of enterprises;
- Develop a methodology for selecting CAD/CAM/PLM systems for various types and kinds of businesses.
When writing an essay master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: January 2015. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.
Literature
- Александр Глинских. Мировой рынок CAD/CAM/CAE-систем. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа: http://www.ci.ru....
- Григоров А.В., Горобец И.А., Лысенко О.Н., Голубов Н.В. Интеграция информационной среды и управление проектными данными предприятий - Материалы тринадцатого научно-практического семинара «Практика и перспективы развития партнерства в сфере высшей школы». В 3-х кн.. - Таганрог. Узд-во ТТИ ЮФУ. Кн.3 2012 №12 –с.72-80.
- Жизненный цикл изделий. Основы САПР. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://bigor.bmstu.ru...
- Михаил Головко. CALS. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://www.osp.ru...
- Основные функции CAD-систем. Основы САПР. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://bigor.bmstu.ru...
- Принципы построения САПР. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://www.ref.by/refs...
- САПР в Украине. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://www.ik.3dscorpion.com.ua...
- Система автоматизированного проектирования. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://freekaznet.appspot.com...
- Что такое PLM. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://www.calscenter.ru...
- Ю. М. Соломенцев. Информационно-вычеслительные системы в машиностроении CALS-технологии. [Электронный ресурс] – Режим доступа http://engineering.ua...
