Abstract
Contents
- 1. Analysis of road transport emissions and rationale for monitoring the concentration of the sum of hydrocarbons
- 2. Analytical review of methods for measuring the concentration of hydrocarbons in the exhaust of motor transport
- 3. Analytical review of modern measuring devices under the control object
- References
1. Analysis of road transport emissions and rationale for monitoring the concentration of the sum of hydrocarbons
Donetsk – a major administrative, industrial and cultural center of Ukraine. The city population is about 1007.0 thousand people, working population is about 675,7 thousand people, a population density is 1,770 people per 1 km2. Figure 1 shows the air pollution harmful emissions.

Figure 1 – Air pollution in the industrial city
Outdoor air pollution is one of the most serious environmental problems in many industrial cities. Effects of air pollution on human health is manifested through a reduction in life expectancy, increasing the number of premature deaths, increased morbidity and a negative impact on children's development.Although recently there is a trend in reduction of total emissions of harmful substances, but the level of air pollution is still relatively high.
Analysis of the data shows that over the past 10 years, total gross pollutant emissions decreased by 15 %. With emissions from industrial enterprises decreased by 32 %, and transport emissions increased by 76 %. If current trends continue, the amount of emissions from mobile sources by 2020 will exceed the corresponding amount of emissions from stationary sources. In this case, the gross amount of emissions in the city will increase by 30‑40 % can be from 280 to 300 thousand tons per year [1]. Analysis of air emissions shows that in 2007 compared with 2000 emissions of carbon monoxide have decreased by 12 %, sulfur dioxide by 44 % and dust by 37 %, but emissions of nitrogen has increased by 48 %.
We can see next trends in the processes of air pollution in Donetsk:
- Over the past five or six years in Donetsk we see monotonic growing of atmospheric pollutions due to increase level of nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde, ammonium and phenol in atmospheric. During this period level of pollution have been the worst in 2003 and 2007.
- For many years the most dangerous major air pollutants were nitrogen dioxide, formaldehyde, dust and benzopyrene.
- The situation of air pollution will be harder because of level of carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide and heavy metals in the athmosphere .
- Today in Donetsk we can see a tendency of increasing og air pollution by nitrogen dioxide and formaldehyde (especially in 2007).
We have said that the greatest danger for air are road transport emissions, as a trend level of harmful emissions from road transport hese increased.The most toxic components of exhaust gases of gasoline engines are carbon monoxide (CO), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrocarbons (CnHm). The composition of diesel emissions is differ from gasoline. In a diesel engine we can see more complete combustion. Carbon is a black nontoxic gas contained in the exhaust. But it adsorbs on the surface like carcinogenic hydrocarbons. We use low-quality diesel fuel that contained sulfur and that is why sulfur dioxide is formed. How do these harmful components affect humans and the environment? CO colorless and odorless gas, it is lighter than air and therefore can easily spread in the atmosphere. It can caus headache, dizziness, fatigue, irritability, drowsiness, pain in the heart. Nitric oxide NO – colorless gas, carbon dioxide, nitrogen dioxide NO2 – red‑brown color with a characteristic odor. Nitrogen oxides in contact with the human body are connected to the water. Here they form a nitrogen compound of nitrous acid in the airways of human body. Nitrogen oxides are irritating to the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, mouth. Some hydrocarbons CH are the strongest carcinogens. Clouds of CH and NOx, that accumulated under the asphalt by the influence of light. In fact ozone decomposes rapidly but not in the presence of hydrocarbons (CH). They slow down the process of decomposition of ozone and it actively reacts with particles of moisture and other compounds. Formed hazy cloud of smog. Ozone corrodes the eyes and lungs and NOx emissions made formations of acid rain. In the case of leaded petrol approximately 50% of lead in the form of soot is deposited on the parts of the engine and the exhaust pipe, the remainder goes into the atmosphere. Lead is present in the exhaust gases in the form of tiny particles of size 1‑5 microns, which remain in the atmosphere for a long time. The lead concentration in atmosphere roadside is about 2‑20 times higher than in other places. The presence of lead in the air causes severe lesions of the digestive system, central and peripheral nervous system. The effects of lead on the blood appears to reduce the amount of hemoglobin and red cell destruction.
Chemicals that coming into the workplace air can cause acute, subacute, chronic poisoning as well as various deviations in workers health. The exposure zone should be established for those compounds which content in the air can have harmful health effects.
Depending on the size of ecological limits as well as other indicators of toxic effects, all chemical compounds can be separated into 4 hazard classes (table 1). Hazard classes allow a differentiated approach to the justification of the needs of control the content of various chemical compounds in the atmosphere.
Table 1 – Hazard classes of chemical compounds
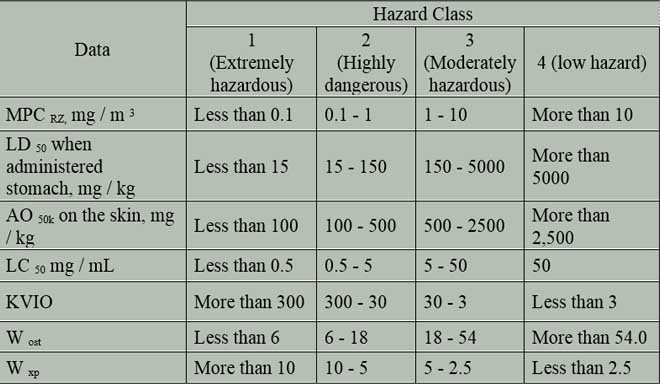
Table 2 shows the composition of the exhaust gases of motor transport [2].
Table 2 – Composition of exhaust gases of motor transport

Hydrocarbons emitted by car engines, under the action of sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides, emitted by the engine, boiler plants and industrial furnaces. As a result of photochemical reactions the formation of ozone causing eye irritation, damage to vegetation, rubber failure.
Professor A. J. Haagen‑Smith who investigated the photochemical reactions in the atmosphere due to the problem of the LA fog and subsequently by other researchers explain the reason for the rapid oxidation of hydrocarbons in the atmosphere and the associated reduction in visibility and increase the concentration of acids aldehydes and influence NOx (during smog hydrocarbon concentration was about 0,0003 %) on the formation of atomic nitrogen and ozone when exposed to sunlight (figure 2) [3].

Figure 2 – Fotoсhemical reactions in air
(Animation consists of 6 frames with a delay of 100 ms between frames, have 7 repeats. Made with Easy Gif Animator.)
Hydrocarbons CxHy is a large group of compounds of the following homologous series: paraffins, olefins, naphthenes, aromatics (including polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons – PAHs). The most dangerous of them are light gaseous hydrocarbons (methane CH4, ethane C2H6, propane C3H8, ethylene C2H4, acetylene C2H2 and several others) and PAHs. The share of methane is only 2–6 %. Other light hydrocarbons present in the exhaust gases of diesel engines and boilers in much smaller quantities [4]. The most representative of them are non–carcinogenic pyrene, chrysene, fluorranten and the most dangerous – phenanthrene C14H10, and especially benzopyrene C20H12.
2. Analytical review of methods for measuring the concentration of hydrocarbons in the exhaust of motor transport
Flame-ionization detector. Conductivity of the carrier gas which increases by elektropolyarizator significantly due to ions formed during the combustion of organic compounds in a hydrogen flame. FID response proportional to the number of carbon atoms in the molecule changes from one class to the other organic compounds slightly. Figure 4 depicts a flame ionization analyzer.

Figure 4 – Flame-ionization analyzer
Advantages: easy to use, fast response, wide linear dynamic range and versatility.
Disadvantages: in the analysis of a particular compound in a complex matrix requires a more selective detector to reduce the number of peaks interfering components. FID gives a weak response to a substance with a low carbon content. Main disadvantage of flame ionization analyzers is their low selectivity to separate organic ingredients at their joint presence. With flame ionization analyzerdetermine either their amount or concentration of the components with the prevailing ionization efficiencies.
Optoabsorption method (fig. 5) compares favorably with other methods of the following features:
- High spectral resolution is determined by the line width of the laser radiation.
- High sensitivity in terms of absorption. The principal limitation of the sensitivity limit is determined by thermal fluctuations in the test environment.
- No signal if the spectral line of the laser source is out of gas absorption lines (but it should be borne in mind the presence of background signal associated with the absorption of radiation windows and walls of the cell with the investigated gas mixture).
- S/N ratio increases in proportion to the power source. Fundamental limitation is imposed on the power of a phenomenon of absorption saturation on the line under study.
- OA‑signal is proportional to the absorption coefficient of gas, which significantly simplifies the handling of measurement data.
- Concentration response (the amplitude of the detected photoacoustic signal from the gas concentration) linearly with concentration in the range of 4‑5 orders of magnitude.
- Measured value (amplitude pressure oscillations) is an intensive parameter of the sample does not depend on its size. Because of this feature of OA measurements are carried out at low volume and length of the measuring chamber.
- The receivers due to the high noise spectral power density of laser sources generally have no value. Stabilization of the laser intensity (or normalization of the reference signal) further increases the sensitivity of the apparatus.
- The area used in OA‑analyzers laser sources covers the spectral range from UV to IR range.
- The possibility of rapid wavelength tuning, which allows for quantitative analysis of operational multicomponent gas mixtures.

Figure 5 – Optoabsorption analyzer
The main disadvantages of gas analyzers are sensitive to vibration and acoustic noise, and the dependence of the sensitivity of the OA detector on the pressure and type of gas to be studied. Selectivity depends on the overlap of the absorption bands, and defined by undetectable components changes the absorption spectrum of the analyte content even when the non–absorbing IR radiation components (e.g., hydrogen or helium) in the presence of traces of OA priemnnke interfering components. Among the principal features of the gas analyzers is the need to calibrate it for measuring the absolute values of absorption coefficients (and hence concentration) emissions.
Optoacoustic method. The basis of the analysis of gases laid OAM effect (fig. 6) of thermal expansion of the gas when it absorbs the probing radiation. When the acoustic frequency modulation (from a few Hz to tens of kHz) radiation power in the absorbing gas environment will be distributed at the same frequency as waves higher pressure zone. These acoustic oscillations recorded in the gas sensor membrane.

Figure 6 – Optoacoustic analyzer
In opto-acoustic gas analyzer drawback is the large additional errors arising due to the influence of atmospheric pressure and temperature, increased sensitivity to industrial vibrations [5].
3. Analytical review of modern measuring devices under the control object
In our time, no gas is difficult to imagine human life. Gas composition is very diverse around us in different devices, allowing them to function. Today, for a variety of purposes apply called gas mixtures. In addition, the car is one of their areas of use. Sometimes it is important to analyze the gas mixture (fig. 7).

Figure 7 – Emissions of road transport
Mixtures of gases analyzed to detect the qualitative and quantitative composition. This procedure called the gas analysis. Car gas analyzers are instruments through which gas and performed analysis. Action type devices are divided into: manual and automatic. Speaking analyzers and manual mode of operation, it is impossible not to mention the chemical absorbed. Their principle of operation is based on the fact that different components of the gas mixture creates a reaction with different reagents.
Change any physical characteristic mixture of gas you can, using the automatic analyzer. They then are nowadays the most common. Automatic analyzers have different road principle, according to which they are divided into three groups. About these groups tell you more.
The first group includes instruments that in their work based on physical methods of analysis using auxiliary chemical reactions. Due to chemical reaction of individual components of the mixture, it is possible to determine the change in volume or pressure.
The second group of devices that basically have physical methods of analysis and additional physical and chemical processes. The latter include thermochemical, electrochemical, and many others. The essence of the flow thermochemical process is based on the measurement of the thermal effect, which is the result of burning gas. Electrochemical processes make it possible to identify the percentage of concentration of gas in the mixture. This is indicated by the electrical conductivity of the electrolyte, changing after he absorbed gas.
The third group includes instruments whose action is based solely on physical methods of analysis. The most common of them are optical and thermal‑magnetic. Gas analyzers, which are based on optical analysis method measured the absorption and emission of the gas mixture, as well as optical density. Thermomagnetic analysis method is used to determine the concentration of oxygen, which have a large magnetic susceptibility.
What you car gas analyzer is chosen, it will certainly find a large number, both advantages and disadvantages. You can talk about them for hours, so I'll skip this point in his article. Today's manufacturers of these devices do not give their preference for one type. They try to equally implement and maintain production of gas analyzers that operate on different methods of gas analysis. However, not all depends on the manufacturer. And if there is an offer, not the fact that there is a demand. Of course, the word will always be up to the consumer. And the best proof of this is the fact that the most common among all automotive gas analyzers are electrochemical. Their success are three factors: low cost, versatility and ease. Since this unit is the most common, is not superfluous to call it negative side. To the main one concerns the low measurement accuracy. Also worth noting that since the analyzer works with corrosive mixtures, it negatively affects its sensitive elements. Their term of office is small.
Devices that are carried out gas analysis can be classified into five criteria: functionality, type, number of components to be measured, the number of measurement channels and according to specifications. According to the functional capabilities of its devices, analyzing gas mixtures are divided into: gas analyzers, detectors, leak detectors, indicators.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion – december 2014.
References
- Сигал, И. А. Защита воздушного бассейна при сжигании топлива / И. Я. Сигал. – Л.: Недра, Ленинградское отделение, 1985.
- Беспамятнов, Г. П. Предельно допустимые концентрации веществ в воздухе и воде / Г. П. Беспамятнов. – Л.: Химия, Ленинградское отделение, 1975.
- Немец, В. М. Спектральный анализ неорганических газов / В. М. Немец. – Л.: Химия, 1988.
- Берлянд, М. Е. Современные проблемы атмосферной диффузии загрязнения атмосферы / М. Е. Берлянд. – Л.: Гидрометеоиздат, 1975.
- Бреслер, П. И. Оптико-акустическое явление в видимой и ультрафиолетовой областях спектра и его связь с фотохимическим процессами в газах. Оптика и спектроскопия. / П. И. Бреслер, Б. Н. Рузин, 1960.
