Abstract
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: January 2015. Full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his adviser after that date.
CONTENTS
- 1. General characteristics work
- 1.1. Relevance of research
- 1.2. Communication with academic programs, plans, themes
- 1.3. Goals and objectives of the study
- 1.4. Subject and object of study
- 1.5. Research methods
- 1.6. Scientific novelty
- 1.7. The practical value
- 1.8. Testing results
- 1.9. Publications
- 2. Content of work
- 2.1. Overview of research on the topic
- 2.2. Geological characteristics of the test field
- 2.3. Methods of analysis of experimental data
- 2.4. Expected results
- 2.5. List of References
1. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS WORK
1.1. Relevance of research
Fuel and energy and raw materials supply of the economy of Ukraine is inseparably linked with increased coal production and development of gas resources of the Donets Basin.
Recently, almost all coal countries are showing great interest in methane coal deposits. The reasons for this interest is the following. First, coalbed methane - a very dangerous phenomenon, which significantly affects the working conditions in the mines. His selection in the mine workings of complex systems requires the use of ventilation c bolshihmi energy consumption. Secondly, coalbed methane is a valuable hydrocarbon feedstock, similar to natural gas oil and gas fields. Efforts of specialists sent for recycling coalbed methane and its use as an energy feedstock. All this will significantly improve the economic efficiency of the coal industry. Third, methane, which by mining released into the atmosphere, a greenhouse gas. Because they contribute to climate change and other Earth hazardous natural processes, its emissions are limited to the Kyoto Protocol for all countries of the world. The solution to all these problems is especially important for Ukraine, where coal is the main energy raw materials, ensuring energy security of the state for the long term. In this context, the problem of developing an integrated Coal and Gas fields in the region becomes an important economic and social importance.
To solve these problems, a more thorough and detailed analysis of the distribution of natural gas content of coal seams and gas saturation of rocks on the mine October mine
.
1.2. Communication with academic programs, plans, themes
In May 1996, the Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine adopted the decree number 191 of the preparation of the national energy program. According to this document in 1998 was created the State program concomitant production of methane gas from coal deposits of Donbass (in 1998 - 2010.). Later, the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine adopted the relevant resolution on the development of commercial production of methane from coal deposits of Donbass (judgment of 27 September 2000 № 1463).
On approval of the program to improve safety in coal mines (Decree number 939 of 06/07/2002)
.
1.3. Goals and objectives of the study
The aim is to study the patterns of distribution of gas content in the field of mine October mine
.
Objectives of research:
- Identify the factors influencing the gas content of coal fields, from literature;
- Obtaining the statistical characteristics of the object under study;
- The spatial distribution analysis of indicator gas content;
- An evaluation of the impact of known geological factors on the object of study;
- Prediction of local accumulations of gas in coal-bearing strata in the field of mine
October mine
.
1.4. Subject and object of study
Object of research - the field of mine October Mine
in the Donetsk coal basin.
Subject of research - geological factors distribution of gas content of coal seams (k8).
1.5. Research methods
Research methods are:
- Formation analysis;
- Structural-tectonic analysis;
- Statistical analysis;
- Spatial and statistical analysis;
- Lithologic and stratigraphic analysis.
1.6. Scientific novelty
Evaluation of the local influence of geological factors on the bearing capacity of the mine October Mine
to further predict local accumulations of gas in coal-bearing strata.
1.7. The practical value
Study of spatial distribution features natural gas content in the field of mine October Mine
will highlight the most productive patterns for gassy methane extraction.
1.8. Testing results
Research results were presented at the VII International scientific and practical conference DONBASS 2020: DEVELOPMENT PROSPECTS EYES OF YOUNG SCIENTISTS.
1.9. Publications
Article 1 will be published in the collection Naukovі pratsі DONNTU
serіya gіrnicho-geologіchna, 2014 p.
2. CONTENT OF WORK
2.1. Overview of research on the topic
Coal deposits have long regarded as complex gazougolnye. The modern technologies allow to produce and cost effective to use not only carbon dioxide but also coal deposits. A striking example of the application and development of these technologies demonstrate Europe. Green Gaz company operates in Europe with ugolnіmi deposits of the Czech Republic (Ostrava Coal Basin), Poland (Silesian Coal Basin) and Germany (Ruhr coal basin). Extraction and Utilization of Coal Mine Methane is produced continuously in the process of mining coal seams. Special state program decided this complex issue back in the 90s of the last century. Since these technologies are widely implemented throughout Europe and continue to be improved (Fig. 1).
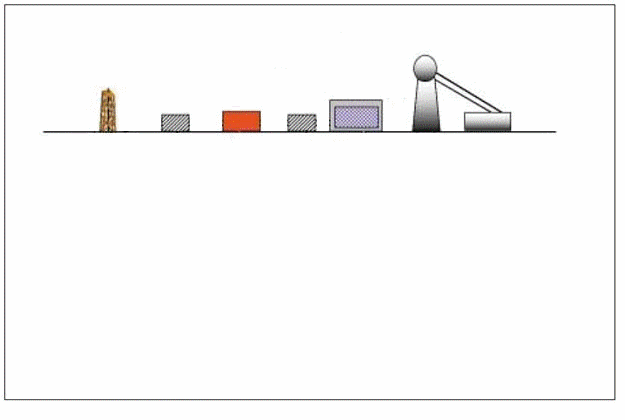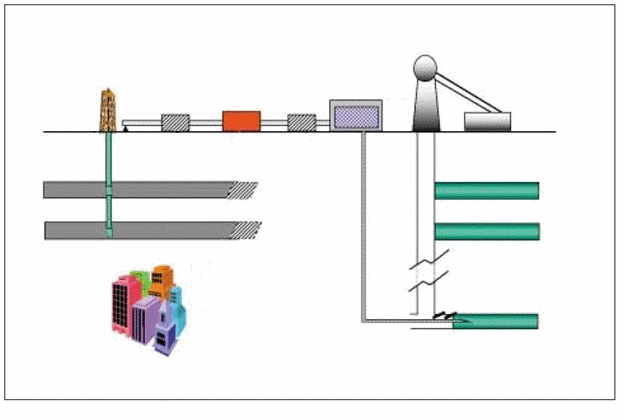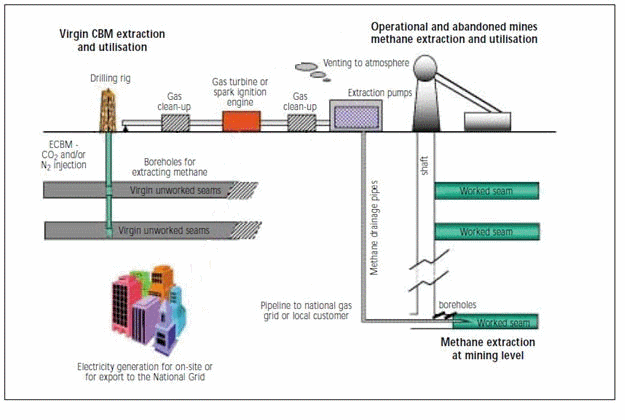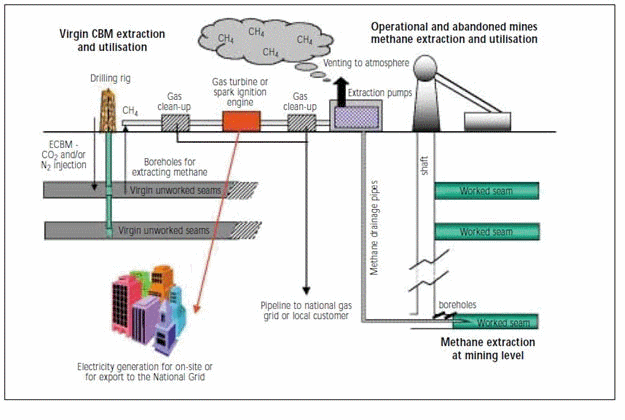
Figure 1 – Options for methane extraction and utilisation (7 image's,2 frames/sec, volume - 121kb)
USA last decades actively increase methane production from shale strata. Currently, she is at least 40% of the total natural gas production in the country. However, this gas is much more expensive than gas classical gas fields in Europe and not in demand. As an investment program of the United Kingdom (Shell) and the USA (the company Halibarton) offered their technologies for extracting shale gas fracturing Callout Ukraine (Fig. 2). In the drilled deep (3-5 km) wells pumped water with special chemical additives (proppants) Under high pressure made the gap gassy rocks (shale strata compacted sandstones). The gas is collected in a certain direction to the wellbore utilizing a setting (Fig. 2). In nastoyascheee time in the Donbass in the process gas field exploration compacted sandstones.

Figure 2 - Fracturing:
1) Dug wells; 2) Underground water intake; 3) Cementing of water-bearing layers; 4) Tight piping; 5) Reservoirs of underground water; 6) Fracture.
The cost of developing unconventional gas deposits is much higher than traditional deposits, due to the high cost of drilling, land acquisition and enforcement of environmental regulations.
Ukraine alone is not able to carry out projects for the development of unconventional gas deposits. They can only be realized through the involvement of technological equipment, expertise and investment from the world's leading companies.
Subject to create a favorable investment climate for projects forecasted volume unconventional gas production in Ukraine will be in 2020, about 2, and in 2030 - 10 billion cubic meters.
Industrial development of gas hydrate reservoirs complicates need drilling under water at great depths and the likelihood of uncontrolled degradation of the formation and the diffusion of methane in the environment. This can lead to the destruction of ecosystems in areas of methane creation and landslide zones in the field of development.
Despite the warnings, this direction of gas supply should not be considered unsound, because the active work of research centers in many countries over the next ten years can help find a solution that will make the extraction of gas hydrates competitive at the lowest negative impact on the environment [7].
Ukraine has a large and almost undeveloped coalbed methane resources. Most promising for the development of deposits are Donetsk and Lvov-Volyn coal basin. Introduction of CMM technology for the coal industry of Ukraine is an extremely important issue, both in terms of the environment, and ensure the country's energy needs. Of particular importance is the selection of CMM to create safe working conditions in the mines. However, there is still the problem of concomitant extraction of methane from coal mining is not solved. In our opinion, the main reasons for this were:
- insufficient knowledge about the distribution of coal bed methane reserves in thickness;
- high cost and lack of investment projects for technological and scientific study and improvement process;
- lack of special equipment, technologies and infrastructure;
- complex geological conditions of extraction of coal seams;
- lack of funding and active support from the state;
- sprayed between public authorities responsible for market development coalbed methane.
Exploring different gas content of coal deposits largely expanded understanding of the impact metamorphism and depth of the coal basin and the structural features, in particular, the physical and mechanical properties of coal-bearing strata at their modern foulness. A relationship was established gas-bearing formations also on: degree of faulting and the presence of powerful sediments, overlying coal-bearing strata; lithological changes from the host rocks; the presence of aquifers near coal seams, etc [2].
In papers Chernitsyna NV major geological factors have the most significant impact on the gas content, are the degree of metamorphism of coal, the depth of their occurrence, lithotype host rocks, structural-tectonic, hydrogeological, thermobaric conditions etal.[5].
Distribution of natural gas in coal deposits Donetsk-Makeevka area very uneven, as evidenced primarily change the depth of the surface methane zone. Its highest mark (130-150 m) are confined to the eastern part of the district. To the west there is a general surface dive to a depth of methane zone 600-800 m.
The central part of Donetsk-Makeevka area with coals from fatty to coke and coking otoschenno-tectonic structure is characterized by complexity and very high gas content of coal seams - from 17.0 to 25.0 m3/t.s.b.m.
Rzhepishevsky MI studied natural gas Donets Basin. They also found that the main geological factors that determine the value of gas content and change are the degree of metamorphism of coal and depth of their occurrence. Influence of the first apparent both from the depths of occurrence of methane zone with a maximum - 600-800 m - slightly metamorphosed coals in the western part of the area to a minimum - 80-100 - in the central and eastern parts, and quantities of coal methane changes from 1-2 to 25 - 30 m3/t.s.b.m. in the same direction in the range of long-flame coal types to skinny and poluantratsitov [6].
Significant increase in bearing capacity of the central and eastern parts of the region is the result of the influence of not only the degree of metamorphism, but also the complexity of the structural and geological structure.
The gas-bearing tectonic structures depends on the time of their formation (during or after sedimentation). Large and small domed brachyanticlinal synsedimentary folds and often characterized by higher gas content than Postsedimentary.
Strong influence on the gas content has another factor, ML Lowenstein explains it as a reduction in the sorption capacity of coal to the same degree of metamorphism as the temperature increases with the depth.
Lithological composition of the host rocks and their physical properties are also factors determining the gas content of coal-bearing strata.
Lithological factor affects the distribution of natural gas because of different permeability uglevmeschayuschih rocks due to their porosity values. Porosity and permeability of the host rocks - and the most important basic parameters characterizing the coal-bearing strata as reservoirs of natural gas.
From all of the above can identify the main factors influencing the gas content of the coal strata:
- The degree of metamorphism;
- Depth;
- Vintage composition;
- Lithological composition of the rocks;
- Tectonic conditions;
- The power of the overburden.
The main tasks of the master's work related to test the influence of these factors on the distribution of natural gas-bearing coal seams mine field October mine
.
2.2. Geological characteristics of the test field
Geologists installed numerous factors influencing the formation of methane in coal formations. Assessing the impact of these factors in a particular coal seam opens up new prospects forecast local accumulations of methane [1].
Initial gas-bearing coal deposits caused uglenasyschennostyu area and degree of coal metamorphism. The present distribution of gases in the pool associated with the peculiarities of the geological development of the basin, depth of coal-bearing deposits, tectonic structure, litho-facies composition of the host rocks and the overburden, groundwater circulation conditions. In the Donets Basin is dominated by regional metamorphism. Influence of the degree of metamorphism of coal seams in their natural methane is very clearly seen in the Donetsk-Makeevka area where developed layers stacked coals almost full range of long-flame metamorphism to skinny. The depth of the coal seam gas content of coal affects how the degree of metamorphism. However, increasing the depth extent of coal metamorphism obscures the clarity of the picture changes in gas content with depth.
Degree of faulting coal-bearing strata is a major factor in the distribution of gas coal-bearing strata of the Donets Basin. Species Donbass coal thickness in comparison with classical hydrocarbon deposits have poor reservoir properties and virtually gas-tight. Improving reservoir rock properties is observed only in the zones of tectonic disturbances of various kinds. This means that more or less considerable concentrations of methane in coal-bearing strata are controlled by structural and structural-tectonic traps [3]. Within Donbass regionally distributed gassy, uglegazonosnye, gazouglenosnye and carboniferous zone. Gas zone and includes Bahmutskiy Kalmius Toretskoy-basin in which the Carboniferous sediments deposited under salt-bearing formations of the Lower Permian. Donetsk-Makeevskiy carboniferous district is located in the southern part of the south-west wing Kalmius-Toretskoy shallow depression in the zone folding. Along with gentle folds developed here sublatitudinal younger superimposed system trending asymmetrical folds. This led to a series of domes and brachysyncline. The bulk of the gas is confined to the axial part of the anticlinal structures, if they are not eroded, but also to areas of their fleksuroobraznyh disorders [2].
The most significant submeridional flexures are located in the central and eastern parts of the Donetsk-Makeevka area - Vetkovskiy, Chaykinskaya, Kalinovskaja, Yasynivsky-Zhdanovskaya. The connection between the localization of gas-bearing zones of fracturing the degree of faulting Donbass mine fields. Typically, zones of fracturing confined kink seams on the wings, to the narrow axial part and periklinalyam folds [3]. Increased gas saturation characterized not only by large flexures, but most are relatively small flexure folds that manifested higher values of gas content of coal and rock exploratory well, but more often - increasing gas content and the development of gas-dynamic phenomena in mines.
Mine field mine October Mine
is part of the Donetsk-Makeevka geological and industrial area of Donbass. For administrative and territorial division, described the area is part of the city of Donetsk and Donetsk region Yasinovatskiy. The size of the mine field is 9.0 km along strike and 3.5 km - down dip. Field area lies between Koksovaya thrust to the west and the east flexure fold representing wings Vetka flexures and thrusts Vetkovskiy number 2, number 3 Vetkovskiy thrust and B
. Coke thrust has an amplitude of 40-55 m, decreasing with depth up to 35 m amplitude thrust Vetkovskiy number 2 increases with depth, from 20 to 50 m, Vetkovskiy number 3 - from 1,6-5,0 60-100 m overthrust B
has an amplitude of 12 m violations main part of the mine field is relatively calm, with gently dipping rocks from 8 to 150. Vetka In large flexures, revealed smaller flexure kinks: North and Central flexure having a local development and poured in the east Vetkovskiy flexure [2].
2.3. Methods of analysis of experimental data
Industrial coal reserves within the boundaries of the mine field constitute more than 96.0 million tons. The mine produces coal grade G, DG, J. On the balance shafts are registered strata suites C27, C26 and C25. Currently, the mine developed two layers l81 Sofia
and k8 Parovochny
. Analyze the patterns of distribution of natural gas presence in the field of mine October Mine
in debugging layers k8.
Statistical characteristics of quality coal seam k8 from a sample of 19 samples are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Descriptive Statistics
| Indicators | Minimum | Maximumм | Average | Standard | Asymmetry | Kurtosis |
| Depth, м | 760,0 | 1148,4 | 952,1 | 112,4 | -0,10 | -0,68 |
| Power,м | 0,68 | 0,96 | 0,83 | 0,07 | -0,04 | -0,31 |
| Foulness | 5,6 | 17,0 | 11,95 | 3,1 | 0,03 | -0,33 |
| Cinders (Ad), % | 3,4 | 24,2 | 9,5 | 4,8 | 1,56 | 3,76 |
| Sulfur (Std), % | 2,2 | 36,3 | 5,3 | 7,6 | 4,15 | 17,64 |
| Devolatilization (Vdaf) | 33,8 | 38,9 | 36,5 | 1,6 | 0,21 | -0,92 |
The table of descriptive statistics that well depth varies in a wide range from 760 to 1148 meters. Power coal seam: ranges from 0.68 to 0.96 m, with an average value of 0.83. Formation refers to the sustained, as the coefficient of variation of power is 18.07%. Boundary value for the same sustained recovery is 20%.
The maximum value of the natural gas content reaches 17 m3 / t s.b.m. However, there are areas with low gas content of 5.6 m3 / t s.b.m. Average value - 11.95 m3 / t s.b.m. Distribution of sulfur and ash content is not subject to the normal law for the remaining indicators values.
Gas content of coal depends on the depth of the reservoir, the degree of metamorphism of coal, bedding conditions (structure), and many other factors. According to several studies, the mean values of natural methane coal during their transition from long-flame and gas to anthracite increase from 8-10 to 30-40, and superantratsitah sharply reduced to a minimum - 0.3-0.5 m3 / t of dry ash-free mass . Foulness many layers is 15-30 m3 / t of coal mined and more. Change of methane in a single formation with increasing its depth is characterized by the maximum rate of increase in the initial stage and a slower pace when the depths of 600-1000 m, where the gas content of coal sorption capacity reaches and stabilizes.
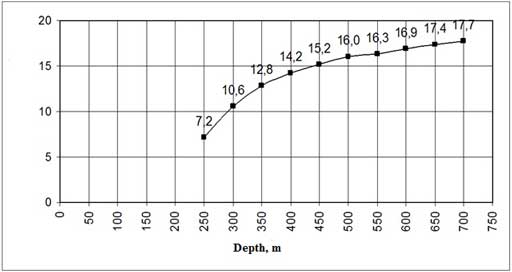
Figure 3. Curve for gas-bearing reservoir m3 of depth
According to the curve, gas content increases with depth. Since the mine October Mine
practiced layers deeper than 1000 m, the connection is lost with the natural gas-bearing grade composition.
Correlation analysis was performed to examine the relationship of the natural gas content with others. As part of the indices does not obey normal distribution, then to assess the correlations should be used Spearman correlation coefficient. Critical correlation coefficient for 19 samples and α = 0,05 is 0,432. In the analysis of the correlation matrix, the following significant correlations:
- Positive correlation between ash content and volatile (0.467) (Fig. 3)
- Negative correlation between gas content and volatile (-0.470) (Fig. 4)

Figure 4. Schematic map of the sulfur content,%
Map data is divided into categories: that of medium (1.5-2.5), sulfur (2.5-4), high sulfur (greater than 4).
In most of the sulfur content of sulfur is in the group Donbass coal (2.5-4%), high sulfur also occupy a large area (about 30%). Same to that of medium coals are virtually absent.

Figure 5. Schematic map devolatilization Vdaf, %
Dedicated here confirmed earlier negative correlation with volatile. That is, in the south-western sector of the reduction in the yield of volatile displays increase in the degree of metamorphism, and hence an increase in the natural gas content. In the study area was confirmed by characteristic Donbass coal as calculated by correlation analysis and graphical rendering of map-scheme.
It is known that an increase in the degree of metamorphism is accompanied by a decrease in the yield of volatile, increasing degree of coalification decrease in ash content. Therefore, both relationships are mapped to link natural gas content with the degree of metamorphism and coalification degree in the field of mine October Mine
(Fig. 6).

Figure 6. Schematic map of natural gas bearing formation k8, m3 / t s.b.m.
Most natural gas content observed in the south-western part of the field of mine October mine.
At the gas reservoir portion exceeds 15 m3 / t s.b.m. In this area also shows a least volatile.
2.4. Expected Results
Thus, the study area of the mine field October Mine
has been tested factors influence the distribution of natural gas content depending on the degree of metamorphism, ash layers and depth. Evidence of the impact of structural and tectonic factors and selection of promising structures for gas utilization study area is a major task for future work.
Thus, the practical significance of the work is confirmed. Installed the most productive part of the gas field of mine October mine
This south-western part of the field where the gas content reaches industrial values, due to the combined action of all geological factors.
2.5. List of References
- Анциферов А.В., Тиркель М.Г., М.Т.Хохлов, В.А.Привалов, А.А.Голубев, А.А. Майборода, В.А.Анциферов
Газоносность угольных месторождений Донбасса
, Киев, Наукова думка, 2004. – 231 с. - Анциферов А.В. Газоносность и ресурсы метана угольных бассейнов Украины / А.В. Анцифров, А.А. Голубев, В.А. Канин и др. // Донецк: Вебер,- 2009. - т.1. – 456с.
- Волкова Т.П., Алёхин В.И., Силин А.А. Выявление локальных газоносных структур методом тренд-анализа // Уголь Украины. – 2011. - №5. – с.33-36.
- Метан в угольных пластах / А.А. Скочинский, В.В. Ходот, М.Ф. Яновская и др. – М.: Углетехиздат, 1958. – 256 с.
- Черницын Н.В. Рудничный газ, условия его выделения, его свойства и меры борьбы. – Пт-г, 1917.-186 с.
- Ржепишевский М.И. Природные газы Донецкого бассейна. – Л.: Госхимтехиздат, 1933. – 6 с.
- Збірник наукових праць за редакцією Г.Л. Рябцева і С.В. Сапєгіна
Сучасні проблеми державної політики у сфері видобутку нетрадиційних вуглеводнів в Україні
, Київ, НТЦПсіхєя
, 2013. - Насырова А.У. Влияние геологических факторов на газоносность Челябинского угольного бассейна – [Електронний ресурс]. – Режим доступу: http://www.coolreferat.com/...
