FIBER-OPTIC NETWORKS
Popova A.
Computer Sciences and Technologies Faculty
Boyko V., Technical Translating Supervisor
Donetsk National Technical University
Nowadays we cannot imagine our life without the Internet. A lot of people daily exchange information over computer networks. Amounts of information only grow over time. So the questions associated with the transferring information remain currently important.
Many people have heard about the transmission of information over fiber-optic networks and that this method provides the highest speed for today. Exactly this gives a great opportunity to develop technology of fiber-optic data transmission. Even today, the capacity can reach about terabit (1000 gigabits) per second.
Another advantage of these technologies is transmission reliability. Transmission over fiber does not have the disadvantages of electrical or radio signal. There is no interference which may damage the signal, and we don’t have to license the use of radiofrequencies (RF).
This connection with the use of fiber-optic communication has several significant advantages:
- Providing a very high speed when transmitting different information.
- Possibility of laying fiber-optic internet-cable on long and short distances.
- Availability of reliable protection of all the transmitted information from unauthorized threats.
- Technology is unaffected to different electromagnetic interference.
- Availability of high resistance, even to the very aggressive products.
- Availability of relatively small dimensions and weight.
- Opportunity to serve durably.
However, not many people imagine the general process of transferring information over fiber.

In a fiber optic network it is not the electrical signal, which is used in conventional cable networks, but the light one. Optical cable is the conductor in this network, which is the transmission medium for the ray of light of the infrared spectrum. In the process of a certain selection of the fiber material and its diameter there is a situation when this medium becomes almost transparent for some wavelengths and the most amount of energy is reflected back into the fiber under the electromagnetic light mode. It allows radiation to pass through the fiber without any loss, and the main task is to take this radiation on the other end of the fiber.
Examples of fiber-optic cable
There are several types of optical fibers with different properties. They differ from each other in the dependence of the step-index fiber on the radius of the central fiber.
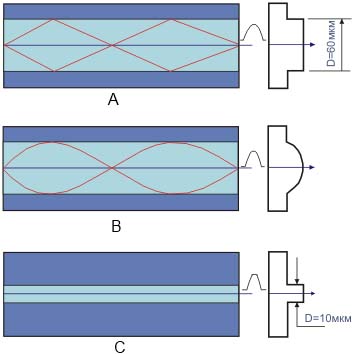
Light ray, which is propagating along a relatively thin core of the single-mode fiber (fig.C), is reflected from the fiber cladding not as often as it is reflected in a thicker core of the multimode fiber (fig.A, B). This separation is due to the number of transmitted modes (rays of the light beam). Rays of fiber optical waveguide is a fiber characteristic and they determine the field distribution and the physical form of the light beam formed by a fiber-optic cable. High power-factor of beam refraction along the axis of the core towards its cladding layer causes the light beam going through the fiber-optic cable tends to stay in the core. Single-mode fiber works in windows of transmission data 1550nm and 1310 nm, with minimal dispersion indicator for windows 1310 nm. Single-mode dispersion-shifted fiber is optimized for data transmit window of 1550nm and provide a wider streak of single-mode fiber transmission in the same window. This allows to construct longer fiber-optic stretches without signal regeneration (100-150km). Single-mode fiber is used in networks with long-range coverage and local networks, and in particular, to work with data transmission systems of high frequency providing the lowest attenuation rate and wide transfer streak.
A multiplexer unit is called as the transmitter and receiver of the light signal and it may convert the signal into a light wave and back. Laser diodes that emit a signal in an optical fiber are the emitter signals in multiplexer . A photodetector is a signal receiver in multiplexer, in which photoelectric effect is used, as a result a directed motion of the electrons appears, that is current electricity as a signal.
Usually, in any company that installs cable optical networks, a separate brigade, or even a whole department is engaged to design installation of optical networks. This is due to different peculiar properties of the optics assembling. For example, fiber optic cable must not be bent at an angle of less than 110-120 degrees. Optical fiber assembling is desirably to fulfill in the corrugated pipe – due to the low level of the strength of a conventional optical cable. It's not hard to break. Laying the optics is often done into a separate channel. There are a lot of nuances of working with such cables like these.

Connectors for fiber optic cable
A fiber network creation requires special equipment, that needs an input. The specialists who could lay such networks are needed as well, as optical fiber is not so easy to connect. That is why these networks are not such widespread among the ordinary users at this stage.
Prospects for the development of fiber optical networks are quite significant. It means that the best way to their production soon will be found, which will reduce the cost of production expenditures. Thus, in the near future the majority of providers will be able to cross over the fiber-optic telecommunication network and to provide the users to obtain the information by means of the Internet with better and more economical way.
References: