Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1 Relevance of a theme
- 2 The purpose and research problems, the planned results
- 3 Electrostatic screening
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
Today the sharp growth of volumes of information transferred through open channels of communication is observed. Interaction between the banks, broker offices and the exchanges removed with branches of the organizations is carried out, the auction of securities are held on ordinary telephone channels. Therefore more and more actual is a problem of protection of the transmitted data. In spite of the fact that concrete realization of systems of information security can differ significantly from each other because of distinction of processes and algorithms of data transmission, all of them have to provide the solution of a triune task:
— confidentiality of information;
— integrity of information;
— readiness to information.
The main directions of the solution of these tasks are non-cryptographic and cryptographic protection.
Non-cryptographic ways of information security is now widely in use (shielding, noise pollution, masking), and also organizational measures for restriction of unauthorized access for violators to the equipment and telecommunications.
1 Relevance of a thene
Relevance of a theme of this degree project is caused by the fact that the understanding of physical processes at electrostatic shielding can promote identification of ways of reduction of information leakage.
2 Purpose and research problems, planned results
The purpose of our researches is using the CST STUDIO SUITE software product of three-dimensional electrodynamic modeling to simulate various ways of electrostatic shielding of various directed transmission lines of high-frequency energy.
Main objectives of research:
- To investigate ways of protection of objects of informatization against information leakage on technical channels by use of means of electrostatic shielding.
- Assessment of ways of reduction of electrostatic influence of external electric fields on the transmitted data.
- Choice of the optimum shield.
3 Electrostatic screening
Electrostatic shielding consists of shunting of parasitic capacity (between a source and the receiver of crosstalk) on the case.
As shown in figure 1 electrostatic shielding is in essence reduced to short circuit of an electrostatic field on a surface of the metal screen possessing high conductivity and to withdrawal of electric charges on the earth (on the device case). Grounding of the electrostatic shield is a necessary element at realization of electrostatic shielding [1].
At frequencies over 1 GHz with increase in frequency efficiency of shielding decreases.
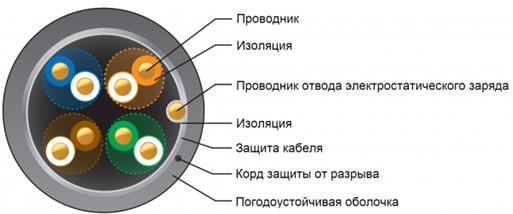
Figure 1 — Example of electrostatic shielding
The main objective of shielding of electric fields is decrease in capacity of communication between the shielded design elements. Therefore, efficiency of shielding is defined generally by the relation of capacities of communication between source and receptor crosstalk to, and after installation of the grounded screen. Therefore any actions leading to decrease in capacity of communication increase efficiency of shielding [1].
At the same time connection of a cover of a wire with the case in one point does not weaken the magnetic field created by the current proceeding on a wire in surrounding space. For shielding of a magnetic field it is necessary to create the field of the same size and the opposite direction. For this purpose it is necessary to direct all return current of the shielded circuit through the shielding wire braid. It is necessary for full implementation of this principle that the shielding cover was in the only way for course of the return current [1].
Narrow cracks and openings in the metal shield which sizes are small in comparison with wavelength practically do not worsen shielding of electric field.
Magnetostatic shielding is used if it is necessary to suppress crosstalk at low frequencies from 0 to 3 – 10 kHz. At high frequencies enly electromagnetic shielding is applied.
Conclusions
In this abstract we considered one of ways of protection of transmission lines against to collateral electromagnetic radiations — shielding. It was established that at high-quality shielding we will receive:
- increase of accuracy and purity of signaling by isolation from hindrances;
- bigger confidentiality of information transfer. If the cable does not perceive radiation from the outside owing to a high shielding, therefore, it also does not radiate.
Summing up the result, it is possible to note that at correctly executed shielding, with observance of all rules, norms and requirements, interception of information signals from technical means of information processing becomes impossible
Currently, the department of Radio Engineering and protection of information
works on improvement of the methods for reducing the level of spurious electromagnetic radiation.
When writing this abstract the master's thesis is not finished yet. Final end: May, 2017. The full text of work and materials on a subject can be received at the author or his head after the specified date.
List of sources
- Способы защиты объектов информатизации от утечки информации по техническим каналам: экранирование [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: bnti.ru/showart...
- Настоящий инженер должен уметь отличать кабель от кабеля [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: rts.ua/rus...
- Электростатическое поле [Электронный ресурс]. — Режим доступа: megabook.ru
- Сапожков М. А. Защита трактов радио и проводной связи от помех и шумов. — М.: Связьиздат. 1959 г. 254 с.
- ГОСТ 21655–87. Каналы и тракты магистральной первичной сети Единой автоматизированной системы связи. Электрические параметры и методы измерений.
- Спесивцев A. B. и др. Защита информации в персональных ЭВМ. — М.: Радиосвязь, 1992 г., 378 с.
- Найтли Ф, Ким Филби. Cупершпион КГБ. — М.:Республика Беларусь, 1992 г., 127 с.
