Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study, the planned results
- 3. The essence and significance of derivatives
- 4. Derivatives as hedging instruments for currency risks
- 5. Classification of derivatives for tax accounting purposes
- Conclusions
- List of sources
Introduction
The abstract explores the essence and classification of derivative financial instruments, reveals their role and economic value. The expediency of the use of derivatives for hedging purposes is substantiated. Keywords: derivatives, hedging, base asset, swap, option, forward contract, futures contract, active market.
1. Relevance of the topic
The market for derivative financial instruments, or derivatives, is one of the fastest growing segments of the financial market, which determines the relevance of its research. Derivative financial instruments have gained significant distribution in market economies in the context of financial globalization. Owing to wide possibilities, the market of derivatives attracts a large number of participants: from private speculators to risk managers of large organizations.
Many companies that work with foreign suppliers on a deferred payment system often face the risk of losses from currency fluctuations. This is also typical for organizations specializing in goods, the prices of which are highly volatile in both domestic and foreign markets (for example, agricultural products, metals, oil and oil products). To compensate for this type of risk, in particular, the policy of many Western companies provides for the use of hedging - currency risk insurance.
2. The purpose and objectives of the study, the planned results
The purpose of this essay is to study the essence, composition and values of derivatives as hedging instruments and to analyze the effectiveness of their use in the modern economy.
3 The essence and significance of derivatives
In the most general form, derivative financial instruments (PFIs) are bilateral or multilateral agreements, the value of which is derived from a certain underlying value. As such a value may be the price of raw materials or agricultural products, stock price or bonds, the exchange rate, stock indices, interest rates, the probability of the occurrence of a credit event, the amount of precipitation, etc. In the economic literature, you can find other terms for the designation of derivative instruments. Widely used directly borrowed from German and English language terms "derivative" or "derivative" (from the word of Latin origin derivation - allotted, disconnected). Often derivative instruments are called fixed-term contracts, as they are in their form represent agreements on the supply of the subject of the contract in the future. From the point of view of the time terms of the transactions, it is customary to allocate spot markets (in other words, cash or cash markets) and futures markets.
In the position (standard) of accounting 13 "Financial Instruments" (hereinafter P (C) BU-13) [1] it is said that the derivative financial instrument is a financial instrument:
- calculations on which will be made in the future;
- the value of which varies due to changes in the interest rate, securities rate, exchange rate, price index, credit rating (index) or other variables that are basic;
- which does not require initial investment.
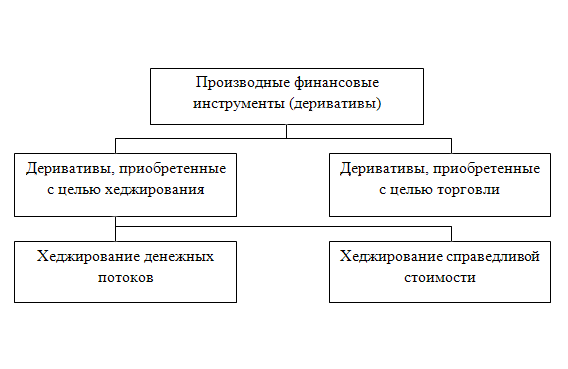
Fig. 1 - classification of financial instruments in accordance with Ï (Ñ) BU-13
Financial instruments are the "goods" of the financial market. Their purchase and sale, is a way of satisfying the interests of sellers and buyers. With the help of financial instruments four main goals are achieved:
- hedging, i.e. risk reduction;
- speculation; obtaining short-term profit;
- mobilization of sources of financing;
- Assistance to current routine operations.
Derivative financial instruments dominate in the first three situations, in the fourth - primary instruments.
According to P (C) BU-13 [1], the classification of derivative financial instruments can be represented in the form of a scheme (Figure 1)
Thus, derivatives are divided into those acquired for the purpose of trading and for the purpose of hedging.
4 Derivatives as hedging instruments for currency risks.
Derivatives purchased for the purpose of hedging are divided into cash flow hedges and fair value hedges.
Cash flow hedging is the hedge of a change in cash flows relative to the risk associated with a recognized asset or liability or a forecast transaction, affect net profit (loss). {Paragraph 4 is supplemented with the twenty-fifth paragraph in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 363 of 23.05.2003} [1].
Fair value hedging is the hedge of changes in the fair value of a recognized asset or liability or an identified part of that asset or liability, relates to a specific risk and affects the net profit (loss). {Paragraph 4 is supplemented by the twenty-fourth paragraph in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Finance No. 363 of 23.05.2003} [1].
5. Classification of derivatives for tax accounting purposes
The tax code of Ukraine [2] relates to derivatives: swaps, options, forward and futures contracts.
A swap is a civil transaction for the exchange of payment flows (cash or non-cash) or other assets calculated on the basis of the price (quotation) of the underlying asset within the amount specified in the contract for the specific payment date (settlement date) during the contract period [2 ].
Option - a civil law contract, according to which one party to the contract receives the right to purchase (sell) the underlying asset, and the other party assumes an unconditional obligation to sell (purchase) the underlying asset in the future during the term of the option or on a set date performance) at the price of the underlying asset determined at the time of entering into such a contract. Under the terms of the option, the buyer pays the seller a premium on the option [2].
In the decision of the State Commission for Securities and Stock Market No. 884 of 4.08.2009. (hereinafter - the Decision) "On approval of the Regulation on the procedure for registering changes to the rules of the stock exchange regarding the introduction of derivatives at circulation on the stock exchange" [3] it is said that options are divided into:
- call option (option "call") - an option whereby the buyer has the right to purchase the underlying asset from the seller, and the seller assumes the obligation to sell the underlying asset and / or perform mutual settlements;
- put option - an option whereby the option buyer has the right to sell the underlying asset to the seller, and the seller assumes the obligation to acquire the underlying asset and / or settle the settlement. The option can be sold without restrictions to other persons during the term of its validity. This definition establishes a limited list of what can be the underlying asset of the option.
A forward contract is a civil law contract whereby the seller undertakes to transfer the underlying asset to the buyer's property in the future within a certain period of time on certain conditions, and the buyer undertakes to accept the underlying asset in the specified period and pay for it the price determined by such an agreement [2].
All forward conditions are determined by the parties to the contract upon its conclusion. The conclusion of forwards and their circulation are carried out outside the bidding organizer by standardized fixed-term contracts;
All forward conditions are determined by the parties to the contract upon its conclusion. The conclusion of forwards and their circulation are carried out outside the bidding organizer by standardized fixed-term contracts;
A futures contract (futures) is a standardized futures contract whereby the seller undertakes to transfer the underlying asset to the buyer's ownership in the future on the specified date (the date of fulfillment of obligations under the futures contract) under the conditions specified by the specification, and the buyer undertakes to accept the underlying asset and pay its price, determined by the parties to the contract on the date of its conclusion [2].
A futures contract is executed according to its specification by delivery of the underlying asset and its payment by means or carrying out between the parties to the contract cash payments without the delivery of the underlying asset.
Table 1 Comparative data of hedging instruments of currency risks
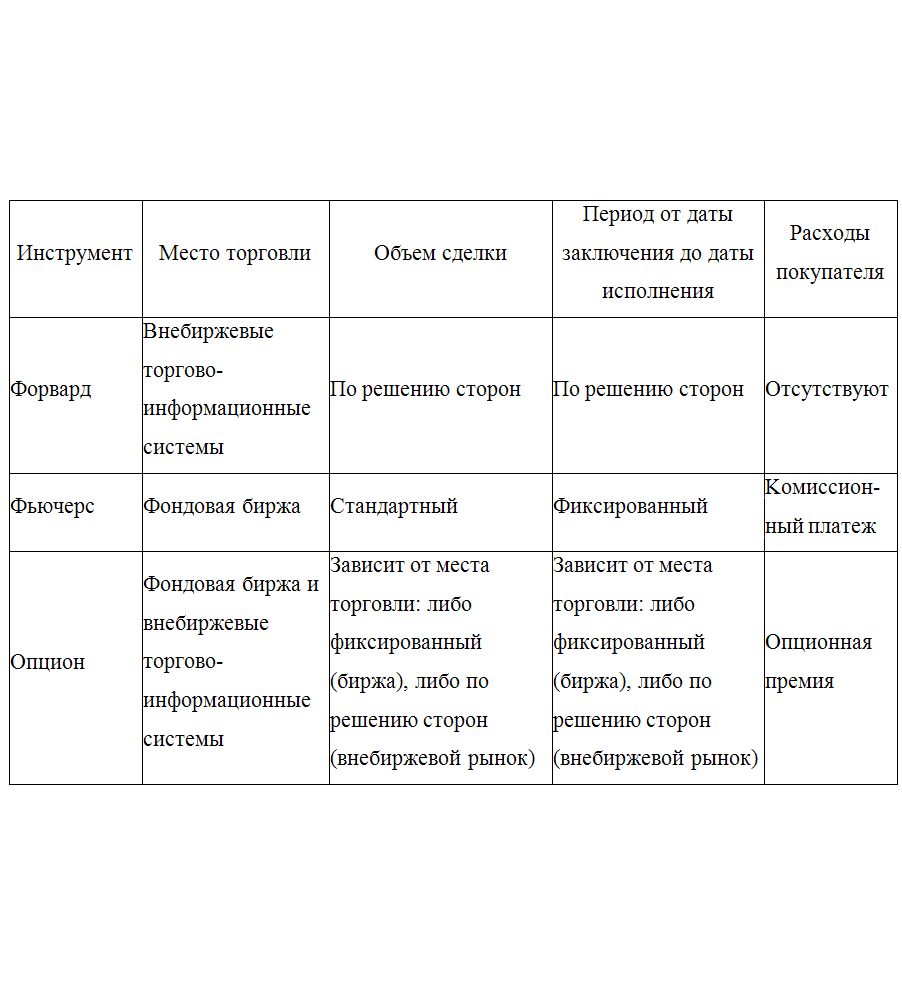
Comparative data of hedging instruments of currency risks
An active market is a market with the following conditions: objects that are sold and bought in this market are homogeneous; at any time you can find interested sellers and buyers [4].
conclusions
Summarizing, we can conclude that derivatives are a separate group of financial instruments designed to hedge foreign exchange risks. Derivatives include the following transactions: swap, option, forward contract, futures contract.
List of sources
- Regulation (standard) of accounting 13 "Financial instruments" Approved by the order of the Ministry of Finance of Ukraine from November 30, 2001 ¹ 559 changes and additions [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://www.nibu.factor.ua/info/instrbuh/psbu13/....
- The Tax Code of Ukraine as of 02.12.2010 No. 2755-VI with amendments and additions in accordance with the Laws of Ukraine [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://zakon4.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/2755-17.
- Decision of the State Commission for Securities and Stock Market No. 884 of 4.08.2009. "On approval of the Regulations on the procedure for registering changes to the rules of the stock exchange regarding the introduction of derivatives on the stock exchange" [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/z0818-09.
- Ukrainian Exchange [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/3480-15....
- The Law of Ukraine "On Securities and the Stock Market" of 23.02.2006 No. 3480-IV [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://zakon2.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/3480-15.
- Makshanova AV Derived financial instruments: concept, types and basic use strategies [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://www.moluch.ru/archive/70/12084/.
- ÄDukhnovskaya L., Reduk T. Tax accounting of securities and derivatives [Electronic resource]. - Access mode: http://dspace.nuft.edu.ua/jspui/bitstream/123456789/9260/1/2.pdf.
