Abstract
Content
- Introduction
- 1. The role of foreign economic activity in the development of an industrial enterprise
- 2. The specifics of the management of foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise
- 3. Factors affecting the effectiveness of foreign economic activity of the enterprise
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
One of the most important areas of operation of Russian enterprises in the modern world is foreign economic activity. Before the fall of the administrative–command system, the economy of our state was a closed mechanism. For many years, the authorities pursued a policy of autarky, which impeded economic and technological progress. With such a policy, enterprises did not need to enter foreign markets, and the development of foreign economic activity was not a priority for them. But, after the fall of the iron curtain, enterprises had the opportunity to use the advantages of foreign economic relations, as well as the entry into the world process of integration and production cooperation. Domestic enterprises began to be active in foreign trade. As a result, an objective need arose for the study of foreign economic activity. After all, for its most effective implementation, it is very important to have sufficient theoretical and practical knowledge in this area, which, unfortunately, is not available to many managers in Russian enterprises. Foreign economic activity began to be actively studied relatively recently, when the planned economy became obsolete. Until that time, it was of no interest to study, since domestic enterprises operated only on a national scale and did not need to enter foreign markets.
The object of the study is the foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise and production factors that have a direct impact on its effectiveness. The subject of the research is the tools and methods for assessing the influence of internal and external production factors on the foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise. This goal involves the following tasks:
- define the role of foreign economic activity in the development of an industrial enterprise;
- study the specifics of managing foreign trade activities of an industrial enterprise;
- consider the factors affecting the effectiveness of the enterprise’s foreign economic activity;
- to analyze the methodological approaches to assessing the impact of internal and external factors of production on the foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise.
Theoretical and practical studies of the specifics of foreign economic activity of industrial enterprises, as well as the main approaches to the organization and management of this process are discussed in the works of V. I. Denisova, L. I. Gerchikova, E. A. Parshina, Sarkisova, L. E. Strovsky, B. A. Slepova, S. K. Kazantseva and others.
1. The role of foreign economic activity in the development of an industrial enterprise
The systematic development of Russia in a market economy environment implies the country's openness and its infusion into the world economy. Any enterprise, firm, corporation, regardless of the form of ownership, must have access to the external market. Only in this case is it possible to guarantee their real entry into international economic processes. A country's participation in international integration implies the free export and import of goods and services. With proper formation of the structure of exports and imports, international exchange of goods may be beneficial for different countries. In foreign trade, a landmark on the development of exports should be considered significant, since the purchase of goods by import can be carried out in the presence of foreign currency or of a competitive product. In order to achieve a greater economic effect, it is important to export high–tech products, which make it possible to get the maximum foreign exchange earnings per unit of labor costs, and import those goods that have the highest labor costs per unit of invested funds. Active export activities of Russian companies stimulate industrial growth, primarily in the energy industry, ferrous and nonferrous metallurgy, chemical and petrochemical, woodworking and pulp and paper industry [1].
Foreign economic activity – an integral part of the work of almost all Russian enterprises. The development of foreign economic activity opens up new opportunities for the company, including the use of the advantages of international cooperation in production, as well as freedom in making decisions to fulfill its production tasks such as:
- freedom of choice of resources for production taking into account the possibilities of the world market;
- freedom in choosing directions and forms of sales of products with maximum profitability;
- freedom of choice of production partner, cooperation, which most meets the economic interests of the enterprise;
- freedom of choice of ways, as well as opportunities to improve the technical level of production, the competitiveness of products and export potential.
The level of development and stability of the national economy, the system of world prices, the legal system of one’s own country and the legal systems of the countries in which the company carries out foreign economic activity significantly affect the foreign economic activity of an enterprise. An enterprise can perform any kind of foreign economic activity, if they are not prohibited by law and meet the objectives that stipulated by the charter. All enterprises that produce competitive products have the right to independently carry out export–import operations. Proceeding from this, in the economic activity of each producer that enters the foreign market, foreign trade activity plays an important role. Enterprises can enter the foreign market independently and with the help of foreign trade. intermediary organizations–resellers [2]. These organizations mainly sell products of not large firms on the world market, but large enterprises that do not have their own foreign trade apparatus may also use their services. Foreign economic activity is a combination of methods and means of trade, economic, scientific and technical cooperation, monetary and credit relations with foreign countries. An important part of foreign economic activity is foreign trade, which is defined as entrepreneurial activity in the field of international exchange of goods. An industrial enterprise should be considered as the main link of the economy, it is there that the production is carried out, the employee is directly connected with the means of production. Being engaged in foreign economic activity it is important to assess the economic efficiency and the effect of foreign trade. It is advisable to carry out if the foreign trade activity of the enterprise is carried out through the implementation of export and import transactions and their scale is not in the least individual number. This condition is feasible if foreign trade operations with counterparties will be carried out at the level of the network of exporting enterprises. While engaging in foreign trade activities it is important to assess the economic efficiency and effect of foreign trade activities. It is advisable to carry out if the foreign trade activity of the enterprise is carried out through the implementation of export and import transactions and their scale is not in the least individual number. This condition is feasible if foreign trade operations with counterparties will be carried out at the level of the network of exporters. It is reasonable to determine the economic efficiency and foreign trade effect of the enterprise in order to [3]:
- justify individual proposals for the sale and purchase of goods;
- develop export and import plans;
- evaluate the current structure and directions of foreign trade turnover [4].
There is a whole set of other indicators of the effectiveness of foreign economic activity of an enterprise, which managers and specialists can independently choose for calculation, depending on which indicator most fully describes the main processes and results of foreign economic activity.
2. The specifics of the management of foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise
The transformation of the foreign economic sphere significantly changed the status of the enterprise. In the conditions of demonopolization and decentralization of foreign economic relations, an enterprise, being an object of management in the system of state management of foreign economic activity, has become a full subject of foreign economic activity. It became involved in foreign relations of the state, not as before, as a technical performer, but in the new conditions became a participant who does not depend on anyone in terms of managing the result of her work, including in foreign economic activity. The transition of the enterprise from the role of the performer to the role of the subject of foreign economic activity has caused the need to reform the management system of foreign economic activity in the enterprise through the emergence of new functions and the formation of a new organizational structure of management, which reflects the increased role of the enterprise in the development of foreign economic sphere. At this stage, the management of the foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise is a complex process of determining and establishing its relations with business entities that are located in different countries. This process consists in the implementation of selected goals, as well as in attempts to achieve the desired state of relations with foreign partners through the use of modern management methods, since such activities are more risky and require consideration of many factors, not only within the country of location of the enterprise, but also those that are related with the functioning of partner enterprises. For the successful activity of any enterprise, a well–thought–out, well–defined organizational and functional structure and a rational management system both in the whole enterprise and in foreign economic activity are needed. The organizational structure of the enterprise is a relatively stable relationship between the elements of the organization.
The essence of the management of foreign economic activity of the enterprise is expressed by such functions:
- planning;
- organization;
- motivation;
- control.
The organization of foreign economic activity involves the choice of the optimal organizational structure of the enterprise. Permissions — this is the right to use the resources of the organization in order to fulfill the assigned responsibility. In carrying out foreign economic activity, management must assign to each employee the organizational structure of foreign economic activity responsible for the implementation of specific functions and activities and transfer adequate powers. Motivation for foreign economic activity — This material and moral incentives for workers in the field of foreign economic activity. Control of foreign economic activity, that is, systematic observation of the activities of specialists, a comparison of planned and actual results of foreign economic activity. Principles that must be observed in the organization of foreign economic activity:
- decision making autonomy;
- combination of responsibility and authority;
- consideration of national economic interests;
- freedom to choose a partner in foreign economic activity;
- ensuring the effectiveness of foreign economic activity.
Factors that reveal the form of organization of management of foreign economic activity (organizational structure) are:
- type of economic activity;
- motives and needs that encourage participation in the international division of labor;
- degree of internationalization of production activities;
- sales method;
- enterprise scale, as well as the volume of actual and potential foreign economic operations;
- nature of foreign operations.
Forms of the organization of foreign economic activity that may be in the enterprise are:
- one specialist in foreign economic activity;
- department of foreign economic activity;
- department of foreign economic activity created at large enterprises, which are focused mainly on foreign trade operations;
- foreign trade firm is a member of large associations with large–scale foreign economic operations. The nature of relations with foreign partners is long–term and developing. The peculiarity is that a foreign trade company can be created as an independent legal entity [5].
When managing foreign economic activity in an enterprise, there is an impact on the preparation and further implementation of foreign economic operations, which is focused on increasing profitability, as well as making profit through participation in the international division of labor. Foreign economic activity of the enterprise can be represented as set of production and economic functions, organizational and economic, as well as commercial. In fig. 2.1 illustrates the scheme of foreign economic functions performed by the enterprise.
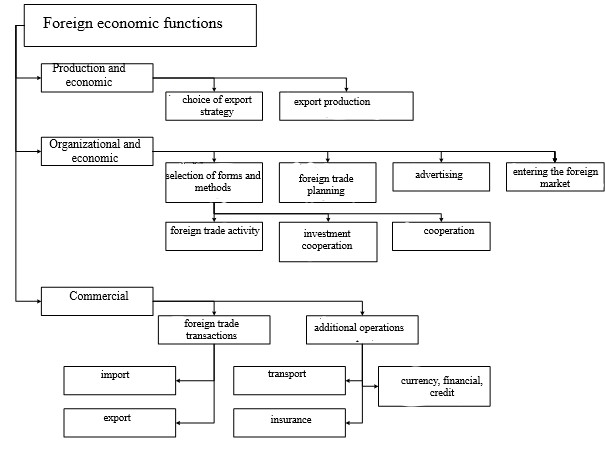
Fig. 2.1 — The scheme of interrelations of foreign economic functions.
At the enterprise level, management of foreign economic activity includes the solution of strategic, production, financial, infrastructure, logistics, information and marketing issues. The need to take into account the peculiarities of management activities at the international level is due to differences in the socio–cultural environment of a foreign country [6]. Properly organized management of foreign economic activity — One of the important tasks of economic entities, which is aimed at increasing competitive advantages. At industrial enterprises, such a foreign trade administration is manifested mainly as an intraproductive structure, which includes 3 groups of departments that carry out the planning of internal processes, marketing work, the adoption and execution of management decisions. The management of the company is engaged in a director and a pair of his deputies, whose quantity directly depends on the amount of work.
At the state level, the management of foreign economic activity is carried out with the help of:
- Ministry of Industry and Commerce.
- Federal Customs Service — central law enforcement agency in the field of foreign economic activity. It provides economic security, protects state interests, fights lawbreakers, and also collects customs duties and fees.
СThe system of customs management in the Russian Federation includes 2 levels:
- Federal Customs Service.
- Customs administrations.
The foreign economic activity of the bank is that it represents the interests of the country in banks of various countries, in international financial organizations, issues licenses for financial transactions in foreign currency to commercial banks. In fig. 2.2 presents the model of the relationship of the integrated management system and elements management of foreign economic activity [6].
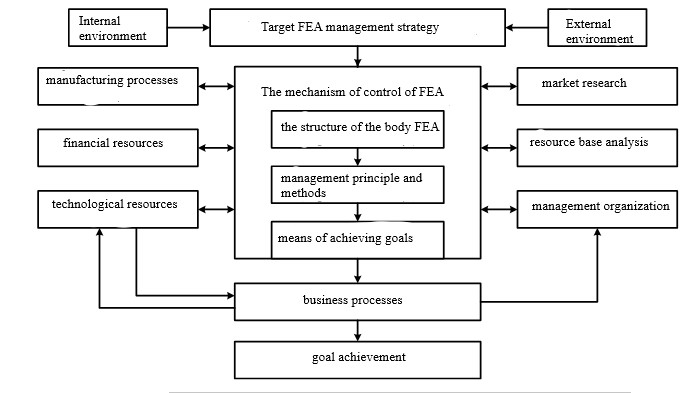
Fig. 2.2 — Model of interrelation of an integrated control system and elements of management of foreign economic activity.
The structure of management of foreign economic activity in the enterprise depends on the goals and objectives that it must solve, on the nature of the specialization of the enterprise in foreign economic activity. The choice of organizational forms of foreign economic activity is greatly influenced by the degree of the enterprise’s dependence on the external market, that is, how much it is included in the international division of labor. At special foreign trade enterprises (such as export or import) management is based on one system, on those where foreign economic activity is only a part of economic activity, — on the other, this implies different options for organizational structures. In fig. 2.3 shows a diagram of the organization and interaction of the subsystem of the organizational economic mechanism of management of foreign economic activity.
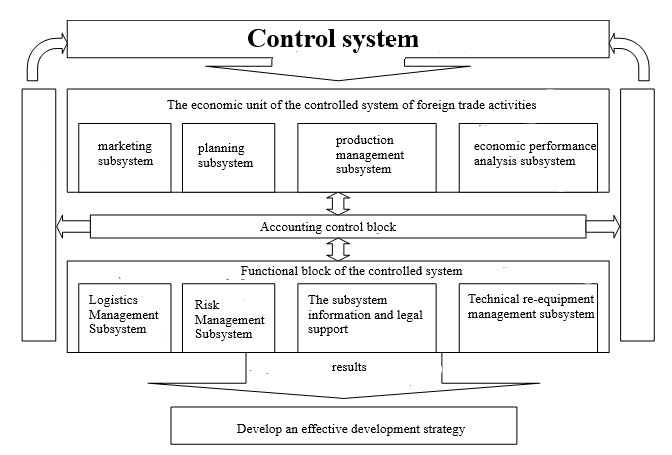
Fig. 2.3 — Scheme of the organization and interaction of the subsystem of the organizational and economic mechanism of foreign economic activity management.
Due to the diversity of specific goals, objectives and conditions, there cannot be one standard structure of a foreign trade firm for all enterprises. As an example in fig. 2.4 shows a control scheme for a specialized foreign trade enterprise [7].
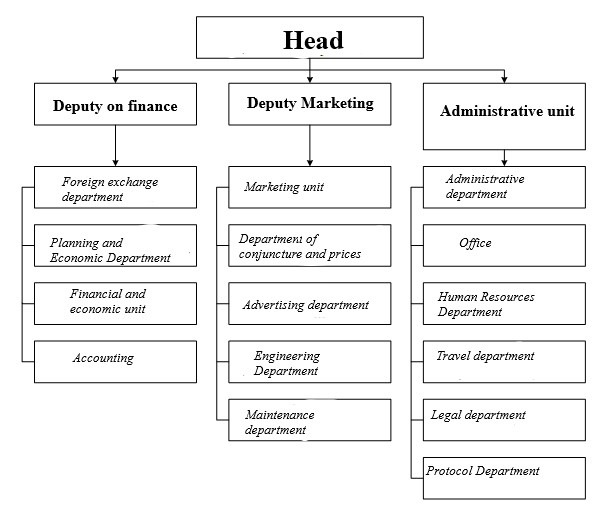
Рис. 2.4 — Management scheme of the foreign trade enterprise.
In the next paragraph we consider the influencing factors.
3. Factors affecting the effectiveness of foreign economic activity of the enterprise
The functioning of the enterprise in the conditions of market relations can not be present without the development and implementation of a set of functional strategies that form a single business strategy. Recently, more and more enterprises, due to objective reasons, are paying attention to the issues of mastering foreign markets and forming an export strategy. Work in foreign markets is characterized by a higher level of risk than in domestic markets. This is due to differences in the socio–cultural, economic, political, legal factors of foreign countries; higher level of competition, high demands on the quality characteristics of the product, packaging, labeling, as well as higher costs associated with international marketing research and the implementation of the export strategy. Therefore, when forming this strategy, it is important to assess how much internal and external factors influence it. Exploring the influence of different factors on the development, as well as the choice of the export strategy of the enterprise, it should be noted that almost all experts in the field of strategic management give their own set of factors of the internal and external environment [ 8 ] . All approaches to the classification of internal and external factors that affect the enterprise and its activities can be divided into two types. A number of authors, including Meskon and Bowman, identify factors of internal and external environments that affect the enterprise at the micro and macro levels, thus distinguishing between the microenvironment and the macroenvironment of exposure, is clearly represented in Fig. 3.1.
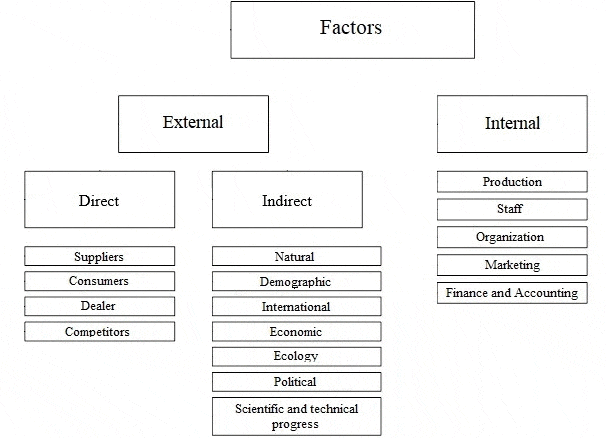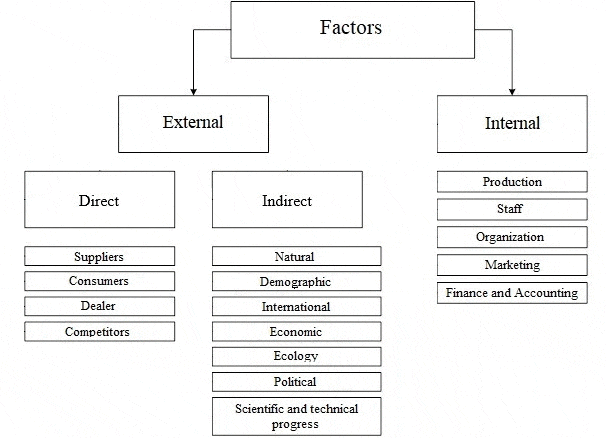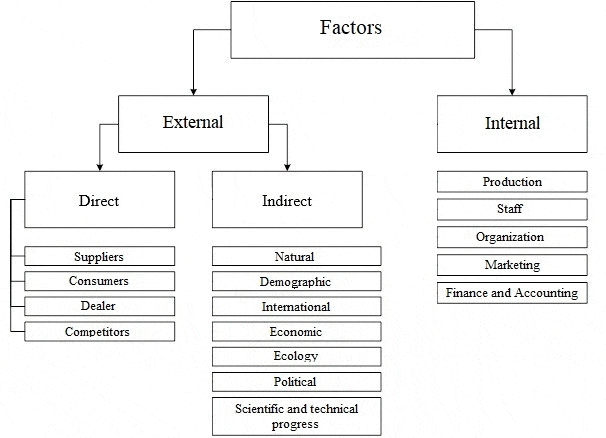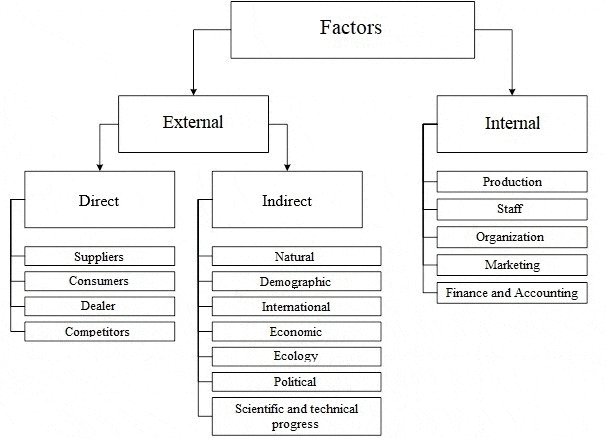
Figure 2 – Factors of the internal and external environment of the enterprise
(animation: 10 frames, 6 cycles of repetition, 105 kilobytes)
(xi – input signals, yi – status code bits, zi – output signals)
Under the internal environment means the economic body of the enterprise, including the management mechanism, which aims to optimize the scientific, technical and production and marketing activities of the enterprise. As for the internal environment of the enterprise, this refers to the full structure of the enterprise, which covers all production enterprises, financial, insurance, transport and other units that are part of the enterprise, regardless of their location, as well as the scope of activities. Under the external environment understand all the conditions and factors that arise in the environment, regardless of the type of activity of a particular enterprise, but do or may affect its functioning. and therefore require management decisions. But, a set of these factors and an assessment of their influence on economic activities are different in each enterprise. Usually, an enterprise in the management process determines which factors and to what extent can influence the results of its activities in the present period and in the future. Conclusions of the research or current events are accompanied by the development of certain tools and methods for making appropriate management decisions. In addition, first of all, environmental factors that affect the state of the internal environment of the enterprise are manifested and taken into account. Macromedia creates the general conditions of existence of the organization in the external environment. This part of the analysis examinespolitical and legal, technical and economic, social and cultural, environmental and similar factors [9].
The study of the working environment involves the analysis of those components of the external environment, with which the organization is in direct interaction, it is: buyers, suppliers, competitors, creditors, shareholders. Analysis of the internal environment is aimed at determining the potential of the organization and, usually, is carried out in such main areas as: marketing, production, finance, personnel, management structure. Internal enterprise management and enterprise management as a subject of the market are two stages in the management hierarchy, which are tightly interconnected by the dialectical unity of the external and internal environment of the enterprise. The external environment of the enterprise is something given, the internal environment of the enterprise is, in principle, a reaction on the external environment. The main goals that the company has set for themselves are reduced to one generalized profit. In this case, of course, it is necessary to take into account both the internal environment of the company and the external one.
The internal environment of the enterprise is situational factors within the organization. The manager forms and changes, when necessary, the internal environment of the organization, which is an organic combination of its internal variables. But for this, he needs to be able to identify and know them [10]. All the diversity of the internal environment of the enterprise can lead to such larger areas as [11]:
- manufacture;
- improvement and development of software;
- marketing and logistics;
- financial management;
- general management[12].
The external environment is a set of active economic entities, economic, social and natural conditions, national and interstate institutional structures, as well as other external conditions and factors that operate in the environment of an enterprise and affect various areas of its activity. The external environment depends on external and internal factors of influence. Analysis of the external environment involves constant attention from managers, so it is carried out through the study of a large amount of information and requires concretization to make correct and timely decisions. Environmental Analysis — This process is designed to control external factors in order to identify the organization’s future opportunities and threats.
The external environment is divided into [13]:
- the microenvironment is an environment of direct influence on the enterprise, which is created by suppliers of material and technical resources, consumers of products (services) of an enterprise, trade and marketing intermediaries, competitors, government agencies, financial and credit, insurance companies;
- macro environment, it affects the enterprise and its microenvironment. It includes: natural, demographic, scientific, technical, economic, ecological, political and international environments.
Summing up this section, it can be said that foreign economic activity is a complex process that requires highly qualified personnel in the field of management to analyze and manage an enterprise, select a development strategy and improve the efficiency of an enterprise, which, to one degree or another, is affected the number of external and internal factors.
Conclusion
In the modern world, foreign economic activity of an industrial enterprise is defined as the production and financial complex of economic relations, which are associated with the expansion of sales markets for products, technological re–equipment of production and improvement of the financial sustainability of enterprises through the development of foreign markets.
Foreign economic activity of industrial enterprises at the present time is mainly associated with the following areas: participation in international exhibitions, provision of services, international trade. International trade is one of the most developed and traditional forms of international economic relations. Countries trade for several reasons. First, the economic resources: natural, human, investment goods are distributed among countries of the world extremely unevenly; countries differ significantly in their availability of economic resources. Secondly, efficient production of various goods requires different technologies or a combination of resources. Today tens of thousands of enterprises and firms are taking part in foreign economic activity. Regardless of a field of activity, a form property and size, they have the right to independently carry out foreign economic operations.
References
- Непомнящий Е. Организация и регулирование внешнеэкономической деятельности: Курс лекций.— Москва: изд–во ТИУИЭ, 2002. — 176 с.
- Сафонов И. Внешнеэкономические связи России со странами Еврозоны в контексте расширения Европейского Союза &mdash М.: Экономика, 2008. &mdash 272 с.
- Основы внешнеэкономической деятельности предприятия: Общее понятие внешнеэкономической деятельности [Электронный ресурс] — https://studwood.ru/1391598/ekonomika/osnovy_vneshneekonomicheskoy_deyatelnosti_predpriyatiya
- Внешнеэкономическая деятельность предприятия / Мир Знаний [Электронный ресурс] — http://mirznanii.com/a/249547-2/vneshneekonomicheskaya-deyatelnost-predpriyatiya-2
- Сущность и формы организации управления ВЭД на предприятии / FREESTORE INC [Электронный ресурс] — http://ifreestore.net/4647/17/
- Шевень Л. Организация управления внешнеэкономической деятельностью предприятия // Экономика и менеджмент инновационных технологий.[Электронный ресурс] — http://ekonomika.snauka.ru/2016/12/13251
- Соркин С. Внешнеэкономическая деятельность предприятия: экономика и управление / Учеб. пособие. — М.: Мир, 1971. — 364 с.
- Наливайко А. Теория стратегии предприятия: Монография. — М.: Финансы, 2004. — 538 с.
- Анализ внешней и внутренней среды организации / Финансовый менеджмент [Электронный ресурс] — http://www.financemanages.ru/fins-334-2.html
- Гриффин Г., Яцура В. Основы менеджмента. — М., 2003. — 614 с.
- Белошапка В., Загорий Г. Стратегическое управление: принципы и международная практика. — К., Абсолют, 2003. — 567 с.
- Моргунов В.И. Международный маркетинг: Учеб. Пособие — М: 2005. — 365 с.
- Фролова Т.А. Экономика предприятия: конспект лекций/ Таганрог: Изд–во ТРТУ, 2005. — 679 с.
