Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. The purpose and objectives of the study
- 3. Analysis of literary sources
- 4. The order of the research
- 4.1 Fieldwork and office processing of measurements
- 4.2 Building a three-dimensional model of the object in Agisoft PhotoScan
- Сonclusion
- List of references
Introduction
One of the most popular types of work in geodesy is performing large-scale topographic surveys. New science photogrammetry begins its development after the emergence of a new way of recording information — photography. It has firmly taken its place in the field of engineering and geodetic surveys. Photogrammetric methods of measuring objects from images immediately attracted the attention of surveyors. This gave impetus to the development of aerial photography of the earth's surface, methods of processing and construction of orthophotos.
Photogrammetry has come a long way from analog to analytical, and to digital later. Continuous improvement of cameras has led to the development of new methods of image processing. Today, the standard photogrammetric products are digital orthophotomap, digital topographic map, digital elevation model, 3D terrain model.
1. Relevance of the topic
Aerial photography, performed from aircraft, was the main method of obtaining photographic material for a long time. A cheaper and mobile way of aerial photo scanning using unmanned aerial vehicles with a digital camera installed on board, which are used to solve geodesy, geology, cadastre, land monitoring, architecture, etc. tasks. developing thanks to technical progress today. Ground-based photo scanning is used to solve local problems as well.
Aerial photography from a UAV is becoming more and more popular over the message for several years. This is facilitated by the appearance on the market in wide access of ultralight UAVs of aircraft and helicopter types (especially quad and hex copters) that do not require specially equipped airfields for launch. Published articles on the experience of using UAVs, assessing the accuracy of orthophotomaps and digital terrain models, new image processing technologies, as well as determining the positions of the survey during flights in specialized geodetic literature more and more. This method of photo scanning firmly secured a place in the field of remote sensing.
The era of bulky photogrammetric stations has long passed. A personal computer with a special software replaced them. There are a number of software products that allow you to perform image processing almost automatically exists. The most popular software products include Pix4Dmapper, DroneDeploy, Autodesk ReCap 360, Photomod and Agisoft Photoscan today.
Agisoft Photoscan will be considered as a program for photogrammetric processing of digital photos in the future. It is necessary to estimate how accurate the geometry of the final three-dimensional object model is, and compare it with the control measurements obtained using traditional geodetic methods based on the results obtained after processing photographs of the object.
2. The purpose and objectives of the study
The purpose of the study is to assess the accuracy of the construction of three-dimensional models.
The object of study is the technology of building three-dimensional models from digital photographs.
The subject of study is a three-dimensional model built in the program Agisoft PhotoScan.
The following tasks in this study are highlighted:
- 1. Perform field work to obtain digital photographic material of the object, as well as control measurements.
- 2. Construction of a three-dimensional model of the object and an assessment of the accuracy of its geometry. .
- 3. The influence of the coordinate reference of photographing points on the accuracy of the final three-dimensional model.
3. Analysis of literary sources
The articles of various authors relating in one way or another to the chosen field of study were studied before starting work on the master’s thesis. The search for articles was carried out in specialized geodesic journals, among them Geomatics
, Geoprofi
, Proceedings of Higher Educational Institutions. Geodesy and aerial photography
, Geodesy and cartography
, Interdepartmental scientific and technical collection
, Geodesy, cartography and aerial photography
.
I began to study the issue with "Instructions for photogrammetric work in creating digital topographic maps and plans" under the publication TsNIIGAK first. The next step was to search for articles on aerial photography from unmanned aerial vehicles. Articles by authors such as Mitin MD, Nikolsky D. B., Brovko E. A., Efimov S. A., Maslyanko V. Ya., Semenov A. E., Chizhov M. N., Petrov M. V., Blokhinov Yu.B., Kurkov V.M., Blykharsky D.P., Florinsky I.V., Kurkov V.M., Perez Valdez Manuel de Jesus, Blykharsky D.P. Volgusheva N.E., Prokofyev N.A., Blykharsky D.P. dedicated to this topic. Many of these authors used the Agisoft Photoscan program as a photogrammetric station for image processing.
Further, the Photoscan user manual and instructions for processing images under the Agisoft publishing house, as well as illustrative examples of operating the program on the YouTube site were studied. Then the search for reports and articles on photo processing and digital model accuracy in Photoscan was started. Foreigners. D.P., Rylsky I.A., Grinko E.V., Kurkov M.V., Soloschenko F.V., Suzdaltsev N.R., Gormash A.V., Onkov I.V., Kurkov V.M. , Blyakharsky D.P., Florinsky I.V., Novakovsky B.A., Prasolova A.I., Permyakov R.V. worked on the problem.
4. The order of the research
A number of field and office work must be performed to complete the study:
- Perform photographing of the selected object, with the determination of the coordinates of the photographing points using GPS measurements.
- Measurement of control points at the facility using an electronic total station.
- Processing of GPS measurement data, obtaining the coordinates of photographing points.
- Processing the data of the tacheometric survey, obtaining the coordinates of the control measurements.
- Construction of a three-dimensional model of the object in Agisoft Photoscan.
- Construction of a three-dimensional model of the object in Agisoft Photoscan.
- Comparison of the obtained data with control measurements.
4.1 Fieldwork and office processing of measurements
The decision to perform ground-based photo scanning of the building, with measuring control points along the facade was made, since it was not possible to perform aerial photography using the UAV, since the latter was not available, and it was not possible to find in the public domain all necessary data for the study. This decision will not significantly affect the accuracy assessment of the three-dimensional model.
After selecting the object of photographing, it is necessary to place marks of future control points on the facade of the building. Then it is necessary to perform a tacheometric survey without reflective method, guiding in the center of the marks. The coordinate list XYZ of the nth number of points is obtained as a result. These results will be the benchmark for comparison with the coordinates obtained from the three-dimensional model built in Agisoft PhotoScan.
PhotoScan provides the ability to set the coordinate system either by the coordinates of the control points, or by the coordinates of the cameras so that the future model has the correct scale. It is necessary to determine the coordinates of the photographing points, since the marks located on the surface of the facade of the building will not be used as reference points, but to control the model's accuracy.
The coordinates of the photographing points will be determined using high-precision GPS measurements in the RTK mode. RTK (Real Time Kinematic) is a set of techniques and methods for obtaining planned coordinates and elevations of high precision terrain points using a satellite navigation system by obtaining corrections from a base station received by user equipment during a survey(Рicture 1).
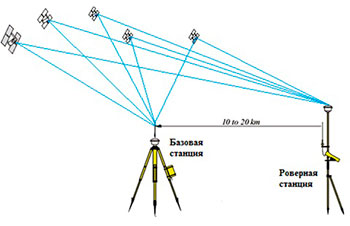
Рicture 1 - scheme of GPS measurements in the RTK mode
It is necessary to install a GPS receiver at the future point of photographing after the device determines the coordinates, and then take a picture. Thus, each photograph will correspond to the spatial coordinates of XYZ.
Photo scanning is necessary to perpendicular to the object, and moving parallel to it, according to the Agisoft PhotoScan User Guide (Рicture 2). It is necessary to use a camera with a matrix of sufficiently high resolution to obtain a high-quality three-dimensional model (more than 5 MPix).
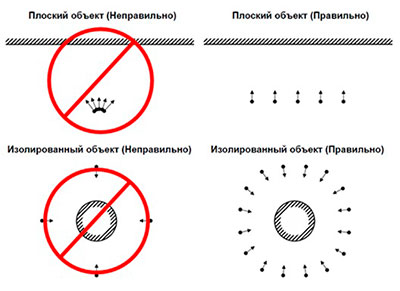
Рicture 2 — Сценарії зйомки об'єкта
You must adhere to the following rules when performing a photo scan:
- Surplus of photos is more preferable than their insufficient number.
- The number of "blind spots" should be minimized, since PhotoScan can reconstruct only those points of the scene that are visible in no less than two frames.
- Frame overlap can be expressed in the following figures: 60% lateral overlap, 80% longitudinal overlap.
- The subject must occupy the largest part of the frame.
- The use of good lighting will increase the quality of the result. However, it is necessary to avoid glare. Sources of lighting are recommended to have outside the frame. Try not to use flash.
Field work is completed with the end of the photo scanning of the object. Next, you need to process the results of measurements of the total station survey and GPS measurements. Two catalogs of coordinates are obtained as a result, one for control points, the second for photographing points.
Next, you need to create them in the .txt format for further upload to PhotoScan. An example of a file containing the reference coordinates is given below.
Рicture 2.1 — An example of a corundum directory
The entries in the coordinate file are associated with the corresponding photographs or markers based on the value of the label field. Labels of camera positions should coincide with the file name of the corresponding image, including the extension.
Then you can proceed to the construction of a three-dimensional model of the object.
4.2 Building a three-dimensional model of the object in Agisoft PhotoScan
First of all, it is necessary to view all the pictures taken of the object, in order to remove bad frames, which can reduce the quality of the future model. Using RAW data converted to lossless TIFF format is preferable, since image compression to JPG format increases the amount of unwanted noise. Then all the selected photos are loaded into the program.
The next step is to add the generated camera coordinate list to the project, choosing the correct coordinate system. Then you need to specify the accuracy of determining the coordinates of the cameras. You can align the cameras after that.
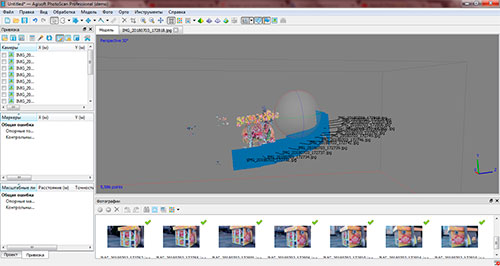
Рicture 3 — Example of camera alignment result
The program automatically performs all calculations of the elements of orientation of images. Building a dense point cloud is the next step. This processing stage takes some time. Processing speed depends on the number of shots and the power of the PC. It is necessary to remove all unnecessary noises
from the future model after building a dense cloud.
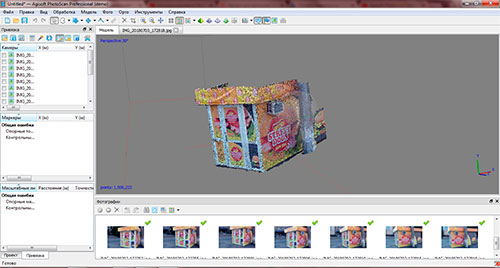
Next, the three-dimensional model is built on a dense cloud of points. Building a texture is the final stage. A three-dimensional model of the object is considered completed after that.
Рicture4 — Dense cloud of points
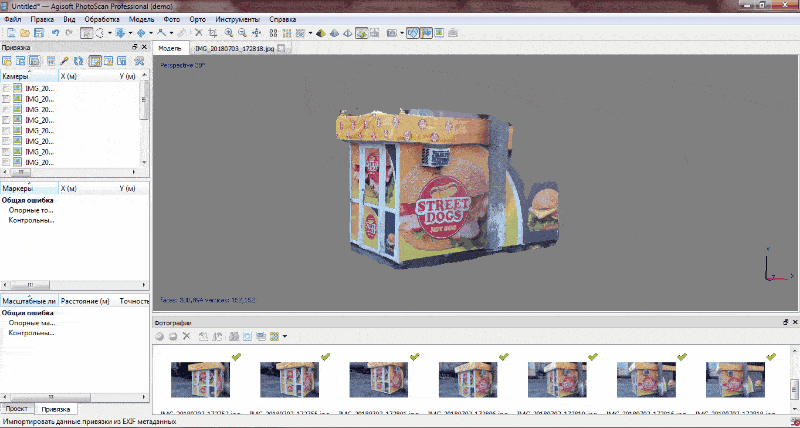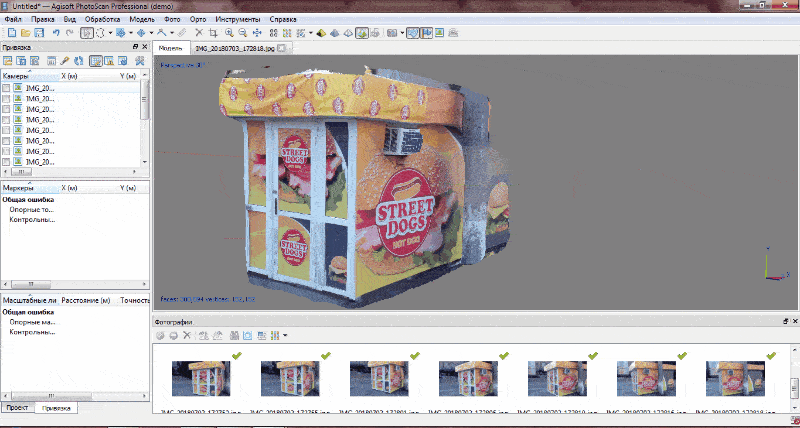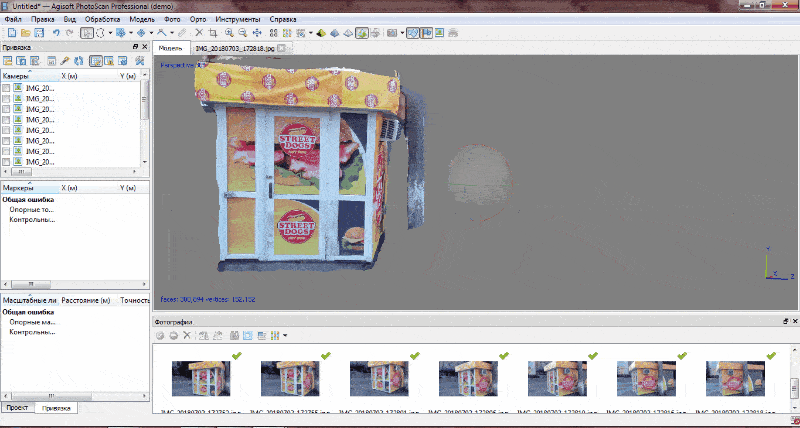
Рicture 5 — An example of a three-dimensional model of the monument
We build a 3D polyline along control point markers and export the coordinate list of the vertices of the polyline. Next, you need to compare how much the coordinates measured by the total station directly on the facade of the building, from the coordinates obtained by the three-dimensional model in plan and height. We can judge the accuracy of the three-dimensional model based on the difference of coordinates.
Agisoft PhotoScan allows you to build three-dimensional models without a reference, but in this case it is not possible to measure the geometry of the model. However, you need at least three points with known coordinates to build a scaled three-dimensional model. PhotoScan will automatically align all other cameras. That is, it is not necessary to know the exact coordinates of all the cameras for the construction of a three-dimensional model, but it is sufficient to measure only a certain part. This circumstance greatly accelerates the implementation of field work, since there is no need to determine the coordinates of the point of photographing each image.
There is the next task here. It is necessary to evaluate how the accuracy of the three-dimensional model depends on the number of images attached. Suppose there are 100 photographs of the facade of a building with the coordinates of the photographing points. The essence of the study is to build three-dimensional models of the object, uniformly reducing the number of associated cameras, without reducing the total number of images. Let the first model be built on 100 tied images, the second one on 50 images, the next one on 25 images, etc., and compare the resulting models to each other in terms of volume. As a result, we will be able to judge whether it is necessary to measure the coordinates of all the images, or it is enough to determine only a certain part to obtain a satisfactory accuracy of the model.
Сonclusion
Materials of articles devoted to aerial photography with the use of UAVs are studied in order to obtain three-dimensional terrain models. Agisoft PhotoScan was selected as a software product for image processing, based on the knowledge gained and the order of robots in it, which is summarized in this paper, was studied.
The goals and objectives of the study are determined as a result, the plan of field and cameral work is drawn up. It will be necessary to evaluate the accuracy of three-dimensional models of the object constructed from digital images in Agisoft PhotoScan after its execution. It will be necessary to draw conclusions about the feasibility of using PhotoScan for scientific and production purposes as a result.
The study has not yet been completed while writing this essay, field work is scheduled for the beginning of 2019. The end of work on the master's thesis is June, 2019. You can get the full text of the work and materials on the topic from the author or manager after the specified date.
Bibliography
- Инструкция по фотограмметрическим работам при создании цифровых топографических карт и планов. —М.: ЦНИИГАиК, 2002. —48 с.
- Митин М.Д., Никольский Д.Б. Современные тенденции развития отрасли беспилотных летательных аппаратов// Геоматика. —2013. —№4. С.27—31.
- Руководство пользователя Agisoft PhotoScan: Professional Edition, версия 1.2// Agisoft LLC - 2016, 113 с.
- Иноземцев. Д.П. Беспилотные летательные аппараты: теория и практика Часть 2. Модель обработки аэрофотоснимков в среде Agisoft Photoscan// Автоматизированные технологии изысканий и проектирования. — 2013. -№ 3(50). С.48-51.
- Гринько Е.В., Курков М.В., Солощенко Ф.В., Суздальцев Н.Р. Опыт ГК «Геоскан». Создание высокоточной трехмерной модели Тульской области. // Геопрофи. — 2018. -№ 2. С.10-14.
- Гормаш А.В., Оньков И.В. Оценка точности ЦМР по материалам аэрофотосъемки с БЛА «Геоскан 101». // Геопрофи. — 2015. -№ 5. С.49-51.
- Курков В.М., Перес Вальдез Мануэль де Хесус, Бляхарский Д.П. Создание трехмерных моделей объектов памятников исторического и культурного наследия с использованием беспилотных летательных аппаратов самолетного и мультироторного типов.// Известия высших учебных заведений. Геодезия и аэрофотосъемка. —2016. №2. С.94-98.
- Пошаговое руководство (Уровень:Начинающие): Построение орт офото плана и карты высот в программе Agisoft PhotoScan Pro 1.2 ( без Опорных точек)//[Электронный ресурс] — https://cloud.mail.ru/public/8BWD/dt2GGzfTL
- Обработка данных аэрофотосъемки с БПЛА. // [Электронный ресурс] — https://russiandrone.ru/publications/obrabotka-dannykh-aerofotosemki-s-bpla/
- Что такое опорные точки (Ground Control Points, GCP, ОП) и как их использовать.//[Электронный ресурс] - https://russiandrone.ru/publications/chto-takoe-opornye-tochki-ground-control-points-gcp-op-i-kak-ikh-ispolzovat/
