Аннотация
Pulipati M., Srinivas K. P. Comparison of Various Short Range Wireless Communication Technologies with NFC. In this research paper we review three promising short–range wireless communication such as Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Bluetooth, zigbee and Near–field Communication (NFC).NFC mobile services are an important emerging area for NFC technology, with great potential for growth. The NFC Forum’s strategy for accelerating the growth of this business area includes recognizing and describing what is needed to realize successful NFC mobile services, such as key technologies, typical use cases, and the structure of the overall ecosystem. The success NFC across a broad range of applications depends on its large–scale adoption by enterprises and consumers. This implies the need for simple, low–cost implementation of the technology in a wide variety of devices. This paper discusses NFC technology in detail along with its protocols, communication modes, comparison with other technologies and also its security aspects.
Introduction
Within the last few years, contactless card technology has been maturing and has been adopted by major sectors such as transport, payment, and retailing. In parallel, mobile phones with the additional offerings of Internet and multimedia services have successfully entered people’s lifestyles. Contactless card technology can now expand its domain of mobile phone. The Near Field Communication (NFC) mobile service, which leverages the current contactless infrastructures, has just started to emerge. In some countries, services benefiting from the convergence of contactless card technology and mobile phones have already been introduced commercially, and these converging services are ubiquitous and successful.
Several varieties of “Contactless technology” exist today. Of most interest to Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and to third [1]party Service Providers is Near Field Communication (NFC) technology. NFC is designed to operate over very short distances, typically less than 4 cm and is foreseen as a strong enabler to meet new customer needs and drive value added business models.
2. What is Near Field Communication (NFC)?
NFC is a standards–based technology used to provide short range wireless connectivity technology that carry secures two–way interactions between electronic devices. Communications are established in a simple way, not requiring set–up by users as in the case of many other wireless communications. As such NFC enables users to perform contactless transactions, access digital content and connect electronic devices by touching devices together.
NFC near field communication provides contactless communication up to distances of about 4 or 5 centimeters. In this way there communications are inherently more secure because devices normally only come into contact and hence communication when the user intends this.
As no physical connectors are used with NFC near field communication, the connection is more reliable and does not suffer problems of contact wear, corrosion and dirt experienced by systems using physical connectors. NFC utilizes inductive–coupling, at a frequency of 13.56 MHz – a licence free allocation in the HF portion of the radio spectrum.
NFC is a form of RFID, but it has a specific set of standards governing its operation, interface, etc. This means that NFC equipment, and elements from a variety of manufacturers can be used together. The NFC standards determine not only the contactless operating environment, but also the data formats and data transfer rates.
3. NFC Applications
NFC technology has evolved from a combination of contactless identification and interconnection technologies including RFID and it allows connectivity to be achieved very easily over distances of a few centimeters. Simply by bringing two electronic devices close together [2]they are able to communicate and this greatly simplifies the issues of identification and security, making it far easier to exchange information. In this way it is anticipated that Near Field Communications, NFC technology will allow the complex set–up procedures required for some longer range technologies to be avoided. Near field communication NFC lends itself ideally to a whole variety of applications. These include:
- Mobile phones, PDAs, etc
- Personal computers
- Check–out cash registers or "point–of–sale" equipment
- Turnstiles
- Vending machines
- Parking meters
- ATMs
- Applications around the office and house, e.g. garage doors, etc
- D. S. Shiu, G. J. Foschini, M. J. Gans, and J. M. Kahn, “Fading correlation and its effect on the capacity of multi element antenna systems,” IEEE Transactions on Communication. vol. 48, no. 3, pp. 502–513, March 2000.
- E. Telatar, “Capacity of multi–antenna Gaussian channels,” European Trans. Telecomm. Related Technol., vol. 10, pp. 585–595, 1999.
- Volker Kuhn, Wireless Communications over MIMO Channels, John Wiley and sons, 2006.
- Claude Oesteges, and Bruno Clerckx, MIMO Wireless Communications: Real–World Propagation to Space –Time Code Design, Academic Press, 2007.
- George Tsoulos, MIMO System Technology for Wireless Communications, CRC Press, 2006.
- F. Molisch, Wireless Communications. IEEE Press – Wiley, 2005.
- W. Lee, “Effects on Correlations between Two Mobile Base–Station Antennas,” IEEE Trans. Comm., vol. 21, pp. 1214–1224, 1973.
- J. Wallace and M. Jensen, “Statistical Characteristics of Measured MIMO Wireless Channel Data and Coparison to Conventional Models,” in Proc. IEEE Vehicular Technology Conference, VTC 2001
- NFC and its application to mobile payment: Overview and comparison. Timalsina, S. K, Bhusal, moh (IEEEexplorer).
- Study of several promising short range wireless communication technologies. Weifang Wang (IEEE explorer).
A further application that was proposed was that NFC connections could be used to configure the connection between two wireless devices. All that was required to configure them to operate together wirelessly would be to bring them together to effect the NFC "connection". This would initiate the set–up procedure; communication could take place over the NFC interface to configure the longer range wireless device such as Bluetooth, 802.11 or other relevant standard. Once set up, the two devices could operate over the longer range allowed by the second communication system.
NFC near field communication is ideally placed to provide a link with the contactless smart card technology that is already used for ticketing and payment applications. It is broadly compatible with the existing standards that have been set in place. Accordingly it is quite possible that NFC enabled devices could be used for these applications as well.
There are many other applications for near field communications, NFC. These could include general downloading data from digital cameras or mobile phones, as well as any other data communication required between two devices.
4. Wireless Short Range Communication Technology
The underling RFID technology is based on wireless peer–topeer communication between two devices defined as either a ‘reader’ or a ‘tag’. RFID can operate in a number of frequency bands and at a variety of transmit powers[3], but for NFC a very low transmit power is used at a frequency of 13.56 MHz. In order for communication to take place the two devices must be in very close proximity, typically within 5 cm.
The tag has no power supply so the reader initiates communication when the devices are close enough to achieve inductive coupling. Sufficient current is induced in the tag’s antenna to power a small chip so that information can be read or written to it. Reverse information flow is achieved through a technique called load modulation. When the devices are inductively coupled .It is possible for the reader to detect changes in the load presented by the tag. Thus changing the load acts as a form of modulation and data rates up to 424 Kbit/s can be achieved between NFC compliant devices.
5. Protocol
The protocol is based on a wireless interface. There are always two parties to the communication; hence the protocol is also known as peer–to–peer communication protocol. The protocol establishes wireless network connections between network appliances and consumer electronics devices.
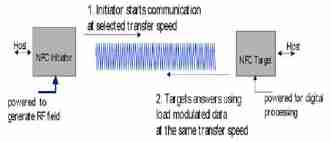
Figure 1.Passive mode of communication
As is often the case with the devices sharing a single RF band, the communication is half–duplex. The devices implement the “listen before talk” policy – any device must first listen on the carrier and start transmitting a signal only if no other device can be detected transmitting.
NFC protocol distinguishes between the Initiator and the Target of the communication. Any device may be either an Initiator or a Target. The Initiator is the device that initiates and controls the exchange of data[4]. The Target is the device that answers the request from the Initiator.
NFC protocol also distinguishes between two modes of operation: Active mode and Passive mode. All devices support both communication modes. The distinction is as follows:
In the Passive mode of communication only one device generates the RF field while the other device uses load modulation to transfer the data. The protocol specifies that the Initiator is the device responsible to generate the RF field[5]. The Initiator device provides a carrier field and the target device answers by modulating existing field. In this mode, the Target device may draw its operating power from the Initiator–provided electromagnetic field, thus making the Target device a transponder. In the Active mode of communication both Initiator and Target device communicate by alternately generating their own field. A device deactivates its RF field while it is waiting for data. In this mode, both devices typically need to have a power supply.
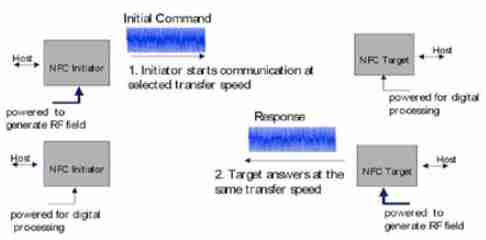
Figure 2. Active mode of communication
Subsequently the application and/or the communication environment may require speed adaptation, which can be done during communication.
The NFC forum defines three ommunication modes, as illustrated next:
Peer–to–Peer mode is defined for device to device link–level communication. Note that this mode is not supported by the Contactless Communication API.
Read/Write mode allows applications for the transmission of NFC Forum–defined messages. Note that this mode is not secure. This mode is supported the Contactless Communication API. NFC Card Emulation[6] mode allows the NFC–handset behave as a standard Smartcard. This mode is secure. This mode is supported by the Contactless Communication API.
Table 1. NFC Forum Issues Specifications
| Type 1 | Type 2 | Type 3 | Type 4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | ISO 14443A | ISO 14443 A | (JIS) X 6319–4 (FeliCa) | ISO14443A and B |
| Memory | 96 bytes and expandable to 2 Kbyte | 48 bytes and expandable to 2 Kbyte | Memory availability is variable(Up to 1MB) | Up to 32 Kbytes per service |
| Speed | 106 Kbit/s | 106 Kbit/s | 212 Kbit/s or 424 Kbit/s | Up to 424 Kbit/s. |
6. Collision Avoidance
Usually misunderstandings are rather rare, since the devices have to be placed in direct proximity. The protocol proceeds from the principle: listen before talk. If the initiator wants to communicate[7], first, it has to make sure that there is no external RF field, in order not to disturb any other NFC communication. It has to wait silently as long as another RF field is detected, before it can start the communication, after an accurately defined guard–time. If the case occurs that two or more targets answer at exactly the same time, a collision will be detected by the initiator.
7. NFC and other Wireless Technology
NFC is complementary with existing wireless standards. It can be used to initiate WLAN, Bluetooth and other wireless connections without going through configuration menus. These connections are established simply by holding the two NFC [8]products close together, or by configuring a device with contactless smart media.
Table 2
| NFC | Bluetooth | IrDA | ZigBee | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Network configuration | Peer to peer | Point to multipoin | Peer to peer | Point to multipoin |
| Range | 0,1 m | Up to 10 m | Up to 1 m | >10 m |
| Speed | Up to 424 kbit/s | Up to 721 kbit/s | Up to 115 kbit/s | Up to 250 Kbit/s. |
| Set up time | <0,1 s | ~ 6 s | ~ 0,5 s | > 1 s |
| Security | Yes (hardware) | Yes (protocol level) | No (except IFRM) | No |
| Communicatio models | Active to active, Active to passive | Active to active | Active to active | Active to active |
8. Set Up of Communication with Other Protocol
Imagine that you would like to transfer a large amount of information between two computers – a desktop and a laptop. Let’s say you want to transfer a presentation file. Using NFC may be slow and we decide to use something with more bandwidth. Let’s say for this example we use Bluetooth. Now, to set up Bluetooth communication between two computers we would need to set it up manually with a password to protect the communication.
8.1 Handover Protocol
This specification defines NDEF messages that enable a Handover Requester to negotiate an alternative communication carrier with a Handover Selector over the NFC link. As a special case, it also enables a Handover Requester to retrieve the possible alternative communication carrier(s) from an NFC Forum Tag[9], but this has some limitations due to the static nature of information stored on a Tag. The Handover Requester, in the scope of this specification, is defined to be the device that initiates the handover operation. The Handover Selector device is defined to be the device that is initially passive and that responds to the Handover Requester. The Handover Selector does not start any activity such as generating a handover message.
8.2 Negotiated Handoverl
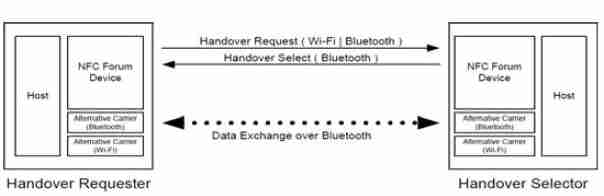
Figure 3. NFC Negotiated Handover
Negotiated Handover allows two devices to negotiate one or more alternative carriers for further data exchange. The exemplary use case shown in Figure 5 illustrates how a Handover Requester uses the embedded NFC Forum Device to exchange connection handover information with the Handover Selector to finally select a matching alternative carrier. In the example, the application running on the Handover Requester first announces its alternative carriers (Wi–Fi and Bluetooth wireless technology) to the Handover Selector, and then receives a carrier selection (Bluetooth wireless technology) as the only choice and finally performs Bluetooth pairing and data exchange.
8.3 Static Handover
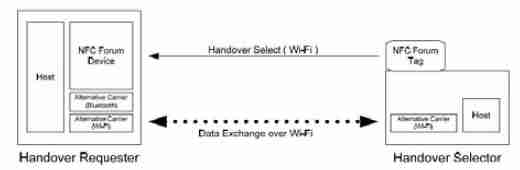
Figure 4. NFC static Handover
9. NFC Device
Developing NFC–based applications for Java handsets is based on the Mobile Information Device Profile together with Contactless API (JSR 257)for contactless I/O, and SATSA (JSR 177) for secure element capabilities. The elements of a Java–based handset that supports NFC. On the top of the illustration is the Java runtime and APIs for accessing SIM cards and Contactless communication channels, as well as the Java MIDlet application. Note that the application consists of two parts, the MIDlet and a Java Card application that may reside on a SIM card or a smartcard, and perhaps uses memory for the key store. Below we see the NFC controller, Baseband processor and RF Unit and there is the antenna. Externally to the handset are readers, tags and smart–cards with which the handset communicates with.
10. Contactless Communication API
The Contactless Communication API Java specification, led by Nokia and defined under the Java Community Process as JSR–257, defines a set of APIs for proximity, contactlessbased communication. The API consists of five Java packages. The Contactless Communication API allows you to Discover and Exchange data with contactless targets such as NDEF tags, RFID tags, and external smartcards. The API also provides support for visual tags.
11. Advantages of NFC
NFC–enhanced consumer devices can easily exchange and store your personal data messages, pictures, MP3 files, etc. Delivering ease of use, instant natural connectivity, zero configurations and smart key access, NFC meets all the needs of today’s connected consumer as well as creating opportunities for new mobile services.
12. Security Aspects
1) Eavesdropping–NFC offers no protection against eavesdropping. RF waves for the wireless data transfer with an antenna enables attackers to pick up the transmitted Monitoring data. In practice a malicious person would have to keep a longer distance in order not to get noticed. Eavesdropping is extremely affected by the communication mode. That’s because, based on the active or passive mode, the transferred data is coded and modulated differently. If data is transferred with stronger modulation it can be attacked easier. Thus, a passive device, which does not generate its own RF field, is much harder to attack, than an active device.
2) Data Destruction –An attacker who aspire data destruction intends a corruption of the communication. The effect is that a service is no longer available. Still, the attacker is not able to generate a valid message. Instead of eavesdropping this is not a passive attack. This attack is relatively easy to realize. One possibility to disturb the signal is the usage of a so called RFID Jammer. There is no way to prevent such an attack, but it is possible to detect it. NFC devices are able to receive and transmit data at the same time. That means, they can check the radio frequency field and will notice the collision.
3) Data Modification –Unauthorized changing of data, which results in valid messages, is much more complicated and demands a thorough understanding. In order to modify the transmitted data an intruder has to concern single bits of the RF signal. The feasibility of this attack, that means if it is possible to change a bit of value 0 to 1 or the other way around, is subject to the strength of the amplitude modulation. However, Near Field Communication technology uses modulation of 100% in conjunction with the modified Miller coding which leads to 4 possible cases[10]. The only case, where a bit might be changed by an attacker is where a 1 is followed by another 1. By filling the pause in two half bit of the RF signal the decoder receives the signal of the third case. Due to the agreement of the preceding bit the decoder would verify a valid one. The other three cases are not susceptible to such an attack.
4) Data Insertion –This attack can only be implemented by an attacker, if there is enough time to send an inserted message before the real device starts to send his answers. If a collision occurs the data exchange would be stopped at once. In order to prevent such attacks the device should try to answer with no delay. Alternatively, again checking the RF field and also the secure channel can be used to protect against attacks.
5) Man–in–the–Middle–Attack– In order to show that NFC is secure against a Man–in–the–Middle–Attack we have to survey both, the active and the passive communication mode.
13. Conclusion
NFC has the potential to be a disruptive technology, changing the way that lives are lived, transforming everyday tasks, making things easier, more intuitive and more effective. NFC wireless communications can be applied in many different ways, some of which are outlined in this paper. However, perhaps most exciting of all is the creation of an environment with all the key components for NFC to become a mass adoption technology. From here, any number of applications can be created to sit within the environment.