Abstract
V.I. Sidorchuk, Ye.N. Kushnirenko, D.S. Sipakov. The method of message concealment based on jargon. . In this article the definition of stenography was described. The topic of data protection from unauthorized access was raised. A comparative analysis of message concealment methods was performed. Based on one of the methods, the author’s method of message concealment was developed.
Introduction
Steganography is often defined as the science and art of information concealment in a so-called container, the transferring of which from one person to another does not arouse suspicion. Unlike cryptography, whose aim is to protect the message itself, the main purpose of stenography is to protect the very fact that contains a hidden message.
Modern stenographic tools mainly work in information environments that have greater redundancy. If you take into account the information which contains large amounts of noise data (such as sounds or images), the written text contains a small amount of redundant information that can be used to hide certain data.
The methods of linguistic stenography are hidden implantation of coded arbitrary information into the texts, relying on linguistic resources. These methods have been known since medieval times. With the development of computer and information technologies, the medieval methods of linguistic stenography were revived at a new level and make it possible, in some cases, to hide the fact of secret correspondence not only from the “athematic censor”, which monitors telecommunications networks, but also from the human himself.
Formulation of the problem
The problem of data protection from unauthorized access appeared in ancient times, and since then, the direction of solving this problem was marked and still exists today known as steganography. The main task of steganography is to ensure that a person does not suspect that the transmitted data, externally of absolutely no value, contains secret information. Thus, steganography allows you to transmit important data through open channels, hiding the very fact of its transmission. The purpose of the article is to conduct a comparative analysis of methods in linguistic steganography for the development of the author's method of message concealment.
Comparative analysis of the methods
The first method is the jargon method. The use of jargon in the text may confuse unauthorized reader. While implementing this method, a database with inserted words and corresponding jargons which will replace the words is created.
This method is simple to implement, and while using it, there is no suspicion about the presence of hidden information in case of saving the text in a readable form. However, this method has drawbacks: the words database is limited to the list of words used by the participants in correspondence; the recipient must also know the used jargons; in case of unsuccessful use of jargon, the intruder can understand the hidden meaning of the message.
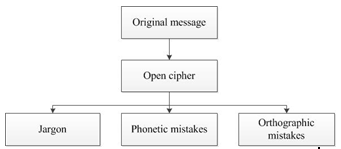
Figure1 – The flowchart of jargon method
The second method is semagramm. The semagramm is a way to hide information through signs or symbols. For example, placing objects on the table in a certain sequence, a certain sequence of numbers, etc. for an outsider won’t be seen.
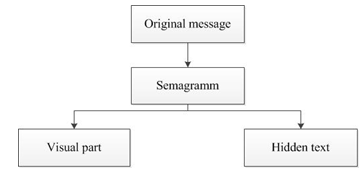
Figure 2 – The flowchart of semagram method
Also, there are text semogramms. Text semogramms are messages hidden inside the text. To send any message, you can use capital letters, spaces between letters or words, features of underscore, etc.
Among the advantages of this method it is worth noting that its implementation is simple and invisible to unauthorized reader.
The disadvantage of this method is the fact that because of its simple implementation, an intruder can quite easily get the hidden information.
The third method is hidden coding. Hidden coding is considered a special case of linguistic steganography. It is also more difficult to implement, but it provides high data secrecy. This method uses a special function that encrypts and decrypts the message for transmission. The method uses a “container” in which the hidden message is placed (see Figure 3). After receiving the hidden message, it is retrieved from the “container” by special algorithm.
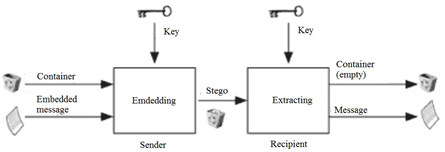
Figure3 – Classic flowchart of hidden coding method
This method has strong decryption resistance, but high implementation complexity.
The fourth method is open coding. It means the following: the hidden message is placed into the text so that it does not catch the eye of the outsider. When it is necessary to analyze, computers and people demonstrate different methods of recognition and perceiving stenographic messages. This method is simple to implement, but easy to give away hidden data.
The last method is phonetics. This method can be used if you know exactly which language the filter is programmed. This filter searches for words in that language which is mainly used by people in the country. Of course, it is impossible to say with certainty how exactly the filter is programmed. But to get closer to understanding, you can use phonetically similar words. This method is most suitable if you use an alphabet different from the one adopted in your country (for example, Latin instead of Cyrillic).
This method is simple to implement, but the information is not actually hidden and an intruder can easily get hidden information.
Thus, having examined each method, a comparison table which takes into account the following criteria for analyzing the methods: implementation complexity, decryption complexity, difficulty in determining the presence of a hidden message was compiled. Each method is scored from 1 to 3.
Table 1 –The comparison of stenography methods
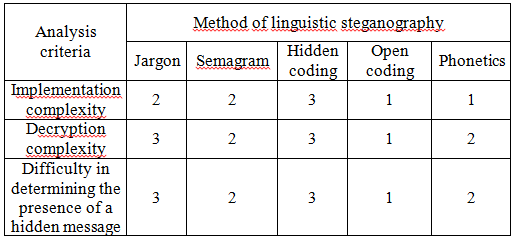
During the research, various methods of linguistic steganography were analyzed, and a comparative table was constructed with the above methods. They were compared in terms of implementation complexity, decryption complexity, and difficulty in determining the presence of a message. After analyzing Table 1 it has been turned out that the method of hidden coding and the method of semagrams are the most effective in the implementation.
Development of author's method
Having examined each method above, it was decided to take the jargon method (aka the method of synonymous substitutions) as the basis for the author's algorithm. Unlike other studied methods, this method can work without words source, that is, only stego-text is required for work
Also, during development, it has been used the codes replacing mechanism in accordance with message bits sequence. In this case, letters according to their ASCII codes will be encoded instead of spaces. Some letters of the Russian and English alphabet have the same form of writing, but different codes (see. Figure 4). Thus, it is possible to use this feature to encode any sequence of bits.
Figure4 – The example of ASCII-codes table
In order to confuse a stegoanalytic, you need to add noise to the stego-text. In digital steganography, geometric transformations were used as image noise or audio files, but with text format other actions are needed. Thus, it is possible to choose an array of letters that will carry the encoded message, and the other letters will be changed randomly.
To increase security, you should use a key. A key will be a word or phrase, the length of which will be equal to the length of the message to be hidden. During the inclusion, the stego-text will have an indent by the key length, and from that place the message will be concealed.
Since noise is used, even the missing words will be changed, but they will not carry any information about the message. According to the key the recipient will know where to start extracting and how many words are in the message.
Thus, methods for hiding a message in a text file contain the following steps:
- checking the correspondence of message and key length;
- encrypting a message with a key;
- translation of an encrypted message into a sequence of bits (each letter occupies 8 bits, that is, 1 byte);
- translation of stego-text into an array of bytes;
- indent for key length;
- encryption of the encrypted message;
- translation of the received bytes of stego-text back to the string.
- large sources or data storages are not used;
- fast execution of data implementation and extraction;
- low probability of transmitted message detecting;
- the algorithm can be used for text of any style;
- the inability to retrieve the message in case of detection.
Thus, the recipient of the message will not be able to extract the message from the stego-text without a specific key. During stegoanalys of the text in which the message is hidden, it is impossible to determine accurately the place where the hidden information is stored and which letters are significant, if there are sentences in Russian and English languages, the task for the intruder becomes more complicated.
Conclusion
The article presents the results of the analysis of 5-6 methods of linguistic steganography, as well as their comparative table. The table allows one to compare methods in accordance with the implementation complexity, the decryption complexity and the difficulty in a message detecting. As a result of the analysis, the jargon method was chosen to develop the author's algorithm for hiding a message in a text file that provides transmission protection data. The author's method has several advantages:
References
1. Большаков .А., А.Ф. Гельбух. Раздельное представление словосочетаний для существительных единствен-ного и множественного числа. // Труды Международного Семинара по вычислительной лингвистике и ее приложениям. Диалог’96. Пущино, 1996.– с. 42–44.
2. FrontLine International foundation for the protection of human rights defenders [Электронный ресурс] / L.Trappeniers [et al.] // Computer. – Электрон. дан. - 2013. - Vol.46, No 2. – P. 24-25. – Режим доступа: https://equalit.ie/esecman/russian/chapter2_7.html
3. Мельчук, . А. Опыт теории лингвистических моделей «Смысл U Текст». Семантика, синтаксис. М.: Наука. – 1974. – 314 с.
4. Стеганография [Электронный ресурс] //Академик, 2018: [сайт] – URL: https://dic.academic.ru/... – агл. с экрана.
5. Электронная библиотека студента [Электронный ресурс.] // Библиофонд, 2018: [сайт] – URL: https://www.bibliofond.ru/...