AbstractContent
IntroductionAs a result of the activity any enterprise carries out any economic operations, makes these or those decisions. Almost every such action is reflected in accounting. In a competitive environment, the survival of an enterprise depends on its financial stability, which is achieved by improving production efficiency through the economical use of all types of resources, reducing costs, identifying existing reserves to increase production and increase profits. The costs of production and production of finished products are reflected in the cost of production, as it shows what it costs the company to produce and sell products. The more economically the organization uses material, labor and financial resources in the manufacture of products, works and services, the more efficient the production process, the greater the profit. 1. Theme urgencyThe relevance of the topic presented in the work is that the cost reduction is the most important factor in the development and increase of profitability of the economic entity, the basis for the measurement of income and expenses. To make the right decisions for maximum profitability and sustainability of the enterprise market need complete and reliable information on the costs of the enterprise, reflected in accounting and reporting. Therefore, it is the accounting of production costs that is one of the most important objects of the management process at the enterprise. Accounting provides the administration of the organization with the information necessary to monitor production activities and make the right decisions on the results of these activities. 2. Goal and tasks of the researchThe aim of this work is to study the theoretical, methodological and practical issues of organization of accounting and audit costs, identify gaps and contradictions in accounting costs, as well as the development of specific recommendations for their improvement. To achieve this goal in the work it is necessary to solve the following tasks:
Object of research: financial and economic activity of enterprises. Subject of research: theoretical and methodological aspects of production costs. 3. Overview of research and developmentIn modern domestic and foreign literature, many authors have investigated issues related to reducing the cost of production. However, economists have not yet formed a consensus on the best ways to reduce the cost of production. The technology of cost planning was considered by V. V. Parkhomenko and A. G. Brodin. The study of the issue of accounting and cost analysis of industrial enterprises attracted the attention of many both foreign and domestic researchers, such as John black, Daren McCabe [1], Michael Meskon, Franklin Khedouri [5], John Shank, Vijay Govindarajan [8], T. B. Algina, O. I. amosh, I. V. Bugay [2], S. F. Golov, V. O. Metz, V. Mnykh, G. O. Partin [6] and others. Their research is focused on improving the methods of rationing, accounting and calculation of production costs, organization of their analysis and budgeting and search for reserves to reduce costs in industrial enterprises. The practical application of the developed accounting methods, calculation, rationing and budgeting of costs and differential analysis of accounting information in the process of management decision-making allowed to more accurately determine and evaluate the costs and financial results during the implementation of individual economic operations and processes in the enterprise-the formation of stocks, production in the main and auxiliary production, enterprise management, marketing research of the sales market and the like. Despite the relevance of the topic, the level of its research and study, deep structural changes in the economic mechanism of the state require continuous improvement of the methodology and methodology of accounting for the harmonization of the financial situation of the enterprise. 4. Methodological basis of accounting for lease operationsCurrently, the Donetsk people's Republic does not have its own Republican accounting regulations and legislative acts, so accounting is conducted on the basis of Ukrainian accounting Regulations (standards). Expense accounting is regulated by P (C)BU 16 "Expenses". There is no special standard on expenses, similar to P(C)BU 16 "Expenses", among IFRS. However, there is no special standard that would regulate the accounting and the order of reflection of expenses-they are spelled out separately. For example, the valuation of material costs is governed by international standard IAS 2 5. The essence and content of production costs as an object of accountingDetermination of the financial result of the enterprise is a comparison of income received by the enterprise, and the costs that have been incurred by them in connection with the receipt of such income. Therefore, the amount of expenses is one of the main qualitative indicators of the enterprise, which determines the effectiveness of its functioning and financial position. According to P(C) BU 16. expenditure refers to a decrease in economic benefits in the form of Disposals of assets or increases in liabilities that cause a decrease in equity (except for a decrease in equity due to withdrawal or distribution by owners), provided that these costs can be reliably estimated. This means that expenses are recognised simultaneously with a decrease in assets or an increase in liabilities. All cash costs of the enterprise are grouped according to three criteria:
Expenses related to profit extraction include the cost of commodity products, works, services, material resources consumed in the production process (material costs); labor costs; expenses related to the management of the production process; the cost of non-current assets (fixed assets, intangible assets) used in the production process. Cost element-a set of economically homogeneous costs. Grouping costs by elements is used in any organization, regardless of the type of activity and their legal structure. The purpose of this gradation is to combine the composition of expenses that will form the cost price. Observing the sign of homogeneity, the costs are divided into the following elements:
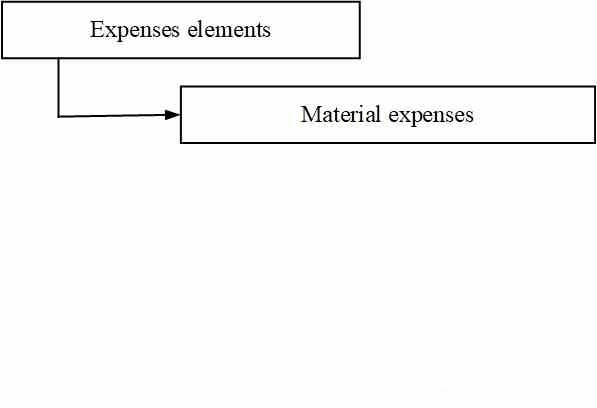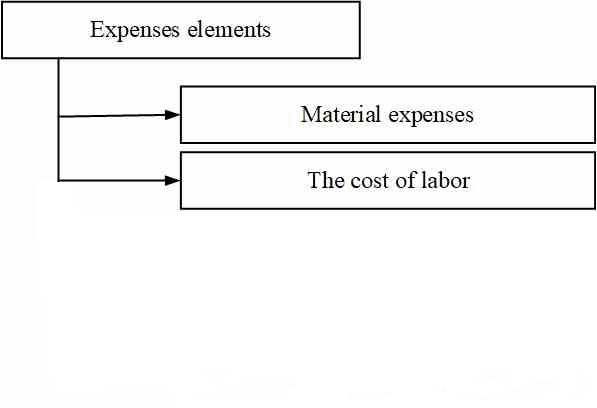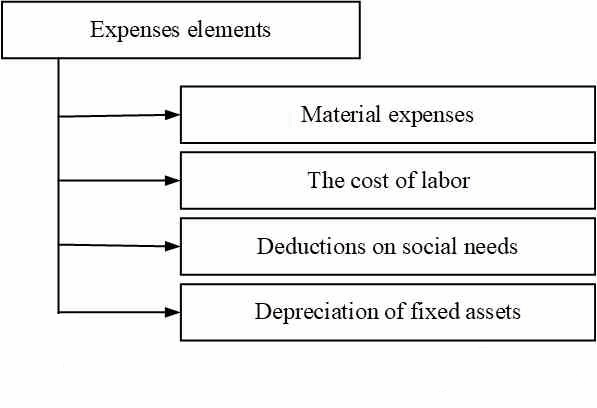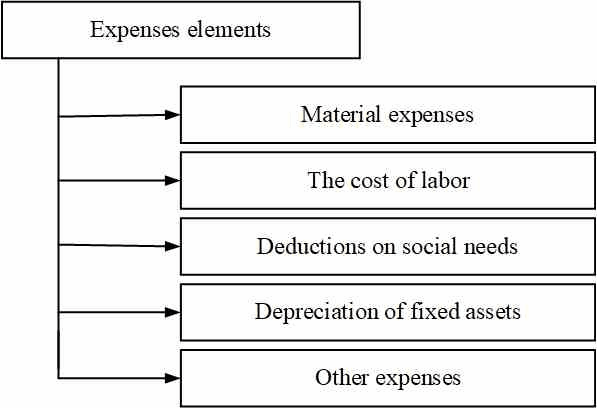
Figure 1 – Cost elements Grouping costs by elements is necessary in order to study the material intensity, energy intensity, labor intensity, capital intensity of products and to establish the impact of technological progress on the cost structure. If the share of wages decreases, and the share of depreciation increases, it indicates an increase in the technical level of the enterprise, the growth of labor productivity. The share of wages also decreases when the share of purchased components and semi-finished products increases, which indicates an increase in the level of cooperation and specialization [3]. Grouping of costs by purpose, i.e. by calculation items, indicates where, for what purposes and in what amounts resources are spent. This grouping is necessary to calculate the cost of certain types of products in diversified production, the establishment of centers of concentration of costs and search for reserves to reduce them. The classification of costs by calculation items is shown in figure 2. 
Figure 2 – Classification of costs by calculation items Under the cost of production, works and services are understood expressed in cash costs of all types of resources: fixed assets, raw materials, materials, fuel and energy, labor used directly in the process of manufacturing products and work, as well as to preserve and improve the conditions of production and its improvement. The cost of production, works performed or services rendered consists of the costs of material, labor and financial resources necessary for the production and sale of the manufactured product. For the correct reflection of production costs in accounting and calculating the cost of each type of product in all cases, it is necessary to know exactly what is spent and where the costs are directed. For this reason costs are classified according to the following parameters:
|
