Summary on the theme of master's work
Content
- Introduction
- 1. Relevance of the topic
- 2. Research goals and objectives and planned results
- 3. ANALYSIS OF HIGH-grinding method COMBINED SAMPLE.
- 3.1 Overview of product design, consisting of materials with different physical and mechanical properties.
- 3.2 Modern methods of grinding (sharpening) the combined samples. Used tool.
- 3.3 Analysis of modern designs of devices for surface grinding on a resilient scheme.
- 3.4 Analysis of ways to find treatment regimes.
- Conclusion
- List of references
Introduction
Modern production characterized by the use of materials with high hardness and wear resistance. Consequently, their machining causes certain difficulties. For finishing such materials typically used grinding wheels made of superhard material (CTM), which include diamond and cubic boron nitride. At the same wheels are used in metal bond that requires the use of EDM and wire EDM changes impact on the working surface of the circle (PKK).
The department "Mechatronic systems engineering equipment" Donetsk National Technical University proposed a new method for finding the optimal treatment regimens using such an index, as the instantaneous current limited range of cutting capacity, the mathematical description of which can be found with the help of an elastic circuit grinding. The method is widely used in the search mode surface grinding vanadium tool steel, carbide, sharpening tools requires significantly less time compared to the classical method of finding the optimal mode of grinding, but requires upgrading the machine in order to implement flexible sanding pattern.
1. Relevance of the topic
Using the parameters for the formation of the PKK electrical erosion, electro-physical-chemical action and mechanical action on a bunch of loose abrasive initiated the development of ways to improve the operational capacity of the cutting grinding wheels.
During grinding samples composed of materials with different physical - mechanical properties optimization of processing performed by analytically - the experimental method or experimentally. The disadvantage of these methods is the high complexity of the search, as well as the limited scope of the recommendations that found experimentally. These disadvantages can get rid if the search mode to perform processing using the current limited range of cutting capacity (PLRZK) which describes the amount of grinding of the material per unit of time grinding on a resilient scheme with the constant pressure of the sample to the PKK.
2. Research goals and objectives and planned results
The aim of the study is to determine the optimal cutting conditions for surface grinding composite samples. Search modes of processing performed using the current limited capacity of the cutting wheel (PLRZK).
To search for patterns of change PLRZK need to solve the following problems:
- Develop design of the planar grinding on a resilient scheme.
- Find the value of technological limitations that are imposed on the regime of cutting machine, grinding wheel and the workpiece.
- Investigate the effect of processing time to change PLRZK grinding on a resilient scheme.
- Develop recommendations on treatment regimens, providing full use of cutting power circle.
The object of study: skive.
Subject of study: treatment regimens using PLRZK, technological values ??ogranicheniy. Rezhimy PLRZK processing using the values ??of process constraints.
3. ANALYSIS OF HIGH-grinding method COMBINED SAMPLE.
3.1 Overview of product design, consisting of materials with different physical and mechanical properties.
Any product which consist of materials with different physical and mechanical properties are: turning tools, milling cutters, core drills, reamers. To perform these diamond grinding tools in their structure a number of changes introduced geometry and structural elements which are shown in these figures. To avoid the possibility of grinding diamond wheels steel holder with carbide insert cutters protruding from the holder [1] . On the front surface made of hard alloy plate overestimation of the tool holder (Figure 1.1a and 1.1b). The size of overstatement is a = 0,10 - 0,15 mm. Was also created space for the socket and hard alloy plate (Fig. 1.1B). Also changed the angle of the insert pocket carbide (see Fig. 1.1g). On the main and auxiliary rear surface made ??overstatement (overhang) of the rear surfaces of the plate carbide tool holder on the value of a. Held undermining rear surfaces of the holder at a depth t = 2 - 5 mm (see ris1.1 b). Working part of the tool is constructed in such a way that the tool holder and sharpened carbide inserts in three different sizes rear corners. The secondary rear surface provide two different sizes angle. When designing cutting edges depending on the specific conditions of various combinations of these changes constructive elements and cutter geometry [1] .
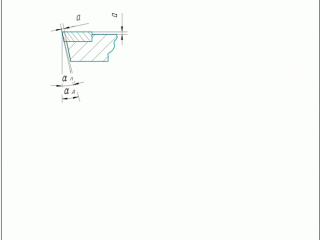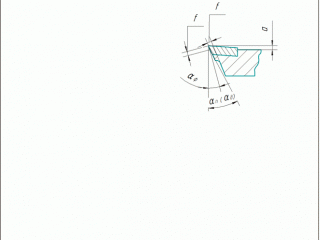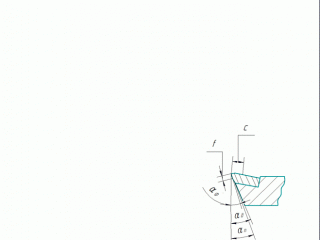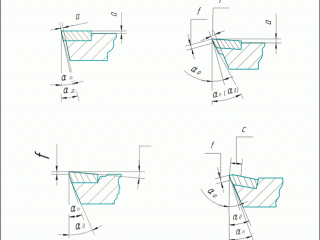
Figure 1 – Design elements and geometric parameters of carbide cutting tools, diamond wheels machined.
Besides cutting tool materials with different physical - mechanical properties are made knives for cutting paper. The working parts are used alloyed steel, hard alloys. As the material of the structural part using hardware [2] . As can be seen from the above examples of the use of diamond grinding, which requires changes in the design parameters, which can be removed when the diamond grinding wheels with electro-physical and chemical effects on the working surface of the circle.
3.2 Modern methods of grinding (sharpening) the combined samples. Used tool.
Using a diamond cutter grinding properties range depends largely on the type of communication in which a layer made ??of diamond. Thus, according to T.N.Loladze and T.V.Bokuchavy, grinding diamond wheels on bakelite base AC 40-B1-100 samples of molybdenum MB1 is only 9% of the cutting properties of diamond, heat-resistant alloy HN7OVMTYU - 6% titanium alloy VT-1 - 3%, steel 40 - 2%, cast iron MF 18-28 - 0.07% [3] . For efficient use of the properties of diamond cutting tool must be securely fixed in a matrix of diamond layer. Lasting property retention of diamond grains in the matrix layer are metallic bonds [9] are compositions based on copper, tin, iron, aluminum, nickel and other metals. However, increasing the strength of fastening using metal grains ligaments resulting in a loss of self-sharpening property circles, whereby the cutting ability RPK with increasing treatment time is constantly reduced. Reducing the cutting ability PKK cutting power increases, increases in the grinding zone temperature, the value of which may exceed the threshold phase-structural changes in the surface layer part. Improve the cutting ability of the PKK can be the introduction of the metal ligaments solid non-metallic fillers: abrasive powders, anti-friction additives, solid lubricants. The solid lubricants such as graphite or molybdenum disulfide besides the above mentioned effects provide a reduction of friction on the surface of communication [5] . Less susceptible to clogging and reduces the temperature in the cutting zone during grinding hard metal circles on the links MO13, MO4, MB1, TM2, which tend to be self-sharpening. However, the listed techniques do not eliminate the problem of reduced performance wheels for grinding a wide range of various materials. Using the parameters for the formation of the PKK electrical erosion, electro-physical-chemical action and mechanical action on a bunch of loose abrasive laid the foundation for the development of operational ways to improve the cutting ability of grinding wheels. Since the implementation of the PKK actions simultaneously with the processing of the intensity of the products of these actions is consistent with the objectives of stabilizing the output indices of processing and storage of certain parameters constant PKK, the PKK such action may be made to the control, and the process of maintaining the cutting ability of the circle - the ability to control the cutting wheel in the process treatment [6] . The emergence of the ability to control the cutting circles in metal bond linked to the development of satisfied Kharkov State Polytechnic University, a team of scientists led by MK Bezzubenko and AI Grabchenko diamond-spark grinding (AlSh) ??and the method of sharpening cutting tools of synthetic superhard materials. AlSh essence lies in the combination process of cutting diamond grains of the workpiece while the electrical effect on the tool and the workpiece due to the introduction to the cutting zone impulsive technological current among ordinary grinding of cutting fluids (coolant). When processing polycrystalline superhard netokoprovodnyh during their grinding is continuous electro-physico-chemical effect on the bond terms in the autonomous region with the aim of electrolytic dissolution and destruction of the EDM, which provides a constant amount of protrusion of grains of the bunch. The process of action on the work surface in terms of the autonomous zone was extended to the treatment of conductive products, and then, a method of grinding with the filing process energy at the same time in the treatment zone and in the autonomous zone.
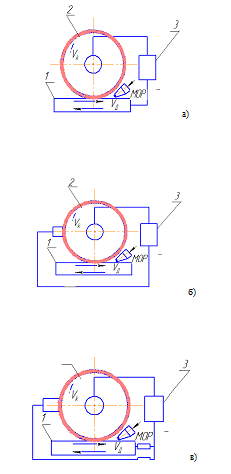
Figure 2 – Methods of grinding wheel cutting capacity controlled by electro-action.
3.3 Analysis of modern designs of devices for surface grinding on a resilient scheme
The device for surface grinding on a resilient scheme is located on the magnetic plate machine 3G71 [7] .Work piece 2 mounted in clamp 3, 4 placed on a slide which is movable in the housing 5 by the guide roller 6. To exclude the possibility of moving parts magnetizing device on the bottom set? Copper gasket 7. The slider is supported by a bearing 8 which is fixed on a small lever arm 9 at high lever arm loads 10 mounted to the movable part of the balancing device and the loads 11, providing the necessary clamping force to the working surface of the sample disk. In order to take a sample from the surface of the grinding wheel at its exit from the cutting zone are 12 copiers, which starts at the moment contact bearing 13. This is ensured by the fact that the housing unit is secured with a magnetic plate machine, and copier with a bracket legs 15 and 14 bar 16 on the compound slide 17. In longitudinal movement of the table bearing 13 is incident on the inclined surface of the cam and bearing down 8 that pushes the slider to the surface of the grinding wheel. As a result, the treated sample from the PKK is lowered. Position cams can be adjusted in a horizontal plane by moving them along the bar 14 and a vertical lifting or lowering the bar 14 by nuts 18 [10] . Due Grind the sample thickness adjustment position relative to the surface 13 of cams changes that leads to a change of the grinding wheel infeed points per sample. To eliminate the influence of the relative position of masses 11 to the pressing force of the sample to the PKK, on a rack 15 is mounted bracket 19, and the lever 9 - line 20. During processing, the relative position of permanent ruler and arm supported by a mechanism of vertical feed of the grinding wheel. To improve the accuracy of measurement soshlifovanogo material on the clamp 3 is set pin 21, which serves as the basis for the measurement of the sample before and after grinding. The measurement of the sample is fixed in the down position slider. To protect the roller guides from entering the coolant housing unit closed film that is water repellent [8] .
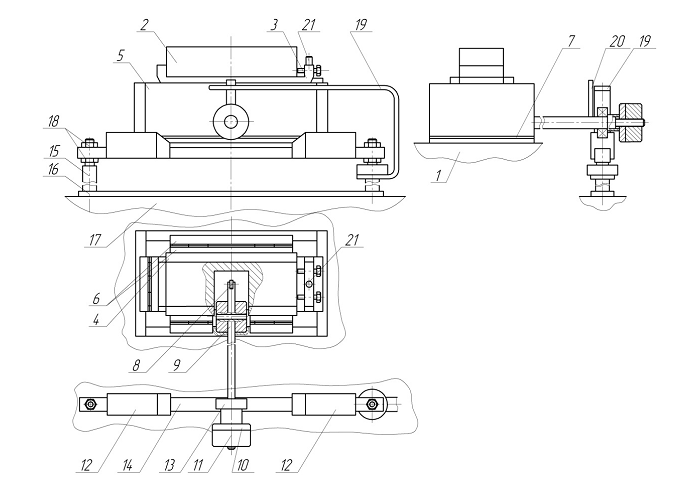
Figure 3 – The device for surface grinding on a resilient scheme.
3.4 Analysis of ways to find treatment regimes
The input data to determine the mode of cutting grinding are: a) information about the material, which is processed and dimensions of machined surface b) allowance for processing, c) the requirements for accuracy, surface finish, and other indicators of quality d) information on the machine; e) the rigidity of the machine-tool-part-circle, and e) the characteristic of the circle, undergoing treatment at the operation.
Cutting data for grinding can be determined by calculation or appointed on the basis of practical recommendations. Calculation of the mode of grinding is advantageously carried out for the conditions of mass production, where small deviations from the optimum processing conditions can lead to significant losses. The calculation modes may also be appropriate for the development of various standards and recommendations relating to the use of grinding tools [4] . The problem of determining optimal grinding is performed in three steps: 1) Establishing a system of equations describing the technical constraints imposed by the requirements of the cutting mode to the detail of machines, tools and production conditions; 2) a mathematical description of the objective function, ie a function that expresses the goal of optimization; 3) The joint consideration of technical constraints and the objective function and the definition on the basis of this optimal grinding.
Conclusion
Reducing the cutting ability of the working surface is mainly due to the absence of pores on the surface of the metal ligaments in connection with what eventually becomes impossible to intergranular chip accommodation space whose volume generated during editing is reduced in the grinding process resulting in deterioration grains as well as a tendency to grasp metal bond with the processed metals and alloys. Reduced cutting ability PKK? Increases cutting power and enhances the temperature in the grinding zone, the value of which may exceed the threshold of structural phase transitions in the surface layer of details. Improve the cutting ability of the PKK can be the introduction of the metal ligaments solid non-metallic fillers: abrasive powders, anti-friction additives, solid lubricants. Using the parameters for the formation of the PKK electrical erosion, electro-physical-chemical action and mechanical action on a bunch of loose abrasive laid the foundation for the development of operational ways to improve the cutting ability of grinding wheels.
In writing this essay master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: December 2013. Full text of the and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.
List of references
- Справочник по алмазной обработке металлорежущего инструмента./ Бакуль В.Н., Захаренко И.П., Кункин Я.А., Мильштейн М.З. Под общей редакцией Бакуль В.Н. – Киев: Техніка, 1971. – 208с
- Типы бумагорезальных ножей. Рекомендации по заточке. Сохранность и уход. Описание классов ножей. [Электронный ресурс].: // Типы бумагорезальных ножей. – Режим доступа (http://www.drukar.org/article10529.html.). – Дата доступа: март 2013г. – Название с экрана.
- Матюха П.Г. Високопродуктивне шліфування ванадієвих штампових та інструментальних сталей / Матюха П.Г. – Донецьк: ДВНЗ «ДонНТУ», 2008. – 222с.
- Абразивная и алмазная обработка материалов. Справочник.; под ред. д-ра техн. наук проф. А. Н. Резникова. – М.: Машиностроение, 1977. – 391 с.
- Узунян М.Д. Алмазно – искровое шлифование твердых сплавов / Узунян М.Д. – Харьков: НТУ «ХПУ», 2003. – 359с.
- Справочник метал листа: в 5 т. / перераб. под ред. С.А. Чернавского и В.Ф. Рещикова. – М. : «Машиностроение», 1976 Т.1. Изд. 3-е – 1976. – 768 с.
- Матюха П.Г. Полтавець В.В. Алмазне шліфування з електроерозійними керуючими діями на робочу поверхню круга. – Донецьк: ДонНТУ, 2006 – 164 с.
- Металлорежущие станки: Учебник для машиностроительных втузов/ Под ред. В.Э. Пуша. – М.: Машиностроение, 1985. – 256 с.
- Матюха П.Г., Габитов В.В. Влияние вида шлифования на шероховатость обработанной поверхности. // Наукові праці Донецького національного технічного університету. Серія: Машинобудування і машинознавство. Випуск 8 (190). – Донецьк: ДВНЗ „ДонНТУ”, 2011. – 214 с.
- Универсальный плоскошлифовальный станок высокой точности с горизонтальным шпинделем и прямоугольным столом. Модель 3Г71. Руководство к станку.
