
Correspondence faculty
Speciality: The telecommunication systems and networks
Theme urgency. The Ukrainian market telecommunication promptly develops. But this development is interfered by two problems. On the one hand it is low solvency of the consumer, and with another - high cost of service of the operator. Service the more cheaply, than is more than users on it. And to increase number of subscribers it is possible only serious depreciation. The major role in this process is played by a choice of the environment of distribution of a signal for organisation "last mile". At construction of a network the choice of this or that technology of user's access plays a main role at an establishment of tariffs as expenses on the organisation "last mile" are proportional to number of users and to the greatest degree influence cost of services
The scientific importance of work. During work recommendations and algorithm which will concern a choice of optimum technology of user's access for different types of subscribers will be developed.
Practical value results of work consists in пременении algorithm for faster and effective choice of optimum technology of user's access at designing new or modernisations of existing networks of providers.
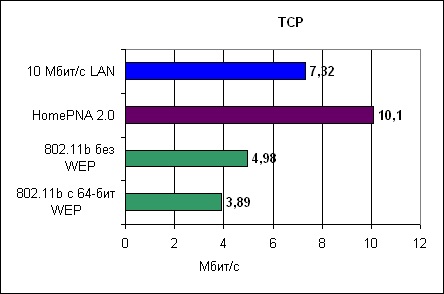
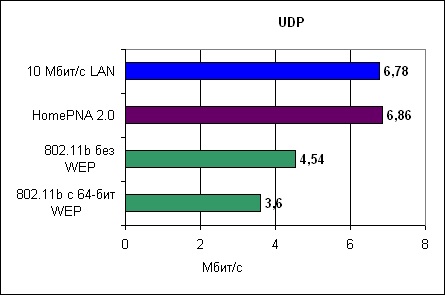
Tests were made by means of NetIQ Qcheck [7]. This program allows to receive statistics on connection a point-point, including throughput and delays at use of reports TCP and UDP. We will compare both theoretical, and real throughput. Theoretical throughput of various standards differs from each other, thus it is necessary to consider and transfer of the office data (in the figures cited in the beginning of article the office data are not considered). As well as in any network Ethernet, real throughput is somewhere in an interval of 50-80 % from the declared.It is obvious that wireless and PNA networks are steadier against hindrances and should work in less friendly conditions, than standard Ethernet on isolated and certificated twisted pair of a category 5. At a wireless communication there are problems of attenuation of a signal at a great distance, what not so is actual for wire networks. Testing was spent both for usual conditions, and for the ideal. We will pay attention to the received results for usual conditions as perfect conditions practically do not meet in a life. For the wireless test we used widely known card Lucent Orinoco on PCMCIA, together with an access point 2wire.Card Linksys was applied to testing HomePNA 2.0 in a combination with Linksys PCI the adapter PCMCIA. Results of testing are received at communication through network HomePNA 2.0, thus adapters have been located in different rooms. In total in apartment there were 4 phones and 640 kbit/with DSL connection which was active at the moment of performance of tests. It is important to notice that DSL and HomePNA do not disturb each other as they work on different frequencies, hence, on one telephone line can co-exist both DSL, and HomePNA. It is important to users DSL to know that the filters protecting a voice communication from DSL of hindrances, will block network traffic HomePNA.Therefore it is necessary to clean all filters from HomePNA networks and to establish them on target contact HomePNA of the device. As to Wi-Fi, tests were spent with carefully measured 20 дБ the relation a signal/noise at remote station, to conformity with program Lucent Link Diagnostic. Such relation is considered minimum, however it is still enough of it for data transmission with a speed 11 Mbit/with.


For research of behaviour of a network at the big loading the previous test repeated, each time adding one more computer. For measurement of scalability of a network transferred the data from several sources to different addressees in the same network. During testing each additional computer told the data to other interface in the same network that increased requirements to throughput approximately twice. Pay attention: on an axis of abscisses the quantity of knots which have been added to two initial is shown. It is important to notice that scalability depends on topology. HomePNA 2.0 is based on the tyre when all computers communicate with each other, like old coaxial Ethernet 10Base2. 802.11b – "star" in which centre there is the point of access processing all data, sent on a network is based on topology. The access point works as the bridge between a wireless segment and segments Ethernet.For this reason the network 802.11b works a little differently, than a network on the basis of topology the tyre. Under the schedule it is obvious that HomePNA 2.0 the quantity of knots in a network is scaled in direct ratio. With two knots speed reaches 10 Mbit/with, at addition of the third – speed falls to 5 Mbit/with. With addition of the fourth – falls to 3,3 Mbit/with. That is we observe quite normal scalability which allows to connect decent number of knots without considerable falling of productivity. The network 802.11b is more difficult for analyzing, because the bridge (an access point) obviously prefers the data arriving from segment Ethernet on беспроводный a segment. Speed of data transmission from one wireless computer to another considerably decreases at simultaneous work.
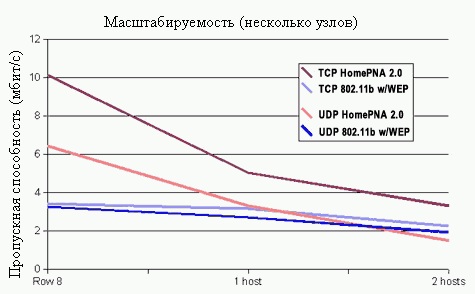
As we see, the result of testing of wire technologies is better than wireless as work of the last is influenced by many parametres, including distance from the transmitter, electronic hindrances and physical obstacles. Even movement on a room of the person can change force of a signal. By results of testing the obvious winner – HomePNA 2.0. It provides a great speed, stable scaling and small deterioration at distance increase so if you search for replacement Ethernet network HomePNA 2.0 – the best choice.
However the wireless communication has obvious advantages. First, she allows to get access to a network from any point inside and outside of the house, irrespective of presence of a telephone nest. Also probably freely to move on the house with the laptop, without caring of wires. With recent introduction of wireless adapters Compact Flash 802.11b even PDA it is possible to connect to such network.