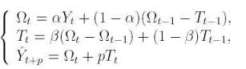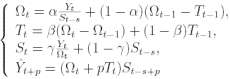|
|
|
|
Chuykov Anatoliy Dmitrievich
|
|
AbstractTheme: “The working out of the computer subsystem of analysis and forecasting of power resources consumption”
1. Introduction. Basing of the topic actuality Aggrasation of the competition in conditions of
permanent prices elevation for row-materials, transport and power resources
makes enterprises to hold the necessary level of profitableness. There are
several ways to low the working expencies. This work is dedicated to one of them
and exactly – to the lowering of power-resources expencies in production. It is
not a secret for everyone that this kind of production costs is the quarter of
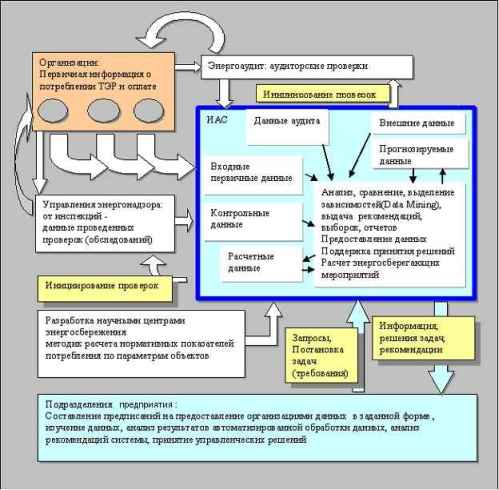
cost price of many goods and services. 2. Goals and tasks of work Information and analytical system (IAS) “Control
and analysis of heat and power resources” is determined to the automation of
control and analysis of resources consumption, financial indicators of payment,
calculations of company’s management in power – usage and making up of
limits
While studing the question of power resources
consumption it should be taken into consideration different parameters such as
seasons, prices and others). 4. Offered practical value The fulfillment of master’s degree work supposes the security of the following values: 1. Collection of the information about the
usage of all kinds of heat and power resources. Balance calculations of
consumption and payment of resources. 5. The review of existing forecasting methods Forecasting process consists of several steps
sequences of which is not always simple. But nevertheless one logic line may be
found there: Holt’s and Brown’s methods In the middle of last century Holt
offered an improved method of exponent smoothing out which was
named after its creator. In this algorithm the indexes of level
and trend are smoothed out by means of exponent smoothing out.
The smoothing parameters are different. The method of Winters Although method of Holt given
below is not very simple, it can not take into consideration
the season vibrations while forecasting. Speaking more exactly
this method can not “see” them in prehistory. There is an expansion
of Holt’s method to the 3-parameters exponent smoothing out.
This algorithm is called the method of Winters. An attempt is
made to take into account the season components of data. The
system of equation describing Winters method is the following: Box – Jenkins methods In the middle of goes of last century a new and
rather powerful class of algorithms for forecasting of temporal rows was
developed. AR(p)+MA(q)->ARMA(p,q)->ARMA(p,q)(P,Q)->ARIMA(p,q,r)(P,Q,R)->... 6. The list of non-solved problems The enterprise has the following tasks according to the power resources consumption policy: - to lessen human factor in the process of
placing of the information into database of analytical system; 7. Conclusion The variant of creating an individual system on
the basis of the ready neuropackage is suitable for small companies and private
persons – investors, traders and owners. Though there are some examples of large
groups which have chosen this variant and reached success. For example, company
DuPont made new material – safety glass, having used in such large western banks
as Citibank, Security Pacific National Bank, The World Bank, Lloyds Bank, The
Federal Reserve Board, Federal Reserve Bank of New York; in insurance companies
– Royal Insurance, Presidential Life Insurance, New York Life Insurance and
others. 8. The list of references 1. Глаголев А. И. , Демин С. С.
2. Гуртовцев А.И.
3. Коваленко М.В., Махотило К.В.
4. Вороновский Г.К., Клепиков В.Б.
5. Бирюков Е.В., Корнев М.С.
6. Вороновский Г. К.
7. Макоклюев Б.И. (ВНИИЭ), Еч В. Ф. (Университет “Дубна”)
8. Макоклюев Б.И., Антонов. А.В., Набиев Р.Ф. (ОАО ВНИИЭ)
9. Балыхин Г.А., Шленов Ю.В., Сергеев С.К
|
|