| |
|
|
|||||
 |
|
||||||
|
|||||||
 |
 |
KATERINA RUDCHENKO ABSTRACT OF MASTER DISSERTATION "The impact of anthropogenic factors on the formation of natural waters hydrochemical zoning" The actuality The actuality Among the important tasks of modern research in hydrology and hydrochemistry faces the challenge to amplify understanding of the impact of different types of human activity on the state of natural waters in order to develop their quality management techniques. Although hydrochemistry is a rapidly developing scince, at this stage there is a lack of methodological developments and background materials for environmental protection and water management organizations, units of hydrometeorological survey and other departments of our country, especially on the protection and rational use of water resources. That is the significance of this work for the Donetsk region - one of the most environmentally tense in Ukraine. A lot environmentally hazardous enterprises, a vastly urbanized territory and high population density along with extremely limited water resources and outdated infrastructure of environmental protection attached particular acuteness of the problem of water protection in the Donetsk region. The state of study of the problem In recent years a significant development in our country and abroad have received researches hydrochemical regime of water resources, since the chemical composition of natural waters should be taken into account in water supply (drinking, technical, agricultural) and in building, especially hydraulic structures, and the prospecting, exploration, mining, and production of various types of industrial products and many other cases. In the U.S. on the issue of human-induced changes in natural water works several major organizations and prominent scholars. For example, U.S. Geological Survey - Thomas C. Winter, Judson W. Harvey, O. Lehn Franke, William M. Alley; Environmental Protection Agency; Department of Geography - Lauren Gordon, Morgan Edwards, Kyle Chandler; Watershed Science Institute, University of Vermont - Jane C . Thapa; New York State Department of Health, Bureau of Water Supply Protection - Marc Deslauriers; Great Lakes Environmental Research Laboratory, University of Michigan - David Jude, and even NASA - National Aeronautics and Space Administration. In theWestern European countries scientific community is also very concerned about the state of natural waters. In my opinion, here is to mention the following scholars Matthias Eiswirth (Dept. of Applied Geosciences, University of Karlsruhe, Germany), G. Strauch, C. Schmidt, M. Bayer-Raich (UFZ-Centre for Environmental Research in Leipzig), T. Schiedek, M. Beier, G. Ebhardt ( "Applied Geosciences", Darmstadt, Germany), Vassilis Z. Antonopoulos, Dimitris M. Papamichail (Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, Greece), P. LA BARBERA, L. LANZA, F. SICCARDI (University of Geneva, Italy), G. Iaffaldano1, S. Martino (University "La Sapienza", Italy), U. MANDER (University of Tartu, Estonia). In Lomonosov Moscow State University there is a school of outstanding specialist in hydrogeochemistry - Professor K.E. Pit'eva, they relate to research technogenesis hydrogeochemical processes. In Tomsk Polytechnic University operates school of professors S.L. Shvartsev and N.M. Rasskazov. Publications of A.I. Gavrishin (South-Russian State Technical University, the city of Novocherkassk, Russian Federation), M.P. Andreeva (Tomsk oil and gas branch of the Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Tomsk, Russia) are also of significant scientific interest. Modern understanding of the geochemistry of Donbass natural waters is associated with the names of A.E. Babintsa, A.V. Shcherbakov, A.V. Suyarko, V.G. Suyarko, I.P. Solyakov, O.A. Shevchenko and other researchers. Despite the fact that hydrochemistry of Donbass is studied well enough, some of the issues, in particular - relating to human influence on the formation of natural waters, remain virtually unexplored. The goal and tasks of research The goal of the work consists primarily in the evaluation and delineation of natural and man-made effects on the formation of Kalmius River (center and south of Donetsk region) hydrochemical regime and assess the opportunities to predict changes in space-time coordinates, optimizing water situation, as well as in the development of methodological recommendations aimed at improve ecohydrochemical studies in the Donetsk region. In connection with this goal author have scheduled for the realization the following tasks:
The description of Data for the research The research is based on the results of long-term study of chemical composition of Donetsk region surface and groundwater, held since 2002. Used more than 510 chemical analysis of water samples. Scientific novelty In the regional aspect for the first time systematized and compiled data on of Donetsk region groundwater and surface water hydrochemical regime, taking into account the impact of man-made factor. Improved theoretical foundations for the natural waters hydrochemistry study and modeling their condition in the face of intense technogenesis. Regional hydrochemical zonality of natural waters is illustrated by Kalmius river basin area and Uglegorsk reservoir area:
Investigated the content of major ions and main pollutants within the set zones. In methodical aspect - an improved method proposed of comprehensive analysis of natural and man-made factors affecting the formation of hydrochemical regime of Donetsk region natural waters. The practical significance of the results The results obtained in present work can be applied in further ixplorations by engineering and research institutions:
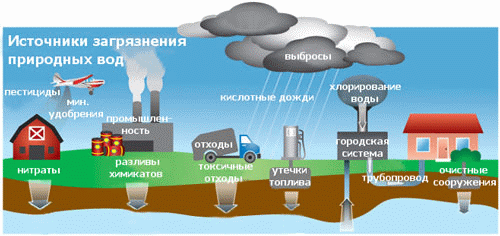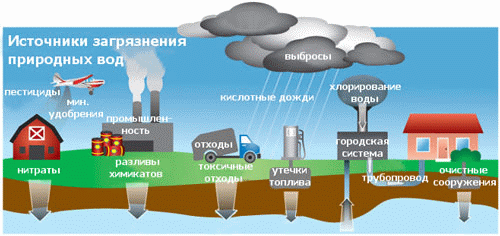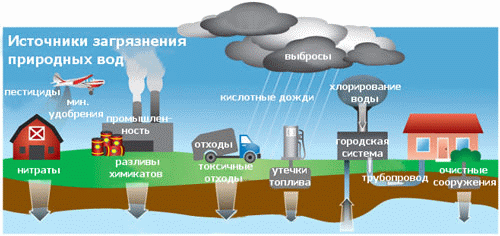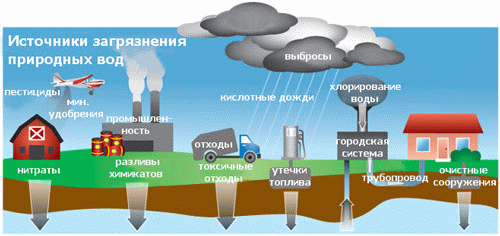
Publications of the research results Autor have published 2 articles, based on the results of research, in the collections of scholarly works, as well as abstracts at scientific conferences. Brief content The first section contains an overview of factors influencing the composition of surface and groundwater, both natural and man-made. Particular attention is paid to human influence systems, regional and local sources of pollution of the aquatic environment. The second section is devoted to the work of natural factors influencing the waters of the Donetsk region, namely:
In the third section the emissions of industrial enterprises, resident territory, development of mineral deposits, storage of wastes are examined as leading human factors shaping the chemical composition of natural waters in the Donetsk region.
Methodology of hydrochemical water zoning investigation is described in the fourth section: described network testing methodology and sampling methodology, methodology of chemical analysis, as well as methods of mathematical data processing. The consept about hydrochemical zonality of natural waters in Donetsk region, formed by natural factors together with man-made is upholded in the fifth section. First of all, the background chemical composition of surface water is set and imposed on it human influence. Then conducted a similar assessment of groundwater quality in our region. A comparison of obtained results permits to assert the existence of not only communication and interaction between groundwater and surface water, but the existence of regional and local hydrochemical zonality of waters. Regional hydrochemical zonality is illustrated by the example of Kalmius River basin, as well as Uglegorsk reservoir area. Local hydrochemical zonality is determined in the local sources of pollution zone of influence: municipal solid waste polygons, industrial areas, etc. In addition the position of local pollution sources is defined within the regional anthropogenic zonality, appointed the anthropogenic replaced "seats" and "windows" of nonreplaced natural waters. In the sixth section assesses the degree of human-induced substitution of natural waters in the Donetsk region, raised the issue of irreversibility hydrosphere replacement processes, reduce human influence and rehabilitation of primary waters. Currently, research is not completed. Finally degree work will be formalized in December 2008. Links 1. U.S. Geological Survey Circular 1139. "Ground Water and Surface Water A Single Resource" by Thomas C. Winter, Judson W. Harvey, O. Lehn Franke, William M. Alley. Denver, Colorado - 1998. - 237 p. 2. Doug Alley, Kay Austin, Doug Bondy, Lisa Bourget. Twelfth Biennial Report on Great Lakes Water Quality. Michigan - 2005. - 84 p. 3. Matthias Eiswirth. "The Role of Urban Infrastructure on Ground Water Contamination – the EU AISUWRS Project". - 10 p. 4. G. Strauch, C. Schmidt, M. Bayer-Raich. "INDICATING ANTHROPOGENIC EFFECTS ON URBAN WATER SYSTEM - INDICATORS AND EXTENSION". - 3 p. 5. T. Schiedek, M. Beier, G. Ebhardt. "Monitoring urban impact on groundwater quality - statistical analyses in Darmstadt, Germany". - 2 p. 6. Vassilis Z. Antonopoulos, Dimitris M. Papamichail. "Statistical and trend analysis of water quality and quantity data for the Strymon River in Greece". - 14 p. 7. P. LA BARBERA, L. LANZA, F. SICCARDI. "Experimental and theoretical memory diffusion of water in sand". - 8 p. 8. U. MANDER. Variation in groundwater quality in South Estonian rural areas. - 14 p. 9. Питьева К.Е. «Гидрогеохимические аспекты охраны геологической среды». М.: - 1998. - 264 с. 10. М.В. Персиянов. Классификационный анализ в изучении химического состава шахтных вод. - 3 с. 11. М.П. Андреевой. Современное состояние подземных вод зоны активного водообмена Кузбасса. - 3 с. Copyright © 2008 Rudchenko Katerina | |||||
| Click to see big photo (JAVA-script) | |||||||
| |
|||||||
| |
|||||||
| |
|||||||
| |
|||||||
| Copyright © 2008 DonNTU, Katerina Rudchenko. Designed for Masters of DonNTU | |
||||||