Introduction
1.Consideration of turbulent streams. Generals
2. Methods of measuring of parameters of turbulent stream
3. The foundation of structure of the developed system
Conclusion
The main task of geomorfology is a study of conformities to law of spatial redistribution of matter and him relief making consequences. The decision of this task requires the quantitative estimations of flowings on an earthly surface processes. Water streams serve as one of main agents of exogenous relief making, and the complex of river-bed and valley forms created by them is the most steady external display of their co-operation.
Research objects for geomorfology in this case are river-beds of the flat rivers and their deformation. It is conditioned that deformations of river river-beds often cause bad or extreme situations in different industries of economy.
The changes of river-beds result in emergency situations on submarine transitions. For example, break of gas pipeline higher than Astrakhan as a result of ground transportation of right bank became the main factor of the giant explosion and fire on the middle of Volga, the caravans of courts higher and below than this place a few days expected completion of fire.
A theory of river-bed process is a complex of morphological theory and hydrodynamics. Indissoluble connection of these two aspects is conditioned that morphological conformities to law, inherent river-bed forms, show up as a result of affecting river-bed bed of current water motion of which submits the laws of hydrodynamics .
It indisputable position underlay hydrodynamic direction in the study of the systems of superficial river-bed flow where, as private, case the river systems enter. A purpose of this direction is a -sovmestnoe decision of equalization of motion of water and equalization of deformation, that, use as mathematical expression of physical laws of co-operation of locomotive liquid and solid.
More detailed hydrodynamic analysis of the system of ruslo-potok can be made at the level of separate bend and consists of receipt of the field of speeds of turbulent river-bed stream in the transversal sections of river-bed in characteristic stvorakh of bend (entrance of stream on a bend, top of bend, point of bend on an exit from a bend).
The new main idea of the scientific essence research is to meter not only the cross flow velocity but the parallel flow velocity of the water flow
Purpose
Develop the system to measure 2 copmonents of velocity vector of the turbulent water flow .
Aim
Research the influnce of the geometry of the probe on the metrological characteristics, also to develop the electronic scheem to amplify and convert the signal of the probe.
Main Idea
The water flow crossing concentrate magnetic field will effect the electricity signal on the electrodes in this field.
Consideration of turbulent streams. Generals
At research of turbulent flow he de bene esse is decomposed on two constituents: osrednennoe at times motion and pulsation motion. The vector of speed in some point of stream can be decomposed on three constituents in the cartesian system of co-ordinates. Designating the osrednennoe at times value of making speed and pulsation constituent through mean and instantaneous values (like for other constituents), it is possible to write down next equalizations for the constituents of vector of speed and for
pressure.
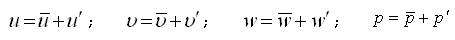
The value of overage making speed on some vector of decomposition in cartesian co-ordinates is determined:
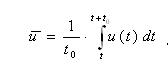
Pulsation making speeds and pressures can be described frequency and amplitude. At turbulent motion of frequency and amplitude of pulsation of speed and pressure change in very wide limits: in every point of turbulent stream pulsation constituents take place in the range of frequencies from units of Hertzs to ten kgc. Always low frequence constituents prevail.
Chaotic character of change speed, pressure and other descriptions of stream in time and in space served foundation for creation of static theory of turbulence . In obedience to this theory a turbulent stream is named homogeneous, if certain descriptions him, the made from sizes, taken in one point of M, does not depend on position of this point, and the made from sizes, taken in two points of M and M', depend on distance between the points of M and M', and does not depend on their position.
A homogeneous turbulent stream is named isotropic, if all properties and descriptions of turbulence are identical in all directions, I.e. in an isotropic turbulent stream there are not primary directions and spatial descriptions of turbulence depend only on distance between the points of M and M' of stream.
Methods of measuring of parameters of turbulent stream
At research of streams often use the concept of general speed – speeds of transfer of some substances or physical fields of environment a stream: admixtures, field of temperatures, field of pressures, field of conductivity, optical chaos etc. In a number of cases it is possible to equate motion of these physical fields with motion of environment, I.e. to consider general speed the rate of movement of the probed stream. In those cases, when the transfer of closeness of environment, general speed, is registered convective speed approximatly equates mass speed
Presently for measuring of speed of streams ten is used on principle different methods. It is caused that majority from them gives satisfactory results only in the certain range of parameters of the probed environments. A size, registered a device, depends usually, as a rule, not only from speed of stream but also from other parameters of environment (temperatures, conductivities, closenesses and t. of p.). By investigation said there is that at the use of most existing devices need to be tuned more carefuly
The existent methods of measuring of speed of streams of liquid can be divided into 3 basic groups: kinematics, dynamic and physical. At measuring of speed kinematics methods some marks speed of which and determined by the proper devices are created in a stream. Marks can be both artificial (thermal, radio-active, ionization et al) and naturally existing in a stream.
Dynamic methods use dynamic co-operation of stream and measuring probe, and also thermodynamics and MGD co-operation.
Methods which apply different physical processes in the probed area of stream behave to the physical methods, flowing of which steadily depends on the value of speed (ionization, acoustic, spectral et al).
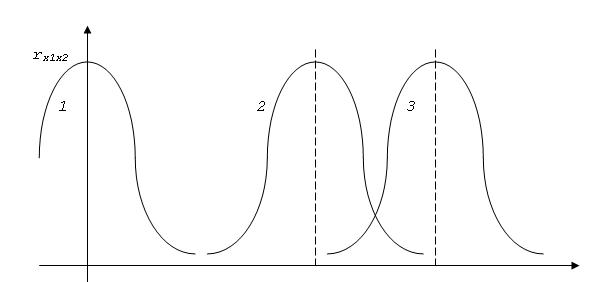
Correlation method. Essence of method is taken to the following. Execute the simultaneous measurings (or record) of fluctuations of some physical size (FV) in two points of kh1 and kh2, located along on a stream. Determine the mutual correlation function of these two fluctuations. Depending on distance between the points of kh1 and kh2 the rationed mutual correlation function changes the kind – there is displacement of its maximum.
Three correlation functions of rxx are below shown for the followings terms: speed of stream is permanent, curve 1 zero length corresponds, curves 2 and 3 – non-zero distance . Thus curve 2 corresponds less distance. If distance is permanent and speed of stream changes, the greater change of a maximum of function corresponds less speed. That the temporal change of a maximum of correlation function can be equated with some characteristic time of transfer of the field of measured FV from point 1 to point 2.
In the case of stationary character of fluctuations of measured FV a change corresponds local speed of transfer of the field of this FV, which often can be considered the rate of movement of stream. The same conclusion is just, if fluctuations have non-stationary character. Thus, knowing distance of l between the points of measuring of some FV in a stream and defining the temporal change of a maximum of function it is possible to define speed.
Optical method. The optical are name measuring devices based on dependence on speed of stream of one or another optical effect. Basic among scopes – doppler measuring devices. The effect of Doppler, consisting in measuring of frequency of radiation, known from physics lies in basis of their work, radiation dispersed locomotive in relation to a source objects .
The chart of Doppler method of measuring of speed of stream is below resulted. Very perspective is a method of laser dDoppler anemometry, in which the instantaneous value of speed is determined on the Doppler change of frequency of laser radiation, dissipated on locomotive in a stream particles.
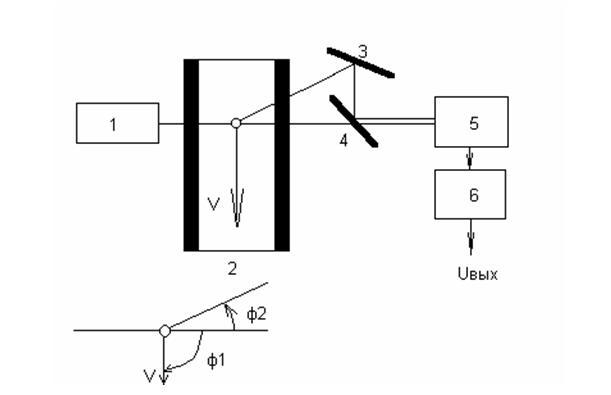
1- radiation source;
2 – pipeline;
3 – mirror;
4 – silvered piece of metal;
5 – fotodetector;
6 – frequence-voltage Coverter;
Uâûõ – Voltage, proportional to speed
Thermodinamical method. The thermodynamical method of measuring of speed is based on dependence of heat exchange between a measuring probe and environment from the value of speed. Thus heat emission can be examined from a probe to the stream (termoanemometry) or from a probe to the probe through a stream (it is a kinematics method already) .
There are two types of termoanemometers. In one – in a stream the heated filament is placed with TP which takes temperature filament, in other – a filament is placed in a stream only. The first are named termoelektroanemometers, and second – by ordinary anemometers
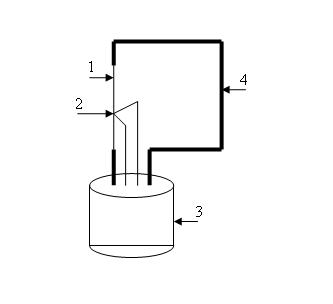
1 – filament;
2 – TP;
3 - ebonite cork;
4 – filament taker
Acoustic method. The action of acoustic (ultrasonic) measuring devices of speed is based on that speed of distribution of sound-wave in a locomotive environment is equal to the geometrical sum of speed of sound in an immobile environment and speed of environment . If to measure total speed, at the known value of speed and known coal between the vectors of speeds it is possible to define speed of stream . Not looking on that in an immobile environment speed of sound is determined a temperature and closeness of environment,
of acoustic anemometers is not. In practice 2 methods of measurings got distribution: time - impulsive and phase.
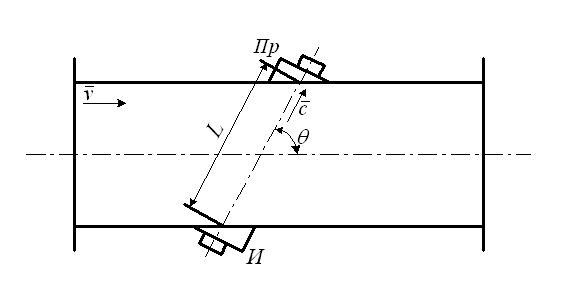
At time - impulsive method of measuring a signal as an ultrasonic impulse is formed an emitter And and caught the receiver of Pr . At the phase method of measuring continuous harmonic vibrations emanate and the difference of phases of signals is measured. In an odnokanal'noy structure a weekend the size of device is difference of phases of the accepted and radiated signals.
MGD method. The MGD (or electromagnetic) method of measuring of speed of stream of liquid is based on the phenomenon electromagnetic induction. It is known from an electrodynamics, that at motion of conducting environment in the transversal magnetic field electromotive force (e.d.s.), which operates in direction, perpendicular the vector of rate of movement of environment and vector of induction of the attached transversal magnetic field, inducts in it. Thus, e.d.s. proportional the rate of movement of environment and value of induction of the attached magnetic field and does not depend on physical properties of environment (conductivities, temperatures, viscidities etc.) .
If in a liquid, locomotive in the transversal magnetic field, to enter 2 electrodes, under an action inducted in the stream of e.d.s. the difference of potentials, proportional speed of stream of liquid, appears on electrodes. T. of e. on the size of difference of potentials of electrodes it is possible to judge the flows of liquid about speed.
Devices, using the described principle for measuring of speed, name conductive measuring devices. In principle works of such devices are stopped up the best possibilities for realization of measuring devices of local speeds, that is very important at research of structure of turbulent streams.
The foundation of structure of the developed system
During the analysis of material it is possible to select requirements to the electronic system:
As it is necessary to get the field of speeds and pulsations of speeds in some probed stream, it is necessary to apply sensors, providing small inertion of measurings, possessing local (by a point) parameters, having necessary exactness and small gabbarity, and also to use the autonomous sources of feed. At consideration of sensors, the most acceptable variant is a MGD sensor with the local field. Separate class of these devices is sensor with quazisphere view.
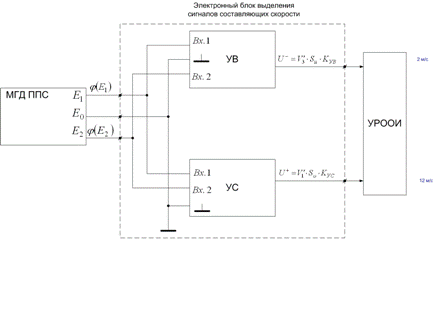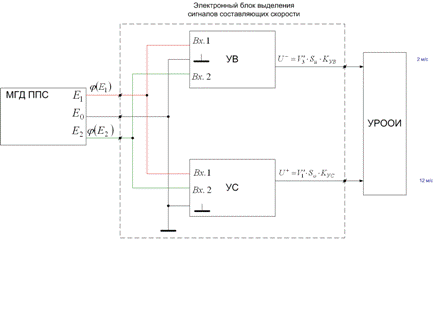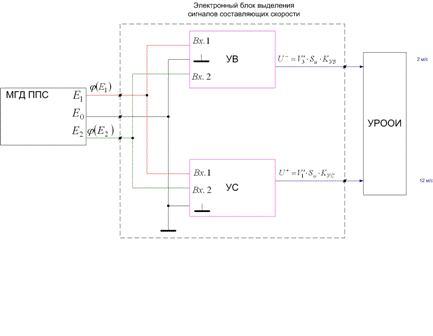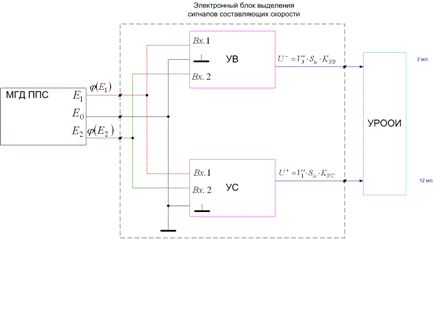
Allowed to find out the analysis of essence of transporting ability of stream and expense of alluviums, that these sizes, in general case, are not equal to each other. An expense of alluviums is resulting from combination of sizes of transporting ability of stream and receipt of alluviums on the examined area of the river.
The review of existent formulas shows that does not exist formulas of expense of alluviums, which would provide sufficient exactness of calculations of charges of alluviums. One of reasons of it also is absence of sertain data of the alluviums given on the model measurings of charges.
Possibly, other going is needed near the estimation of expense of alluviums, which can be based not on the parameters of stream and particles of alluviums, I.e. at system (structural) level «–», and on the parameters of waterflow and river on the whole, I.e. at system level «–».
For the prognosis of change of river-bed not so much it is necessary to know the absolute values of parameters of the system before and after outer influence, and it is more important to know direction (vector, degree) of change of relief forming factors. For example, information that by some appearance make increase of receipt of alluviums from waterfall or overhead area of the dat taking about exceeding of receipt of alluviums above former transporting ability, on the basis of what it is possible to do the prognosis of change of morphological forms.
As for the decision of tasks of gidromorfology it is necessary to know not only the geometrical parameters of the system (river-waterflow) but also physical parameters of stream (as given above – field of speeds). Because it is impossible to get the reliable picture of the field of speeds a mathematical design (influencing of cavities is possible, nanosov-kholmov and many other factors influencing of which it is impossible fully to take into account).thus, it is necessary to conduct measurings. And because for the transfer of particles not only longitudinal (directed along the flow of the river) speed is responsible but also transversal (vertical constituent of speed) that must be measured constituents of vector of speed. It is also necessary to specify that over the use of overage descriptions of stream brings to distortion of result. Application of osredneniya is justified only for the receipt of preliminary picture of process.
The similar systems absent presently, consequently there is a necessity for their development.
© DonNTU, Timoshenko Igor , 2008



 Curriculum
Curriculum  Article
Article
 Library
Library  Links
Links Search report
Search report  Individual task
Individual task
