


| Speciality: | Ecology in chemical technologies |
| Theme of master's work: | Activation of alkaline earth metal compounds in the reactions of interaction with sulfur dioxide |
| Scientific advisor: | The Doctor of Chemistry, professor Valery Shapovalov |
The main task of this research is to study process of interaction of the calcium carbonate with dioxide sulfurs and to discover most effective special activator .
The sulphurous anhydride which containing in rather small concentration in departing gases of industrial enterprises is the basic source of atmosphere pollution because of its high toxicity both for animals and plants. Therefore a problem of sanitary protection of cleanliness our air is first of all the problem of extraction the sulphurous anhydride from the so-called poor sulphurous gases which are let out in the atmosphere.
Scientific novelty of the research consists in using special activators for intensifying the process of adsorption of dioxide sulfurs by alkaline-earth metals.
During the research the process of activation of alkaline-earth metals in reactions of interaction with dioxide sulfurs will be studied along with its thermodynamic and kinetic characteristics.The most effective and rational activator for future using in technological cycle of the industrials working on sulphurous kinds of fuel will be selected according to research results.
All clearing processes of sulphurous anhydride are expedient for dividing into two basic classes, which are different on a physical condition of an applied basic reagent for extraction of sulphurous anhydride from gases[1]. The first class includes processes with the absorption of sulphurous anhydride which is carried out at rather low temperatures ('liquid' methods). The methods carry to the second class based on interaction between gas and a firm phase. Each of these classes can be essentially subdivided into three primary groups, which are different in usage the methods of extracted sulphurous anhydride. The first group includes the processes which main object is only clearing of gases disregarding possibilities of salvaging of extracted sulphurous anhydride. Products of the basic interaction of sulphurous anhydride with an absorber are a withdrawal. Cyclic processes and methods concern to the second group with reception of commodity sulphurous anhydride or elementary sulphur. During these processes make absorber regeneration. The third group of clearing processes of gases includes processes at which extraction of sulphurous anhydride is carried out together with its usage to receipt new chemical substances.[2]
Because for liquid methods require preliminary cooling of departing gases, big power expenses and heavy water expense, for the thermal power stations working on sulphurous kinds of fuel, more expedient are the clearing methods based on interaction between gas and a firm phase. As absorbers are used oxides of manganese, iron, calcium, their mixture, coal, zeolites, etc.
The usage in the quality of adsorbent a calcium carbonate is represented rational for the following reasons:
The process of absorption the sulphurous anhydride in the absence of oxygen occurs according to reaction
Energy of Gibbs is 41.789 kilojoule/mol, the thermal effect of reaction is equal 49.170 kilojoule. Settlement adiabatic temperature is 381.69 К.
At heating of the formed sulphite of calcium occurs it disproportion:
Energy of Gibbs is 142.174 kilojoule/mol, the thermal effect of reaction is equal 147.600 J, settlement adiabatic reaction temperature is 663.87K disproportion also will occur to heat allocation. In the presence of oxygen in a mixture the following reaction can proceed:
Energy of Gibbs is 289.719 kilojoule/mol, the thermal effect of reaction is equal 326.070 kilojoule. Taking into account possible fusion CaSO4 adiabatic reaction temperature is 1512 K. When temperatures are above 873 K it is also probably partial decomposition of a carbonate of calcium.
The absorption research dioxide of sulfurs by the calcium carbonate in vitro shown that at temperatures to 500°C active absorption does not occur. But with addition of special catalysts efficiency of reaction essentially increases. Picture 1 is the curve DTA of absorption process of sulfurs dioxide by the carbonate of calcium in the presence of special activator (10% of weights). On the given curve it is possible to judge intensity of process. The weight of a reacting mixture after absorption process has increased by 16%.
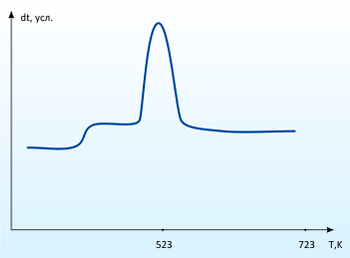
Infrared spectrum of reaction product is presented in picture 2. Comparison of the spectrum with tables of characteristic frequencies allows to draw a conclusion that in the given sample are present anions SO32-, SO4 2-,CO32-.
Together with the data on change of weight the product of reaction it is possible to draw a conclusion that the absorption process dioxide of sulfurs takes place with formation as sulphite, and calcium sulphate with enough low temperatures. Due to that the mixtures of the carbonate of calcium with special activator is of interest as an absorber at the enterprises using sulfur-bearing fuel.