Faculty of Computer information technologies and automation
Department: Automations and Telecommunications
Specialty: Telekommunication Systems and Networks
Theme of master's work:
«Bandwidth research and optimization for communication channels in the telecommunication network that provides Triple Play services for the conditions of the borough»
Scientific superviser: Boyko V.V.
Abstract
Introduction
The situation in the global telecommunications market is required in increasing of their products’ competitiveness. In last years, access networks areas the most dynamic segment of the telecommunications field. They are directly related with the provision of operator’s services to subscribers, so this networks are well compensated. The reason of that is development of telecommunication technologies, which can provide growing costumers’ needs.
One of the most popular conception is providing triple-play services of «Triple Play», which means providing users with telephony, data transfer and TV services at one time in a single network. Moreover, high-speed Internet and video require significant bandwidth network resources. One of the most popular optical technology in access networks is FTTB / ETTH technology, this solution is very suitable for data, voice and video traffic transfer s using a simple and inexpensive Ethernet network technology and optical communication lines. For large operators, who are building huge networks with reservation systems, the most successful technology is considered using FTTB / ETTH.
Connection of the work with the academic programs, plans, themes
The master's qualification work has been executing during 2009-2010 according to the scientific direction of the Automation and Telecommunications department of Donetsk National Technical University.
Tasks and objectives of the master's work
The aim of this work is bandwidth research and optimization of communication channels for access networks which provides Triple Play services on the example of Voroshilovliy district in Donetsk. This task should be solved:
- Analysis of the district for which the network is developing;
- Calculation network’s parameters in accordance with the requirements of services;
- Development and selection of topology and technologies that will be used in the network;
- Development of structural network map;
- Development of a functional network map;
- Selection of required equipment for the network;
- Check network parameters using its model;
Analysis of the object and description of the information model
The object of this work is telecommunication network for Voroshilovskogo region in Donetsk, which is inhabited by about 97,3 thousand people, has an area of 10 km2 and has following characteristics:
- Waterways: The Kal'mius river; pond № 1, № 2, № 3;
- Streers: Artem St., University St., Shchorsa St.; avenues: B. Khmelnitsky ave, Illich ave; Pushkin boulevard, Shevchenko boulevard;
- For functional purposes it is the administrative area, but it may be divided into the following parts:
- The administrative sector;
- Residential communitoes;
- Private sector;
- Park zones.
There are locater administration, financial, trade, culture, health, science and education, information and social security, regulators, consumer services, communications, law, transport institutions.
But in this work will be considered only costumers of the residential sector. This district will be divided into parts, where will be placed required equipment.
Characteristics of the subscribers from the district
Before building information model have to get information about the number of existing subscribers. To do this, I make a little calculation using statistical data.
Mid-statistical family includes two working and two non-working (one retired, one student or one student and one child of preschool age) man.
Probabilities of families with a certain number of members listed in Table 1.1
Table 1.1 - The average composition of families
Quantity of family members |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
More than 6 |
Probabilities |
0,0215 |
0,1359 |
0,3413 |
0,3413 |
0,1359 |
0,0215 |
0,0026 |
Number of family members varies in the range 2 ÷ 5 people with a probability of 0.954, so when calculating the number of families Nfam we should focus on the lower boundary of the estimated range 2 ÷ 5 people:
Nfam= N / (n-2σ), (1.1)
For the conditions of Donetsk.
n-2σс = 4-2 = 2 pers.
Equation (1.1) takes into account families, which differ by number of members with overstatement.
Nfam= N / (nsr-2σс) = 97300 / 2 = 48,650 families
In this work, which takes into account the greatest possible number during next 10 years and as well as that it will be not the sole operator services in this area - the number of subscribers will be equal to approximately 60% of the families, this equal to 29000 subscribers.
Information model of the object and quality requirements
All users of this telecommunication network will be divided into four classes A, B, C and D. Depending on that, there will provide the following services built on the priority useing them by subscribers:
Class «A»:
- IP-Telephony.
Class «B»:
- Access to the Internet.
Class «C»
- Video on Demand, VoD (MPEG-4).
Class «D»
- IP-Telephony.
- Access to the Internet.
- Video on Demand, VoD (MPEG-4).
Depending on the class, subscribers receives the appropriate billing. Each class receives the full range of services, but according to the class they choose – they will be use certain services more often then others. This method is based on statistical data and provides an opportunity to create tariff packages for the network operator.
Table 1.2 Shows the percent usage of each services for the selected classes:
Classs |
IP-Phone, % |
Internet, % |
VoD, % |
«А» |
80 |
10 |
10 |
«B» |
30 |
50 |
20 |
«C» |
30 |
10 |
60 |
«D» |
33 |
33 |
34 |
Table 1.2 - The percent usage of each services.
It is assumed at the initial stage following the distribution of subscribers for the each class:
- 15% of - class «A»
- 20% - Class «B»,
- 50% - class «C»,
- 15% - Class «D».
Due to growing demand for modern technology of video transmission, it is going to increase number of Class «D» users in the future.
The service «live video, HDTV» - is a new direction for television, if an ordinary TV (PAL or SECAM) provides an image 720 by 576 pixels, HDTV is allowed to watch TV shows, movies 1920 by 1080 pixels for the frame rate 30 per second. We will use MPEG-4, which allows us send the image with transfer speed up to 9 Mbps/sec. In multicast mode will be broadcasting 50 the most popular international, state, local TV channels.
The service “Video on Demand, VoD” - provides subscribers the opportunity to review their favorite show, movie or a direct broadcast on TV. Video is available in a simpler format, 720 by 576 pixels (PAL) with transfer speed up to 2Mbps/sec.
The service «IP-Telephony» - is a system which provides the transfer of audio signals using IP-based networks. The signal transmits in digital form through the communication channel, it re-encods, so that redundancy is removed. For that we use codec G.729, which allows send traffic with transfer speeds up to 8 kbps/sec.
The service «Internet access» - is a broadband Internet access, provides reliable operation in the network and fast access with transfer speeds up to 2 Mbps/sec.
Requirements for the quality of these services are given in Table 1.3.
Services |
Bmax |
Тave,с |
С |
Р, % |
Тdel., ms |
VoD |
2 Mbps/sec |
3600 |
1 |
1 |
600 |
IP-Telephony |
8 Mbps/sec |
300 |
6-8 |
5 |
150 |
Internet |
2 Mbps/sec |
1200 |
1-3 |
0,5 |
50 |
Where Bmax (Bandwidth ) - The speed at which generated by the user traffic should be transferred through the network.
Tave - is average duration of using the service in seconds at one time.
C (count) - the average number of calls per hour.
P (Packet loss) - the percentage of lost packets during transmission.
Tdel - the maximum time of delay.
Schematic design of the transport network (course work)
In modern optical access networks different network topologies are used . Selecting the optimal topology depends on many factors related to specific design criteria (density of subscribers, their location, services, etc.), as well as from the base optical technology.
For a multi-service networks providing Triple Play services there are several options for implementing. Let’s take a closer look at the network structure.
Main units:
- Kernel - the central node, provides interaction sites of aggregation network. The main equipment, servers, etc. are established in the kernel.
- Aggregation node - provides connectivity access nodes (CAP).
- Access node (CAP, community access point) - the object of communication, performing the direct connection of subscribers with UTP-5 cable inside houses. In one house may be a few CAP.
Access level topology
Network the “Star” topology. Each CAP links with subscribers’ apartments using UTP-5 cable. Subscribers are linked through individual port on the CAP. Depending on the choice of equipment from 24 to 48 subscribers per CAP module. At the subscriber's apartment installed client equipment.
Aggregation level topology
Network has topology of the ring. The logical ring is organized inside the ring, each logical ring includes 5 CAPs. Maximum number of CAPs in the ring is 60, or maximum number of logical rings is 12 on one switch of aggregation node (12 rings from 5 CAP in each logical ring). Rings are closed at the aggregation nodes (Figure 2.1). Number of rings can be several.
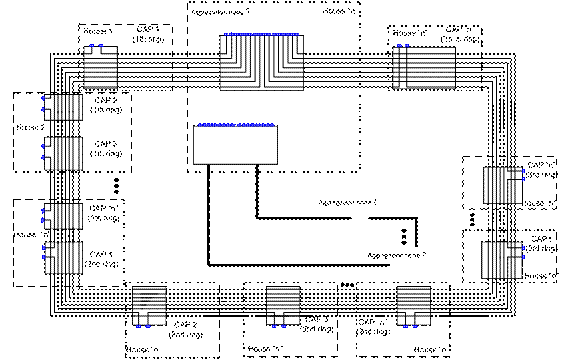
Figure 2.1 - Example of the ring construction.
The main level topology
Network has the ring topology. The logical ring is organized inside the ring, the number of nodes for the aggregation level in the logical ring is not more than 3.
Rings are closed at the nodes - the kernel. Topology similar network topology aggregation (Figure 2.1) Except that in the ring no more than 4 units of aggregation.
The kernel level topology
Network has topology of the ring. Number of kernel-level equipment is not limited.
From each aggregation lays fiber optic cable from roof to roof of houses where CAPs are located (Figure 2.2).
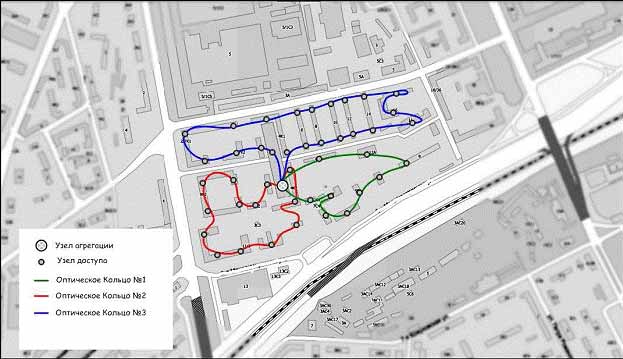
Figure 2.2 - Construction of CAPs rings from aggregation node.

Figure 2.3 - general topologies
Description of the network technology
This network constructing solution is using of FTTB / ETTH technology.
The ETTH transfers data, voice and video with a simple and inexpensive network Ethernet technology. The unique aspect of this decision is that using of Ethernet technology with optical fiber lines for transmission provides high speed network access.
Gigabit Ethernet (1 and 10) is very attractive in price / quality ratio and it’s great choice for mainstream use in the construction of a Metro Ethernet providers networks.
Attractive solution for wiring inside buildings will be a fifth category twisted pair cable. Designed as a technology of local networks, Ethernet technology provides bigger and cheaper bandwidth comparing with DSL, cable modems and wireless solutions.
A typical architecture is realized by 10 - or 100-megabit Ethernet-channels in each apartment connected to the CAP switch . For the connection a house with the fiber-optic network gigabit or multi-gigabit Ethernet-connection is organized. Traffic aggregation for ring networks makes by the switch of the third level.
The maine force for the ETTH technology adoption is an excellent cost-effective Ethernet technologies, which today provides several advantages:
- No need in a firm specialized modems and network cards;
- Use of uniform worldwide standards of a low cost equipment and establishment;
- Easy upgrade from 10 to 100 Mbps, 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps;
- Great protection of individual subscribers from each other;
Recent data from market research shows that the total monthly cost Mbps bandwidth is falling in Ethernet networks much faster than in the networks that are based on alternative technologies.
For subscribers is selected access protocol using PPPoE (point-to-point over Ethernet), which allows to organize a PPP connection point to point through a multicast medium Ethernet. PPP protocol randomly designed specifically to provide subscribers access to the network, allowing it contains built-in authorization session management mechanisms, controls IP addresses, etc.. Protocol of PPP, as the link layer protocol, you can send not only IPv4 traffic, but also other network layer protocols, for example, IPv6.
Calculation of the subscribers load network parameters
The methodology used for the traffic calculation is probabilistic characteristics of the data flows which are generated by different network applications.
Traffic is calculated separately for each service on each network node. Equation (1.1) for the calculation is:
 (1.3)
(1.3)
where k - number of network services;
i - node number;
j – subscribers class;
![]() - The expectation of traffic that is generated by the k-th service on the i-th node;
- The expectation of traffic that is generated by the k-th service on the i-th node;
![]() - Data transfer rate (in Mbps) – is average communication channel bandwidth, which is enough for high-quality transmission of the k-th traffic services;
- Data transfer rate (in Mbps) – is average communication channel bandwidth, which is enough for high-quality transmission of the k-th traffic services;
![]() - The number of subscribers in the i-th node, who use the k-th service;
- The number of subscribers in the i-th node, who use the k-th service;
![]() - The fate of the k-th service for the j-th class of subscribers on the i-th node;
- The fate of the k-th service for the j-th class of subscribers on the i-th node;
Data transfer rate ![]() is determined by (1.4):
is determined by (1.4):
![]() (1.4)
(1.4)
where ![]() - the maximum channel bandwidth;
- the maximum channel bandwidth;
![]() - the ratio between the maximum and average bandwidth needed to ensure the k-thservices.
- the ratio between the maximum and average bandwidth needed to ensure the k-thservices.
Calculate the load on the network. Calculating of loads assumes that the CAP sets at five-floor or four-floor houses, total number of residential subscribers is 80, with planned of 60% of subscribers connected to our network will be approximately 48 apartments.
According to our subscribers classes:
- Subscribers Class «A» 15%, or 7 apartments;
- Subscribers of class «B» 20%, or 10 apartments;
- Subscribers Class «C» 50%, or 24 apartments;
- Subscribers Class «D» 15%, or 7 apartments.
The overall network load defined first for a single CAP node:
Firstly, calculate the load for each type of service:
- for the «Internet» service 2,82 Mbps.
- for the «IP-Telephony» service 0,14488 Mbps.
- for the «VoD» 38,96 Mbps.
The overall value for CAP will be sum of all loads 41,92488 Mbps.
The required bandwidth of the external canal in defined as the amount of bandwidth required Internet service and IP telephony: 0,14488+2,96488 = 2,82 Mbps.
In one ring can be up to 5 CAPs aggregation node can handle up to 12 rings in general. It means that total load on the node aggregation could equal 2515,4928 Mbps.
Taking into account previous data about the number of subscribers in the region the number of CAPs and aggregation nodes can determine.
![]()
![]()
The total network load for all subscribers is 25364,5524 Mbps.
Also it is required to include the multicast HDTV:
![]()
where ![]() is bandwidth of the communication channel, which is enough for high-quality HDTV services;
is bandwidth of the communication channel, which is enough for high-quality HDTV services;
N - number of channels of TV which are broadcast in the network.
Total network load will be equal to 25 814,5524 Mbps.
Following problems of master's work are not completed at the moment.
With the simulation of telecommunication network tools, is planned to reach the required quality at the lowest cost resources. Analysis of the effectiveness of decisions.
Simulation will consist of several experiments:
- Modeling functioning of the multi-service network without using of prioritized traffic types.
- Modeling functioning of the multi-service network with using of prioritized traffic types, depending on the type of caller, day time and other.
- Modeling the functioning of the site multiservice network with other optimization solutions.
On the results will be made conclusions about the effectiveness and quality of decision making.
Note
While writing this abstract the master’s qualification work is not completed. Date of the final completion of the work is on 1st December, 2010. The full text of the work and materials on the work theme can be received from the author or his scientific supervisor after that date.
Список литературы
- Величко В.В. Телекоммуникационные системы и сети: Учебное пособие. В 3 томах. Том 3. - Мультисервисные сети. / Е.А. Субботин, В.П. Шувалов, А.Ф. Ярославец. - М.: Горячаяя линия - телеком, 2005. - 592 с.
- В.Г.Олифер, Н.А. Олифер «Компьютерные сети” 2-е изд., Питер 2003
- Столлингс В. Современные компьютерные сети. - [2-е изд]. - СПб.: Питер, 2003.- 783 с
- Официальный документ «Архитектура оптических сетей доступа FTTH (Fiber-to-the-Home)», подготовил Иван Герасимов, системный инженер-консультант, http://www.cisco.com/
- Филимонов А.Ю. Построение мультисервисных сетей Ethernet. - СПб.: БХВ-Петербург, 2007. - 592 с
- Вегешна Ш. Качество обслуживания в сетях IP. - М.: Издательский дом «Вильямс», 2003. - 368 с
- В.Варгаузин, статья «Волоконно-оптические компьютерные сети доступа», 2002 - http://www.telemultimedia.ru
- В. Спирин, статья «Варианты реализации широкополосной сети по технологии «волокно в дом», 2002 -http://www.telemultimedia.ru
- Tim Hills, «Ethernet FTTH Triple-Play Services», 2006, http://www.lightreading.com
- Vesna S. IP Quality of Service./ Srinivas Vegesna. – Cisco Press. – 2001. – 368 p
