Abstract of Master's Work
"Develop specialised computer systems
determine the temperament of the person physiognomic characteristics "
Alleged scientific novelty
Differences
Analyze the image of a human face in deciding on the type of temperament on the morphology of types proposed by Kulikov [8]:
- match temperament derived from the image with the results of psychological tests to determine the temperament;
- make recommendations about the type of work, suitable to the temperament of that employee.
- Slot with the name of the emotions;
- Slot with reference to the corresponding node hypertext with an explanation;
- Slots with the rules by which one can determine the appropriate emotion.
- Eyebrows;
- Eyes;
- Nose;
- Cheeks;
- Lips;
- Chin
- Изард И. Эмоции человека – Москва, 1980. – 189 с.
- Анохин П. К. Психология эмоций – Москва, 1984. – 220 с.
- П. В. Симонов. Мозг: эмоции, потребности, поведение.// Избранные труды, том 1. Изд. Наука, 2004. – 340 с.
- Н. А. Бернштейн. Физиология движений и активность. М.: Наука, 1990. – 140 с.
- Чарльз Дарвин. О выражении эмоций у человека и животных. Изд. Питер, 2001. – 120 с.
- Пол Экман. Психология лжи. Изд. Питер, 2003. – 175 с.
- Irfan A. Essa and Alex P. Pentland. Facial Expression Recognition using a Dynamic Model and Motion Energy. M.I.T Media Laboratory Perceptual Computing Section Technical Report No. 307, International Conference on Computer Vision ’95, Cambridge, MA, June 20-23, 1995.
- Г.В.Щекин Визуальная психодиагностика: познание людей по их внешнему облику. М., 1992.
- Ekman P., Friesen W. A new pan-cultural facial expression of emotion. Motivation & Emotion. 1986. Jun. V10 (n2): 159–168.
- Распознавание человека по изображению лица и нейросетевые методы [Електронний ресурс] / Д. Брилюк, В. Старовойтов - Режим доступа к статье: http://www.masters.donntu.ru/2008/kita/baglikov/library/4.htm
- Хакен Г. Принципы работы головного мозга: Синергетический подход к активности мозга, поведению и когнитивной деятельности. – М.: ПЕР СЭ, 2001. – 351 с.
Practical value
The developed software automates the process of determining the temperament newcomer employee staffing agency, analyzing the photograph of his face, identify the propensity for the type of work performed, provide quick access to any employee, will reduce time and labor office manager, thereby increasing its efficiency.
Analysis of existing development
Currently, the Institute of Psychology at the Academy of Sciences Philippines is in the process of creating computer expert system, which is designed to perform expert functions determine the emotional states of the presented face image. The image is entered into the computer as a digital photograph of referring to the photograph of the face of one man from the front. In the first phase subsystem must be able to distinguish between the expression of the person and the second, using its initial data, the other subsystem determines the emotional state. Development of the subsystem is based on the establishment of an expert system, driven by knowledge and has a modular structure.
To build a knowledge base system - the core of the expert system, which describes the expression of human faces to determine the emotional state of the facial expressions, used the method of application of knowledge based on frames. Each emotion corresponds to a separate frame, and they all have a similar structure. These frames contain the following slots:
The second slot is connected with actual knowledge, and the slots with the rules - procedural, with their help, the system can perform expert functions. To develop the rules by which one can determine all sorts of emotions, was chosen expression system descriptions person created Ekmanom P. and W. Friesen FACS (Fasia1 Astion Soding Sustem) [6].
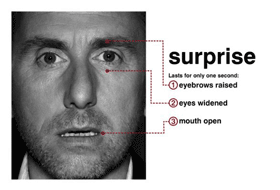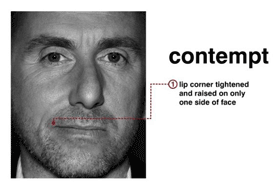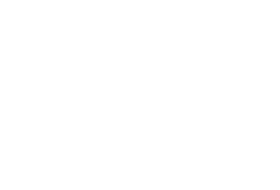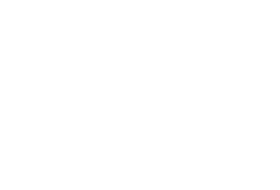
In the target system includes frames, consistent with such emotional states: happiness, surprise, anger, disgust, contempt, fear, sadness. Each of them contains a unique set of rules, written as codes FACS. Each rule corresponds to the factor of "certainty" that determines how well it is generally consistent with this emotion. Each emotion and the individual units of the FACS corresponding Boolean variable, which shows there is in the rule that action or not. Then, for example, the definition of anger meets entry:
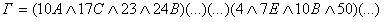 (1)
(1)
This entry corresponds to form filing productional knowledge and can be read like this: if the "act only 10A and 17s and 23 and 24B, or only valid ... or are only 4 and 7E and 10B and 50, or apply only ...", then "wrath." Similarly, you can describe all the emotions, or any other mental condition.
The difficulty lies in transforming the image photo portrait at the code FACS. In our case, the main difficulty lies in the fact that you need to recognize the expression of face images of different people irrespective of changes in angle, scale and lighting conditions at the time of shooting, as well as the various changes related to age, hair, etc.
To solve this problem was used synergetic approach. Unlike the special sciences, Synergetics explores common patterns of development of systems of different nature. The image in the computer describes an array of so-called pixels, which contain color codes corresponding to the point of the monitor screen. Each pixel is attributed to some definite value grayness v j. Thus, the image is a vector
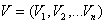 (2)
(2)
with a set of values of gray. The set of images is the set of vectors Vk, with each index corresponds to k = 1, ... ..., M.
These are the images that we are going to recognize. Synergetic approach substantiates the link between pattern recognition and the formation of structures by the so-called order parameters. Recognition of the image is nothing like the image of the prototype. Forming for storing the image of the prototype leads to the emergence of a new order parameter, which subsequently is responsible for the recognition of a manifestation of this image, ie for the formation of structure. Instead of a large number of factors on which depend the different states of the system, Synergetics considers a few order parameters, which control the components of the system state and which, in turn, affect the order parameters. Moving from the consideration of the components of the state vector of the system to a smaller number of parameters of the ordered state of the system defines one of the basic principles of synergetics - the principle of subordination (the subordination of the state vector components of the order parameter).
In the synergetic computer using the formula:
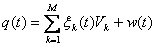 , (3)
, (3)
where - Order parameter belonging to the prototype Vk, w(t) - the remainder, then close to zero.
Thus, recognition is reduced to the mode competition, which resulted in all modes, except for some k-th, tend to zero, as proposed by the image of q (0) in tends to V k0. V k0 is the response of the presented image.
As can be seen from the above, training the system setup reduces the formation and storage of images of prototype Vk or V+k. This can be done if we use the potential function of the form:
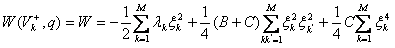 (4)
(4)
As you can see from this representation the potential function depends only on the order parameters. To recognize the potential W must be minimized by the dynamics of the gradient vector q, and the prototype vectors are regarded as fixed. (More details about the method see made to Article 3 of the library)
Approbation
The system is under development and not yet been tested.
Conclusion
Let us return to the psychological aspect: Kulikov developed modern morphology, temperament types, which can be used in visual psycho diagnosis [8]. Thus, to determine the type of temperament, and in the future and a taste for the work carried out to analyze images of human face and to provide basic facilities:
and use them to determine the identity of the type of temperament.
Despite its conventional features of the relationship of temperament and some morphological characteristics of the external appearance of man, modern research has yet confirmed the possibility of "recognition" of certain temperaments of facial features of their respective owners. FACS system is an innovative and flexible, thus can be worked out rules and created frames that can recognize the temperament of the stationary expression mimicry.
References
Important note
When writing this Autosummary master work was not yet completed. Final completion: Dec. 1,2011. Full text of work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.








