DonNTU | Master's portal | RU | UA | EN
 Eugene Masyakin
Eugene Masyakin
Faculty of Computers and Information Science (CIS)
Department of Computer Engineering (CE)
Speciality “Сomputer systems and networks”(CS)
“Development and research of FPGA based hardware-oriented methods and structures of analog tests generating”
Scientific Supervisor: Ph.D., assistant professor of the department CE Yuriy Zinchenko
Autobiography | Abstract
Development and research of FPGA based hardware-oriented methods and structures of analog tests generating
Introduction and actuality
The modern world is inconceivable without electronics. Every day, hour, minute new devices are being created, instruments, systems that make human life more comfortable, safer. Sitting behind the wheel of a modern car, a person interacts with tens and hundreds of electronic systems, with different levels of complexity: from simple oil sensors to automated self-parking systems. D / A technology, usually plays the role of mediator between the environment and digital systems. The exception is the military industry, where such devices are widely used because of their high reliability and durability compared with purely digital systems. At the same time, the widespread use of technology dictates more and more stringent requirements for reliability, testability. [1]
Aims and Tasks
The aim is to develop and research high-performance structures and methods for generating analog hardware tests using modern FPGA-technology.
The problems solved in the course of this work:
- analysis of existing systems for generating analog test;
- development of a method and structure of the generation of analog test based on DSP and FPGA;
- development of software and hardware on FPGA;
- making experimental research.
Science novelty consists in
The supposed scientific novelty consists in development of methods and structures of analog tests generating based on DSP and using FPGA. Expected that the developed structure will provide a high fast-acting, compactness, and also low cost.
Existing development
Today the main tool of the test-engineer is an automated test equipment (ATE). They are the leading manufacturers of companies such as Teradyne, Agilent, World Test Systems, DMT, and others. However, the majority of these systems are designed for testing digital devices, and do not allow to fully automate the process of constructing a test for analog-digital circuits. Because, building a functional analog test requires high performance. [2]
Levels of representation of D/A circuits for generating tests
Analog circuit can be represented by the following levels of abstraction.
By way of presentation of D/A devices are:
- The structural level - representing D/A devices as components and connections between them;
- The behavioral or functional level - representing AC devices as thier input-output relationship: a system of differential equations, graphs, algorithms, and so on.
Levels of specification are:
- transistor level - the block diagram appears with a list of components and a list of connections between them, which are supplemented by detailed models of components.Behavioral representation of scheme at this level is described by nonlinear differential equations in partial derivatives;
- structural/functional level - structural representation of the scheme at this level is a signal directed graph (SOG), which graphically shows an idealized system of equations. Behavioral performance at this level is described by the transfer function of the circuit.
The advantages of the functional level of abstraction is the convenience of modeling, efficiency and no need to simulate faults inside the circuit components.At the same time the structural level of abstraction allows efficient simulation of real defects in analog components [2]
Structural and functional analog tests exist.The main difference between them is the origin of faults and process modeling. Functional testing is often assumes that the faulty components and thus generates a list of malfunctions, which includes catastrophic and parametric faults.Structural testing uses the statistics of manufacturing defects [2]
Analog circuits have complex dependencies between input and output signals. Many analog circuits are nonlinear systems (eg, MOSFET, used as an amplifier). The values of the circuit parameters vary widely even in healthy circuit. Deterministic models are not effective for analog circuits, so the signals are determined by the nominal values with an acceptable range of their changes, which are determined by simulating the process of measurement errors and fluctuations in the manufacturing process of IP. The statistical distribution of analog faults is usually not known with sufficient accuracy to accurately predict the coating fault test sequence.Some reports indicate that the analog circuits with catastrophic failures are not detected by standard manufacturing tests. [2]
Using DSP-processors in modern automated systems for diagnostics
The DSP-based ATE is nearly always more accurate than analog ATE. In
particular, it is more accurate for non-linear analog circuit measurements, because
vector processing increases the accuracy of a set of vectors compared to the accuracy of an individual sample.
Figure 1 presents traditional analog ATE. It has no synchronization between the blocks of generating effects and analysis of reactions.
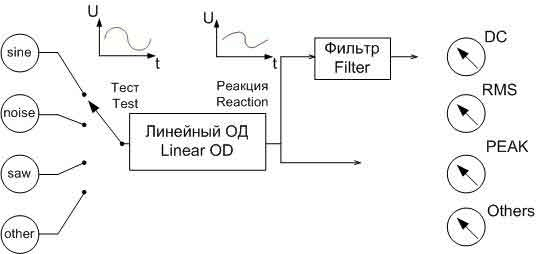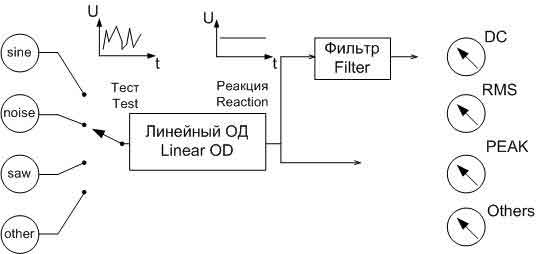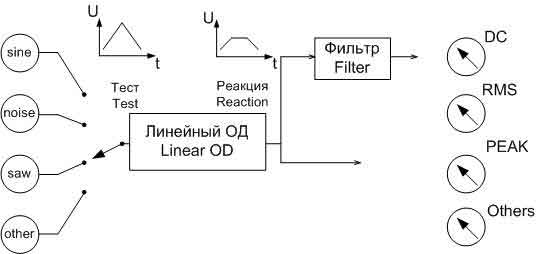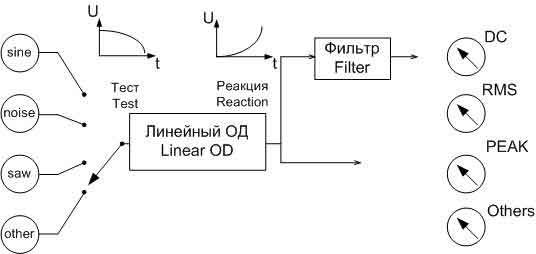
Figure 2 represents ATE based on DSP, which has the proper synchronization, and consists of the ADC, DAC, memory for actions and reactions, DSP, which is controlled by software.
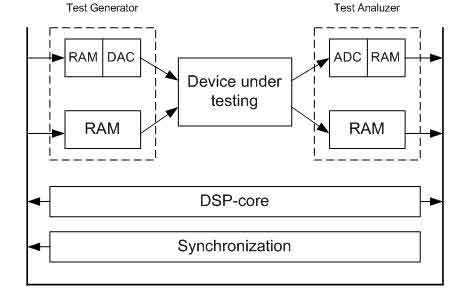
DSP can emulate a wide range of measuring instruments. The tools are now routines that handle the vector of numerical values. The vector may be a set of samples of the signal frequency spectrum, and so on. Tester creates a set of vectors in the form of test signals. Synthesizer signals are those of the vector to the DAC, whose output is connected to the restoring filter for a continuous signal with limited bandwidth. The resulting signal is fed to the test device from which you removed the reaction. [2]
Sampler performs digitization of analog signals taken reactions using high-speed ADC and stores the samples in RAM. When the device acts as a test of analog-digital circuit, the signals from the outputs of the digital part is written into the input memory, and tests for the digital part are applied to the object of diagnosis (OD) of the output memory.
Figure 3 shows the process of synthesis of analog signal, and Figure 4 the process of digitization.
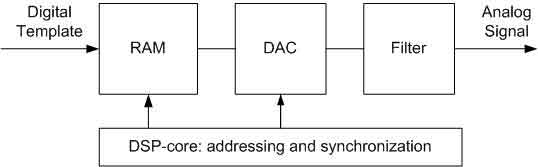
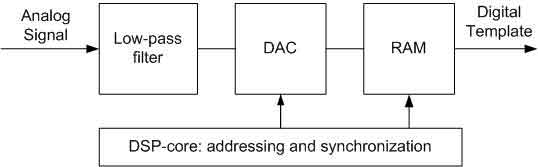
The advantages of ATE based on DSP-cores
There are following advantages building ATE using DSP-cores:
- accuracy;
- speed;
- ease of use;
- more measurement information;
- the size and power. [2]
The disadvantages of ATE based on DSP-cores
But also there is some disadvatages:
- Bit depth required to achieve acceptable accuracy, and requirements for bandwidth make DSP expensive.
- When you only have one dimension, a purely analog testers are cheaper.
- Flexibility of equipment is a challenge for an inexperienced operator, as it is necessary to know the theory of their use.
- Tester should know the physical and mathematical principles that lie behind each test and the source of errors. [2]
The advantages of using FPGAs for implementing DSP-oriented devices
In developing systems for digital signal processing (Digital System Processing, DSP) is the traditional approach, which uses DSP-processors for general purpose, but required specific processing algorithms implemented (mostly written in C). Recently, however, is increasingly possible to observe the use of hardware-based methods using the programmable logic integrated circuits (FPGAs) with FPGA-architecture as preprocessors and coprocessors. This approach allows to obtain significant productivity, gains lower cost and power consumption of the system. However, its widespread distribution hampered by the developers of DSP-systems do not always have experience in design based on FPGA. [7]
FPGA architecture is more flexible at its base can be implemented parallelization of operations, to significantly improve the performance of the whole DSP-system. The most typical examples of such use FPGA - Implementation of Fast Fourier Transform, digital down conversion, blocks of forward error correction. [7]
Additional opportunities for parallel operations of signal processing, optimal distribution of functions in a system with an FPGA co-processor ensures the availability of built-in FPGA processors. Microprocessor MicroBlaze (soft processor, in the terminology of Xilinx) provides for the possibility of implementing it on different FPGA series and it is often convenient to organize the management of system. [10]
Research Summary
By this I`ve got the following results:
- Existing methods for generating analog test were overviewed;
- Debug FPGA-board Xilinx Spartan 3AN was selected as an element base for the implementation of hardware and software generator analog test;
- Experimental device for generating analog test was developed and researched.
Structure of the developed device is shown in Figure 5.
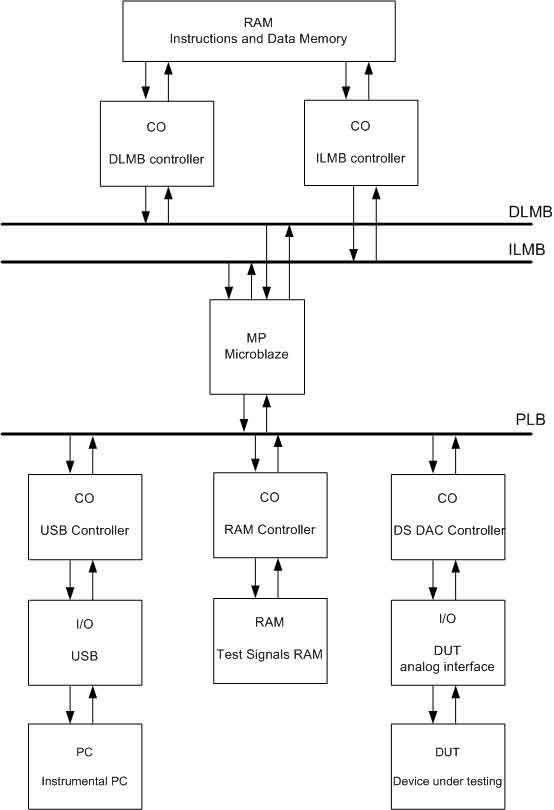
Conclusions
Existing systems of automatic generation of analog tests are not always effective, full-automated diagnostic systems for the analog-digital circuits are not created, so the problem of developing of methods for automatic generation of analog test is very actual.
References
- Давыдов П.С. Техническая диагностика радиоэлектронных устройств и систем / Давыдов П.С. // М.: Радио и связь, 1988. — 256 с.
- Agrawal V.D Essentials of electronic testing for digital, memory and mixed-signal VLSI circuits / Agrawal V.D, Bushnell M. L. // Boston: Kluwer Academic Publishers, — 2000, 650 p
- Bapiraju Vinnakota. Analog and mixed-signal test / Bapiraju Vinnakota // Prentice Hall PTR, 1998. — 261p.
- Prithviraj Kabisatpathy Fault Diagnosis of Analog Integrated Circuits / Prithviraj Kabisatpathy, Alok Barua, Satyabroto Sinha // Springer, 2005.
- A. Birolini, Quality Reliability of Technical Systems / A. Birolini // Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1994.
- F.J. Langley, Printed Circuits Handbook / F.J. Langley // McGraw-Hill Publishing Company, Inc., New York, pp.21.1-21.26
- Перекрест А.А. Преимущества использования сопроцессоров на базе ПЛИС FPGA в системах цифровой обработки сигналов [Electronic resource] - Access mode to article: http://www.electronics.ru/issue/2006/6/18
- J. Galiay. Physical versus logical fault models MOS LSI circuits: Impact on their testability / J. Galiay //, IEEE Transactions on Computers, Vol. C-29, pp. 527-531, June 1980.
- Рувинова Э. Внутрисхемный контроль жив и будет жить // Рувинова Э./ Электроника: Наука, Технология, Бизнес, № 5 - 2001г.
- Ридико Л. DDS: прямой цифровой синтез частоты [Electronic resource] - Access mode to article: http://ru3ga.qrz.ru/UZLY/dds.htm