Abstract for masters project
The work purpose
The aim of this work is to develop a software system of logical inference in a complex to a universal software tool for constructing knowledge bases with the use of ontologies as the second part of the shell tool that provides analysis of the functioning of complex economic processes.
To do this you must create an ontological knowledge base that contains the methods of construction and operation of certain types of businesses.
Relevance of the topic
Trend of development tools, analysis models of economic processes, such as models of the business plan of the enterprise, leading to what has become urgent to solve not only problems of analysis (evaluating the effectiveness of the enterprise), but synthesis (synthesis of the required business plan). In other words, do not build separate business models and to analyze them and perform the synthesis of the desired business model followed by analysis of the finished model. In the synthesis process should be not the desired process, and analyzed a set of requirements to a process for the possibility and efficiency of their implementation. Model space and time [1], which may occur within the process models serve as a means or mechanism for evaluation and analysis of data requirements.
Scientific novelty
1. The method of creating rules of inference based on a production model that will accurately track the relationship between versions of objects in the knowledge base.
2. Method of organizing the system interface output with the end user.
3. Algorithm for the organization pass on knowledge modules that make up the knowledge base that can reflect the desired algorithm for the analysis of complex economic processes.
Overview of software systems for financial and economic activities
In this review, as an illustration of the use of expert systems technology in the financial activities are examples of some of the most common specific development of EC [2]. The scale of studies and proposals on the market of EC in the field of finance can be judged by an international scientific conferences and business directories in which the cost of specific applications ranging from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars [3].
The IDE G2
The main purpose of the software product family G2 Ч to help companies retain and use knowledge and experience of their most talented and skilled employees in intelligent real-time systems that improve product quality, reliability and security of production and lowering production costs. Tools G2 [4] is an evolutionary step in the development of traditional expert systems from static to dynamic domains.
The main purpose of the software product family G2 Ч to help companies retain and use knowledge and experience of their most talented and skilled employees in intelligent real-time systems that improve product quality, reliability and security of production and lowering production costs. Tools G2 is an evolutionary step in the development of traditional expert systems from static to dynamic domains.
Financial Analysis: PROF
One of the main advantages of the program for financial analysis, "Financial Analysis: PROF" [5] is the ability to create on the basis of financial statements (balance sheet and income statement) of the analytical text report on the financial status of the organization in a short pomezhutok time after the start of the program, with the possibility of edition of the report template.
Draft SUPER
The project [6] will develop tools that support analysis, editing and creation of business processes aimed at improving the flexibility and adaptability of organizations. The planned instrument will be based on semantic annotations of artifacts relating to the business process management (operations processes, services, etc.). This abstract will create more efficient queries, and perform automated concluded that, in turn, will allow users to perform "semantic" search component of business processes, "semantic" making the business processes and "semantic" interaction of business processes.
Currently, the projected system ontology ("SUPER Set of Ontologies for Business Process Management") consists of 8 sections, the operation of which is shown in Figure 1.
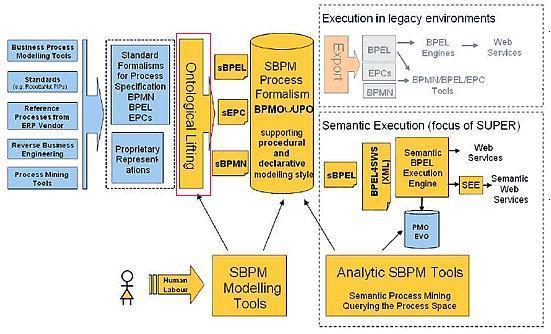 Figure 1 - Scheme operation SBPM.
Figure 1 - Scheme operation SBPM.
Planned research and development
The task of analyzing the functioning of complex economic processes based on multilevel models of space and time in practice means the following:
1. An investor who decides to invest in construction companies for the production of certain products such as bakery, wants to explore possible ways of creating this company.
2. He may invite an expert to establish such an enterprise and, using his experience, in dialogue with them to get answers to specific questions such as:
Ч At some point in time we can construct access roads;
Ч Can I install equipment in parallel with the construction of a warehouse of finished products;
Ч Whether in the first year already have a ready industrial building, etc.
Such questions indicate the feasibility of building an analysis of the enterprise in ways attractive to investors.
The disadvantage of involving an expert is expensive, opaque and unchecked confidence level of information received.
Answers to such questions can be obtained by building in an environment of a software package capable of analyzing the performance of the enterprise business model, built one way or another. For example, it could be a package Project Expert.
However, a similar problem could be solved with an appropriate software package, if it had these features:
Ч Gain experience of proven solutions obtained from any source and actually build the knowledge base;
Ч Experience of these decisions is a description of the object structure, taking into account the space and time;
Ч Provide an analysis of complex economic processes based on multilevel models of space and time, using the means of organizing such an inference in the knowledge base.
This problem can not be solved practically in one of the known packages. However, for these purposes, you can use universal tooling system for constructing knowledge base using ontology developed Master V. Bolotov [7], based on world model proposed by MIT associate professor DonNTU AV Grigoriev. Specificity of this model is taking into account physical semantics of subject areas, including multi-level model of space and time, as well as focus on supporting the establishment of instrumental shell to generate intelligent CAD.
Proper analysis in this case lies in the numerous checks of the results of certain features of the process of construction and operation of the business, user-defined in previous times, in particular business development at subsequent times.
In fact, in the main problem is to construct a system of logical inference [1]. This means that must be fulfilled the following stages:
1. Creating rules of inference based on a production model that will accurately track the relationship between versions of objects in the knowledge base.
2. Organization of user interface, which will convert the input considerations absorption and directives to the user's mind, understood and accepted the system and output messages ES - to a form familiar and understood nomu for the user.
3. Algorithm for the organization through all the knowledge modules that make up the knowledge base that can reflect the desired algorithm for the analysis of complex economic processes.
The result of the practical operation of the system output must be a specific life cycle process of construction and operation of the company meets the required structural features.
Methods for solving tasks can be described as follows
1. Business model is an alternative set of life cycles of various sizes, eg 2 years, 3 years, 4 years. Selecting an appropriate method has stage set number of years of your company.
2. The life cycle of a hierarchy of modules of domain knowledge [8], taking into account the specific time frame, such as life-cycle of dimension 2 is a union of 2 models of spaces: 1 year, 2 years. Accordingly, life cycle of a 4-stage model presents 4 of the space.
3. Selecting a life cycle such as the dimension of 3, involves the implementation of links between models of space. For example, Year 1 is associated with the second, 2 nd only to the 3-meter.
4. Model of space each year is a unit of knowledge. He has a hierarchical structure of the set of classes and their instances (objects).
5. After completing the synthesis of a certain module of knowledge will be obtained internal structure of the block, where there will be sub-blocks, and connection between them. The collection of links defines a variant of the external borders of the lower modules of knowledge that is given this name, sub-block [8].
We give an example of generalization relations at the level of ordinary properties. Suppose there is a lot of prototypes belonging to some type of block A: A '= (P1 ^ P2 ^ P3). Each link, which takes place in at least one prototype gets its original number of cross-cutting within the type.
Characteristics of the individual prototypes belonging to type A, both sets of relationships shown in Figure 2.
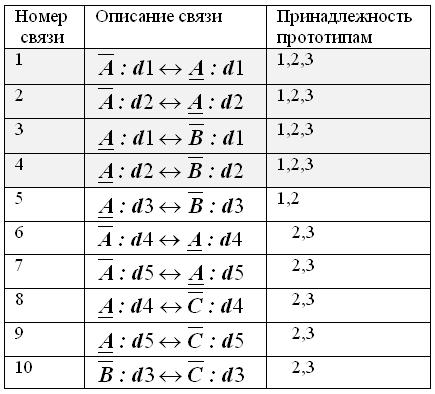 Figure 2 - Description of the set of bonds in the type of unit
Figure 2 - Description of the set of bonds in the type of unit
6. On the existing list of submodules of knowledge select the 1 st submodule and provides synthesis of its internal structure. Then go to the underlying level and so on until the basic units that are not modules. Then return to Step 1 above and again moving down and then act in a similar manner, avoiding the tree of modules from top to bottom left to right. When he reached the last extreme right submodule end conclusion on the fact of watching all the modules.
7. Dialogue the user selects a specific alternative in the knowledge module is built on these principles:
Ч Message on the stage at which it is located;
Ч Consider only those options sets of sub-blocks, which are possible in this scenario;
Ч Each such option sub-blocks can be identified by number and list the actual sub-blocks;
8. Actually synthesis consists in choosing the appropriate module of knowledge from knowledge base [9] is used in some context, for example, "structures" which, for example, occurs in 1-year, and then its restriction to a particular decision. The collection of such specific solutions in all possible contexts and will be the required solution. In our case, this description of the life cycle of business development with the desired characteristics. This decision is issued to the user as the results of the output. If there are many results, you are given everything.
he work program of the system suggests a generalized representation of a life cycle of many of the same economic facilities, and each life cycle is tied to various conditions of operation of the facility. In fact, the output of a generalized description of the structures formed by a number of features assigned to different life cycle at different points in time (Fig. 3).
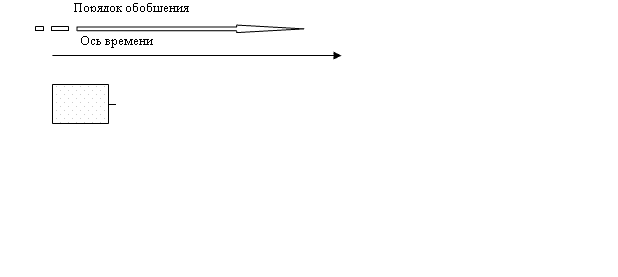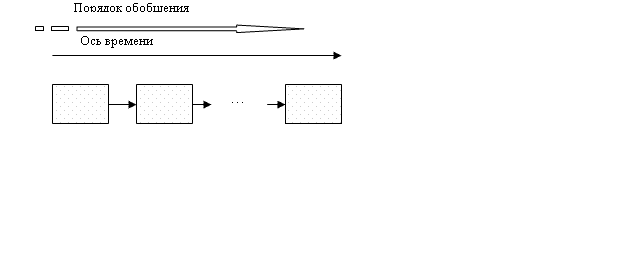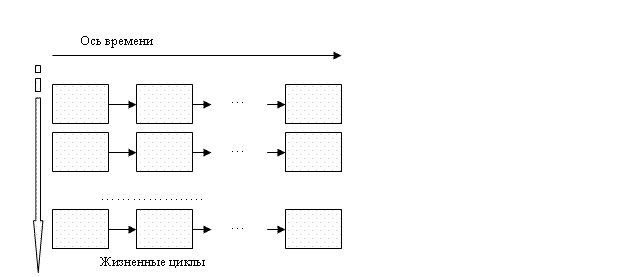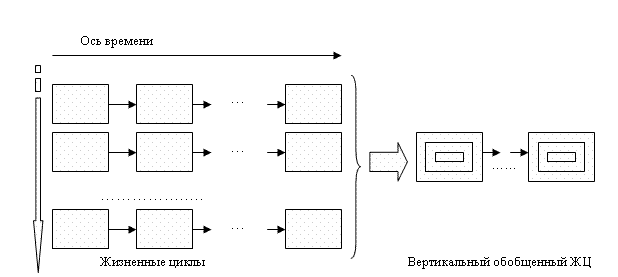 Figure 3 Ч Vertical synthesis of life cycle
(Animation: Volume Ч 24 KB, 7 shots, 8 cycles of repetition)
Figure 3 Ч Vertical synthesis of life cycle
(Animation: Volume Ч 24 KB, 7 shots, 8 cycles of repetition)
Conclusions
Existing systems for functional analysis of complex economic processes, in particular modeling of the enterprise, have a variety of disabilities. Planned software system allows users to plan your travel for him features of the process of construction and operation of enterprises with the ability to track these requirements in time through a process of inference.
List of references
1. Grigoriev A. Organization of temporal and spatial inference in conceptual models of intelligent CAD // Scientific Labor Donetsk State Technical University. The series: Information, Cybernetics and Computer Science. Ч Donetsk: Donetsk State Technical University, 2008. Vol. 9. Ч S.296-311.
2. Review of the application of ontologies in modeling and management. Kudryavtsev, DV Business Engineering Group [electronic resource]. Ч Mode of access: http://bigc.ru/publications/bigspb/metodology/ontologies_for_modelling.php
3. Expert systems in financial and economic activity. Articles experts and employees Torah Center. [Electronic resource] / An Internet resource. Ч Mode of access: http://www.tora-centre.ru/library/razn/finan.htm
4. Creating expert real-time systems using G2. [Electronic resource] / website for students of Physics Faculty of Electronics and Computer Systems Dnepropetrovsk National University. Oles Gonchar. Ч Mode of access: http://lib.dnu.dp.ua:8001/l/1561.htm
5. Program for financial analysis Financial analysis: PROF. [Electronic resource]. Ч Mode of access: http://www.finanalis.ru/index.php?leaf=progs.htm&ELEMENT_ID=2249
6. Semantic Business Process Management. Integrated Project SUPER. [Electronic resource]. Ч Mode of access: http://ip-super.org/
7. Bolotov V. Tools create knowledge bases on the basis of ontology. Ч Mode of access: http://www.masters.donntu.ru/2010/fknt/bolotova/diss/index.htm
8. Grigoriev A. Complex CAD models as a system of interconnected levels of reality. Scientific works of Donetsk State University. Series "Information Science, Cybernetics and Computer Science, (IKVT 2000) 10. Ч Donetsk, Donetsk State Technical University, 2000. Ч S. 155-167.
9. Grigoriev A., Kasparov A. Features of the metaevristicheskoy shell of CAD // Scientific Labor Donetsk State Technical University. The series: Problem modeling and design automation of dynamic systems. Ч Donetsk: Donetsk State Technical University, 1999. Vyp.10. Ч S. 217-222.
|



