

Topicality
In today’s market firms are more focused on the consumer, which is manifested in their quest to meet the needs of potential consumers. For a particular consumer high quality certain goods or services means that there is such a combination of consumer characteristics, which meets his needs. One such important properties is the value of the goods or services, which largely depends on the costs associated with various operations and works. Reduce overall costs can be achieved by applying the concepts and principles in the practice of logistics companies.
The purpose and objectives of the study
The aim of this paper is to introduce an enterprise logistics system that will allow the following:
• minimize the storage of products;
• reduce time traffic;
• rationally distribute the vehicles;
• respond quickly to consumer demands;
• promptly process and give information.
Subject of study
The subject of the study are the logistics systems and methods for their introduction in Ukrainian enterprises to improve their functioning.
Scientific novelty
Today in certain sectors of the domestic market has come an era of genuine competition, ie competition associated not only with the price and quality goods, but also with the quality of care. Ironically, in this part of the traditional (Soviet) Logistics completely ignored the human factor, leaving the customer one on one with a tragic question: «Who stitched suit?» [2].
Practical significance
Application of logistic systems enable Ukrainian enterprises not only to improve their profitability, but also to gain the trust of consumers.
Analysis of recent studies and publications: The pioneers in this area are D. Bowersox and D. Closs, which concluded its works in the book, «Logistics. The integrated supply chain», which invariably reissued in the U. S. since 1974 in Ukraine, development of logistics as dedicated not a few publications, namely:
— Status and trends of development of the logistics market in the segment of FMCG. New conditions of contracts for customers of logistics providers, Oleg Kalenskii, director of strategic marketing and sales, the company «HC».
— Logistic audit as a technology for improving the efficiency and competitiveness in the example of Ukrainian retail, Andrei Radchenko, CEO Ukrainian League of Logistics and Warehousing; rapporteur Valery Yuhimov, director of LK Centre.
— Improving the efficiency of supply chain management, Cyril Rudnev, Director of Sales for Smart Business.
— The practice of risk reduction at the junctions of their supply chains, Artem Skorobogatov, head of logistics lines of «International Law Offices, the International Association Forwarderlaw.
You can also highlight a number of foreign publications on logistics in Ukraine:
— Business case: the construction of integrated logistics solutions for the Ukrainian importer, Felix Kherson, head of marketing and sales AsstrA Logistics AG (Zurich, Switzerland).
Special Report: «TRACECA project is supported by the EU,» John Standingford, transport expert project of European Union «International logistics hub between Europe, the Caucasus and Asia.»
The first mention of «logistics» dates back to the days of ancient Greece, Byzantium and the Roman Empire, where the term generally means food distribution or supply of military forces the necessary resources.
In the early 50’s. XX century. The term «logistics» has been applied in business, and to the 70 th years. entrenched in this environment. During the historical period, there were also significant changes in the global economy, which explain the phenomenon of logistics off [1].

The main ones are as follows:
• The information technology revolution and the introduction of personal computers (PCs);
• globalization of the market;
• changes in state regulation of economic infrastructure;
• pervasive philosophy of TQM (total quality management);
• Increase partnerships and strategic alliances [1],[5].
Logistics has been used in many fields of industrial and human activities.
Logistics within the company is directly related to the concept of material flow. Material flow — in a state of motion of material resources, work in process and finished goods to which the logistics operations or functions and are associated with physical movement in space (loading, unloading, transportation, sacking production, downsizing, etc.). Classify the material flows can be on the following principles:
— Relation to the logistics system:
• appearance;
• internal;
• input;
• output.
— Composition of wealth:
• odnoassortimentny;
• multiassortment.
— The scale:
• Mass;
• large;
• the average;
• shallow.
— Nature and massiveness gruzoedinits:
• heavy-handed;
• Lightweight.
— The degree of compatibility gruzoedinits stream:
• compatible;
• incompatible.
— Consistency gruzoedinits stream:
• bulk cargo;
• liquid cargo;
• navolochnye goods;
• commodity-unit-loads [2].
In a market economy, the survival of enterprises gain their competitive advantages are possible only if they are necessarily continuous organizational and technological transformation, with the aim of bringing real-life production to its optimum design, kept pace with the knowledge, techniques, technology, organization and management. Optimal project organization must conform to the current level of technology, art and culture of the organization and management of enterprises.
Modern organization and operational management of production (material flows) must meet several requirements.
— Provision of rhythmic, coordinated work of all branches of production under a single schedule and uniform output.
— Maximize the continuity of production processes.
— Ensure maximum security plan calculations and the minimum complexity of planned work.
— Ensuring sufficient flexibility and agility to achieve this objective, in the event of various deviations from the plan.
— Ensuring continuity planning guide.
— Ensuring that the system of operational management of production type and nature of the production.
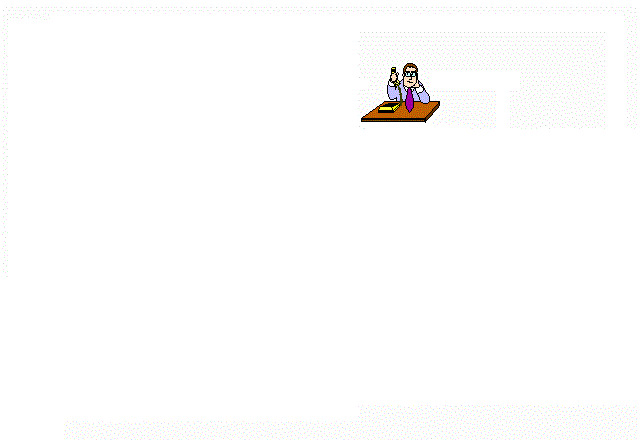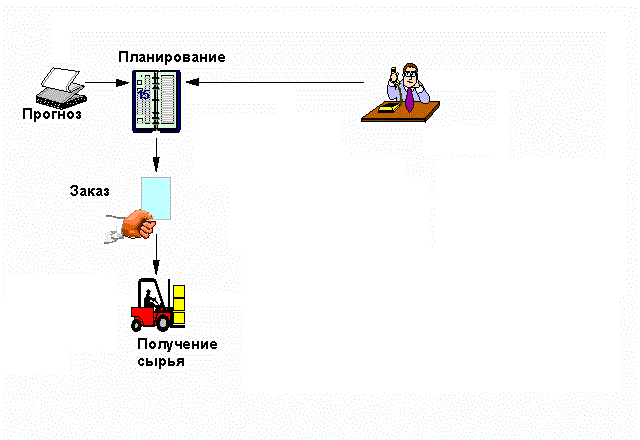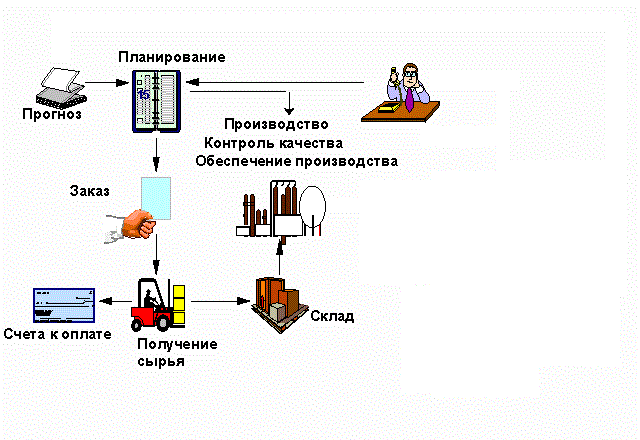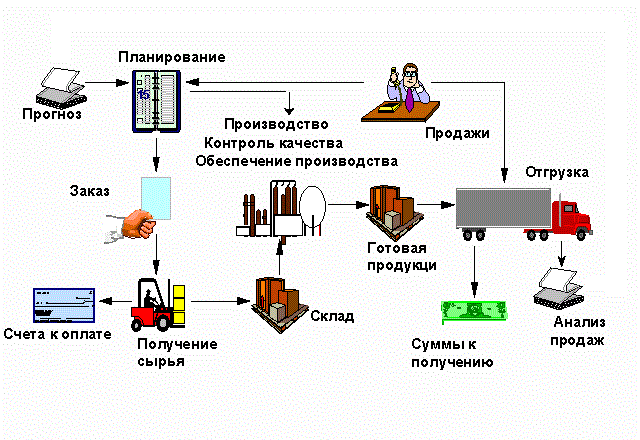
To ensure these requirements are applied logistic systems.
Warehouse Management System (Warehouse Management System) — control system, which provides automation and optimization of all processes of the warehouse company profile.
Purpose of introducing such a system are as follows:
• active inventory management;
• increase the speed range of goods;
• to obtain accurate information about the location of goods in a warehouse;
• Effective management of goods with limited shelf life;
• receiving a tool to enhance the development of processes for handling goods in a warehouse;
• Optimizing the use of warehouse space [4].

The system of customer relationship management (or CRM, abbr. From the English. Customer Relationship Management System — a system of customer relationship management) — the corporate information system designed to automate the CRM-company strategy, in particular, to increase sales, optimize marketing and improvingcustomer service by storing information about customers (contractors) and the history of relations with them establish and improve business processes and then analyzing the results. The term «CRM-system» refers to software (SW), aimed at implementing the concept of CRM.

System of supply chain management (Supply Chain Management, SCM) designed to automate and control all phases of enterprise supply and to control all movement of goods across the enterprise.
The objectives of SCM are:
• increase the level of service;
• Optimization of production cycle;
• decrease in stocks;
• increase the productivity of the enterprise;
• improving profitability;
• Control the production process [9].
According to AMR Research and Forrester Research, with the introduction of SCM companies have competitive advantages such as reducing the cost and time of order processing
In the transition of Ukraine’s economy to market relations, the importance of logistics increases. There are five factors that determine the importance of logistics in the period of transition:
— The economic factor. In modern conditions the fore seek opportunities to reduce production costs and distribution costs for profit. Logistics allows us to relate the economic interests of producer goods and consumer.
— Organizational and economic factor. In a market, as the emergence and development of new organizational forms that implement promotion processes, are becoming increasingly important form of integration of management and coordination, provision of logistic processes of interaction between manufacturers, consumers, brokers, warehouses and transportation.
— The information factor. A market economy promotes the development of information links, which are the cause and a consequence of market relations, vzaimoobuslavlivayut each other. Computers are most closely linked market and logistics, as its subject, tool and component of the logistics processes are information flows.
— Technical factor. This factor is manifested in the fact that the logistics of the system and its subjects and objects of governance are developed on the basis of modern technological advances in transportation and warehousing management and computerization.
— State support of promotion processes. Under modern conditions there arises the problem of regulation promotion processes not only at the enterprise level, but also across regions, as well as on a national scale [3].
Claim scientific approaches and practices of logistics coincided with the beginning of Ukraine’s transition to market relations. As shown by international experience, the need for a particular theoretical apparatus and practical tools to logistics management depended on a number of conditions prevailing at a particular historical period. These conditions include the following: the level of development of productive forces, the level of technological development, political environment, maturity of market relations.
Findings from this study and perspectives:
Without going into a detailed economic analysis can be formulated in general terms, fundamental difficulties that exist in the development of the logistics concept in Ukraine:
• severe general economic situation and social tensions in all strata of society;
• underestimation of the long-term significance of the sphere of circulation (supply and sales), which the West holds key positions in logistics (historical sphere of circulation in the country behind the sphere of production, resulting in slow progress to the final consumer goods, poor service quality and consumer etc.);
• lagging infrastructure of the economy, even from the average world level: the irrational development of distribution structures, low level of development of modern systems of electronic communications, underdeveloped transport infrastructure (particularly in the areas of roads), technical and technological level of development of vehicles;
• The low level of production and technical and technological base warehousing;
• weak development of manufacturing industry of modern packaging, etc. [3].
References:
1. Business training, Mc Gill, Henry Mintzberg, [electronic resource], http://www.training-world.ru/business/logist/305/
2. Johnson, DS, Wood DF, Vordlou DL, Murphy, Jr., PR Contemporary Logistics, [Book]-M.: Williams. −2004. −624 Sec.
3. Distribution and logistics, [electronic resource], http://www.ukrlogistika.com.ua/
4. White A. W. Control of production and inventory in an age of computers. Moscow: Progress, 1978.
5. Logistics, ed. Professor BA Anikin, Moscow: INFRA-M, 1999
6. Gordon MP, Karnaukhov SV Logistics of product distribution. — Moscow: Centre for Economics and Marketing, 1999.
7. Hadjinsky AM Fundamentals of logistics. — M.: ITC Marketing, 1996.
8. Oklander MA The contours of the economic logistics. — K.: Naukova Dumka, 2000.
9. Mathe, E., Tiksi D. Logistics of the company: transl. with the French. / Gen. Ed. VSZagashvili. — M.: Pogress, 1993.
10. Golikov, EA Marketing and Logistics .- Moscow: Publishing House «Scientifically,» 1999.
Whlie writing of this abstract master thesis is not completed yet. Final Completion: December 2011. Full text of the paper on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.