Speciality: the "Environment metallurgy"
Content
Introduction
1. Theme urgency
2. Goal and tasks of the research
3. The object of the research
4. Novelty of work
5. The practical importance of results
6. Water companies steel
6.3. Rolling Shop
7. Requirements for quality of water of the technical and training systems water supply industry
8. Water system hazyaystva drainage and waste-free technologies in metal production
Conclusion
Literature
To date, metallurgical and metalworking enterprise is are among the main consumers of water. The total amount of water consumed per 1 ton of steel is 200 - 220 m3 is 22 times higher than in EU countries. Therefore, in recent years, the iron and steel plants on a large scale are carried out organizational and technical measures aimed at rational water consumption and reducing waste water discharge into water bodies, as well as by the construction of sewage and other water facilities in order to prevent contamination of natural waters.
The relevance of this topic is vozvrastayuschem consumption of water resources in the metallurgical industry and the lack of conditions for the region.
2 GOAL AND TASKS OF THE RESEARCH
The purpose of this paper is to analyze the consumption of water in the metallurgical and find solutions to reduce water consumption.
The main objectives outlined in this paper are:
- The allocation of the factors influencing the increase in water consumption;
- Search the main sources of industrial water supply, with minimal damage to the OS;
- Consideration of the prospects for the introduction of low water and waterless technology;
- Finding ways to reduce water consumption in metallurgical processing.
The object of study is water consumption of metallurgical production
Consideration of the prospects for alternative water supply sources for metallurgical enterprises
5 THE PRACTICAL IMPORTANCE OF RESULTS
The result of the proposal will yavlyatsya ways to reduce water use in industry and prospects for the introduction of low water and waterless technology
Metallurgical plants consist of three main departments: blast furnace, steelmaking, rolling and many other auxiliary facilities. To conserve water, most smelters use of water recycling.
Typically, the water recycling system consists of separate cycles for each of the shops and facilities, other than water quality and necessary water pressure of the networks (Fig. 1).
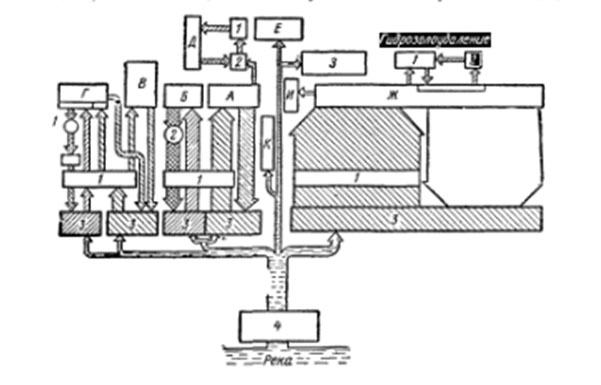
Figure 1 - A - blast furnace plant, B - gas cleaning; B - steelmaking shop; T - Rolling shop; D - filling machines, E - Coke plant, F - CHP and parovozduhoduvnaya station, SW - department of refractories, and - chemical water treatment, and K - Other shops, 1 - pumping stations cycles of water recycling, 2 - ponds, 3 - spray pond; 4 - the first lift pumping station.
Total water consumption for industrial needs of the modern factory with a full metallurgical cycle, including coke and refractory production, power plants and auxiliary shops, 1 ton of smelted iron repartition it in steel and rolled up 220 m3, including 3 to 5% of fresh water .
The basic amount of water (about 75%) is spent at a metallurgical plant in cooling design elements, units (blast furnaces, steel melting and heating furnaces) and the condensation of vapor on the blower and power stations. Up to 22% of water consumed is for cooling directly to the equipment and products (gas and metal), as well as the transportation of solids, while water and heated, and fouls. A small amount of water (about 3%) is spent on other small needs.
For the main shops of metallurgical plant requires uninterrupted supply of water.
In the blast furnace shop rodukty production - iron and slag - produced from the furnaces into ladles. Water in the smelting of iron consumed in the hydration of the charge, the cooling of blast furnaces and stoves, and accessories for small needs. In addition, the water in the blast furnace shop is spent on the slag granulation, cooling of cast iron casting machines and podbunkernyh premises.
Water blast furnace can be single-band or two-zone. With all the single-band water supply cooling water is fed into the blast furnace coolers under one common pressure, sufficient for its admission to the highest point. In the two-band water supply water for the bottom of the oven (steam out, shoulders, tuyere zone furnace and leschad) is served by one (low) pressure, and for the top - with a different (high) pressure. In recent years supply of large blast furnaces satisfied with single-band. As with single-band and two-band for water supply, water is supplied to the domain shop for two independently operating conduits and networks (parallel conduits), as shown in (Fig. 2).
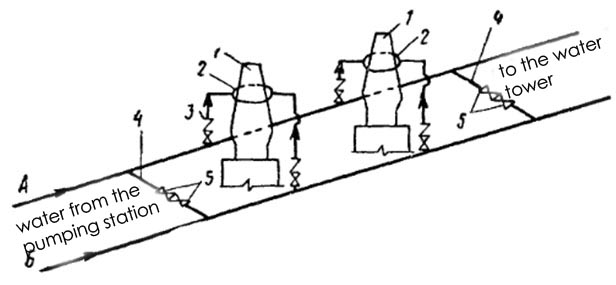
1 - blast furnaces, and 2 - Water-ring stove, 3 - check valves, 4 - jumpers, 5 - valves.
Figure 2 - Water blast furnaces
Water blast furnace - recycling, waste water from refrigerators stoves ovens and fittings merged into the receiving box and goes for a cooling tower or spray pond, chilled water pumps and climbs again served in the shop. The required pressure in the recycled water network at the blast furnace is from 45 to 70 m depending on the efficiency of the furnace.
Currently used mostly semi-dry granulated slag, and a new blast furnace - a wet granulation in the trenches with the clarification of recycled water in the sump. Consumption of recycled water in the wet granulation is 8 m3 per 1 ton of slag is lost in both cases about 1 m3 per 1 ton of slag.
Total water consumption in the spill of 1 ton of pig iron up to 4 m3, with about 20% of water is lost. Water recycling with purification of waste water from the broken pieces of iron and lime in the sump. The losses in the system recharged with fresh water.
In the steelmaking shops is made of cast iron, steel smelting.
Steel production can be done in the following ways: converter, open hearth and electrofusion, and sometimes use a combination of these methods. Melted steel is poured into molds and sent to rolling mills. At the present time is widely used in the continuous casting of steel ingots for the subsequent long rolling sections.
In the converter shop water is consumed for cooling blowers and oxygen machines, gas scrubbing, as well as various small needs; purified gas released into the atmosphere. Total water consumption ranges from 15 to 26 m3 per 1 ton of steel produced, including 4 - 5% of fresh water.
In the Electric shop melted high-quality alloy steel and ferroalloys. Melting is carried out in electric furnaces in which the necessary melting temperature of the combustion space is provided by electric arcs formed between the charge and the electrodes.
Water in the Electric shop is spent on cooling clamp electrode holder (it is necessary to avoid excessive heating clamp current of great strength, passing over the electrodes, and also stand out in the furnace hot gases) to cool the electrodes in the places they pass through the roof, where the cooling water flows through the tube rings to cool and release zavalochnyh-puff boxes, transformer oil, etc. In addition, the water is spent on cleaning the exhaust gases from the melting front, releasing them into the atmosphere.
In each steelmaking shop (converter, electro oven) arrange two cycles of water recycling: a series of uncontaminated cooling water to the cooling tower and the cycle of gas-purification of polluted water from the sump and the cooling tower. Production tests are conducted on the use of recycled water, without gas cleaning cooling.
In the steelmaking shops, water is supplied in the form of a soul on cooling were located in the molds that are installed on trucks. Consumption of this water is taken into account in the total consumption of water in the shop and is 30 - 50 m3 / h, including 10 - 15% of fresh water.
In rolling mills steel ingots are rolled into the metal of the variety of backgrounds. The technological process of rolling is divided into two main cycles: the heating of ingots before rolling in a heating furnace or soaking pits and hot-rolled bars.
In the rolling shop of the bulk water is used for cooling rollers and bearings in order to avoid over-heating them in constant contact with hot metal, rolls sprinkled with water from them above the perforated pipes or gutters.
The water pours down on the rolls, cools it and washes away the dross, crumbling with a rolled metal. Wastewater flows into the channel under the cage. The bulk of the scale of many large mills can be removed in the car, mounted under the hopper, through which poured scale. On most modern mills are poured under the standard scale transport water to the shop settling pits, and for transportation of slag consumes water used consecutively or repeatedly (sometimes after cooling the furnace). The water consumed per flush and transport scale continuously. After the workshop (primary) water clarifiers further purified from small scale and oil in the secondary settling tanks and then fed to re-use. In some plants, instead of secondary clarifiers have adopted open hydrocyclones.
The water in the rolling mill is spent on cooling as oil and air (for large electric motors) in a closed tube refrigerators. It is desirable that the temperature of cooling water was not above 25 ° C. In some cases, water is still on the hydration of air supplied to the engine room or workshop. For this purpose, use water that has the qualities of drinking water. Mode of consumption of water mills and the number of very different view of the variety of mills, as well as due to the fact that at the same mill may be different varieties of rolled metal and profiles.
Waste water from the pickling bath containing acid and iron, and under present conditions are sent to the plant for the extraction of iron sulphate. Runoff and leaching of the metal after etching coming to neutralize the lime and bleaching; same goes here, and lime water. Neutralized and clarified waste water from washing the metal normally used for the same purpose with your self-loop water recycling.
Water recycling rolling mills, usually with a separate (different tubes), water supply: the heating stoves - clean water, to the rolling mills - contaminated water (Fig. 3).
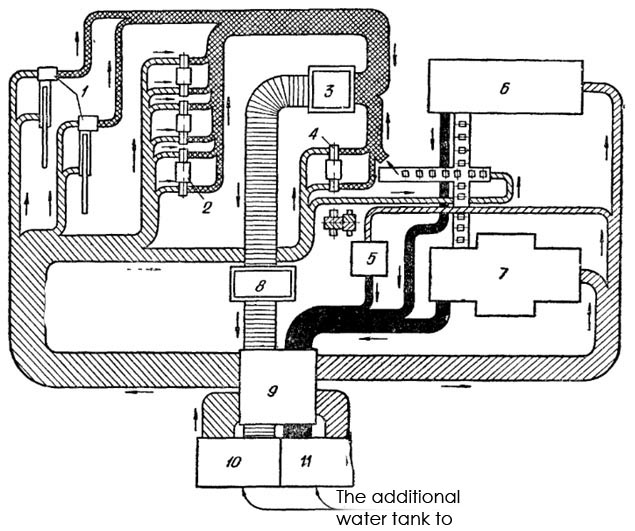
1 - scissors, 2 - rolling stand, and 3 - the primary sump (pit scales), 4 - crimp cage 5 - oil cooling, 6 and 7 - heating furnace number 1 and 2; 8 - secondary clarifier 9 - recycled water pump station, 10 - coolers contaminated recycled water, 11 - Coolers clean recycled water.
Figure 3 - Water supply rolling mill
In the rolling mills, emphasis should be given to ensure continuity of water flow to the heating furnaces. The water flows here on hearth or glissazhnym pipes, which is continuously moving bars of steel, heated prior to rolling. In the event of termination of water flow to the heating furnaces within a short time (as soon evaporate the remaining water in the pipes) glissazhnye and hearth burn down the pipe, and the promotion of steel ingots in the furnace stops. As a result, the cycle is broken metal rolling and heating furnaces require repair.
Termination of the water supply to the rolling mills are also not allowed, although it is not there a danger, both for heating furnaces. In the event of termination of flow of water mills should be shut down to prevent damage to bearings and rollers; permissible only short-term reduction of water supply for 25 - 30%.
7 REQUIREMENTS FOR QUALITY OF WATER OF THE TECHNICAL AND TRAINING SYSTEMS WATER SUPPLY INDUSTRY
The problem of protecting the environment is one of the major and pressing issues of today. The main challenges facing professionals in this respect, lies in the fact that the mustache ¬ loviyah further growth in output reduce the cost of water and the volume of wastewater to reduce emissions into the water basin, reduce the amount of solid waste and eliminating the negative impact chit production of steel production on the environment. For economic reasons, ecological requirements, and limited supplies of water in natural sources in industrial plants is recommended to construct a system circulating water supply, where water is used many times.
Depending on changes in water quality in the process of recycling of water is divided into:
A. "Clean cycle" - the water that is heated only when you use;
Two. "Dirty cycles" - water that is contaminated only;
Three. "Combined" - for water, which when used together and heated, and fouls.
For industrial companies of the 1st group process water is regulated by limiting the temperature of water used. Its optimum value of about 150S.
In a system of water recycling carbonate hardness of water used as coolant Ca and Mg, should not exceed 2.8 ... 3.0 mEq / l, and allowable concentration of suspended matter is taken depending on the speed of water in the cooling apparatus. These consumers do not allow increasing solids content above 50 ... 100, sulfate higher than 40; hydrogen sulfide greater than 0.5, higher oil 1 ... 2 oxygen above 4 ... 6 dry residue higher than 1000 (mg / kg) mg / l.
Water used as a medium for the laundering and Hydrotransport material is released only from the coarse mixture. This applies to customers in Group 2.
For consumers, the third group of water must be chemically treated and the total salt content in it should not exceed 100 ... 2000 mg / kg, depending on the pressure produced by the steam. Almost all industrial water users do not impose specific requirements for its color, smell, taste and content of the bacteria.
The current industry-leading work on the preparation of water in the water supply system is aimed at maximizing the use of water in the circulating system and the creation of closed water systems of individual plants, industries, and in the future, enterprises as a whole. Figure 4 shows one of the options for water treatment.

1 - lift pump station, and 2 - drum nets, 3 - peagentnoe economy; 4 - cloisonne mixer, 5 - vortex chamber flocculation, 6 - horizontal settler, and 7 - Enter the reagents for the deodorization and filtration process intensification: 8 - a quick filter, 9 - installation for disinfection of water, 10 - tank of clean water, 11 - Pump Station II boom.
Figure 5 - The main water treatment flowsheet.
One of the main areas of water conservation is making further reductions in consumption of fresh process water sewage by improving manufacturing processes.
Current is to increase the utilization of water from alternative sources of supply. However, the most readily available non-conventional sources of water supply enterprises of ferrous metallurgy can become surface runoff and past biological treatment of municipal wastewater.
The use of these waters for the needs of the industry has a dual effect. First of all, is significantly reduced dumping household sewage into water bodies. This leads to a significant reduction in the required amount of dilution water (10 - 15 fold) and at the same time reducing the consumption of fresh water from prirodnh sources. To solve this problem, identify technically and economically feasible scheme of purification of water after biological treatment plants. Systematic problem solving will continuously improve the performance of water resources and approach the drainage regime.
8 WATER SYSTEM HAZYAYSTVA DRAINAGE AND WASTE-FREE TECHNOLOGIES IN METAL PRODUCTION
Creating a closed bsstochnyh water systems based on the organization of water recycling systems, including the use of the allocated area with surface water and the company treated municipal wastewater, local waste water treatment and regeneration of spent process solutions in order to re-use in production with simultaneous recovery and recycling of valuable components as well as the development of new technologies, characterized by a significant reduction in consumption of raw water and the formation of polluted runoff, or total exclusion of water from the manufacturing operations. Creating a closed system of water recycling industry is based on a radical change in the existing principles of organization of water supply, sewerage and wastewater treatment.
Water management company should be considered as a complex system, including water and sanitation, and wastewater treatment is seen as preparing them for reuse. The basis of closed water systems are the current local water cycles in which consumers are combined with the same requirements for water quality and similar contaminants. The quality of recycled water is determined on the basis of evidence-based claims. Local current system are combined into a single set of water management by using the cascade principle - the original water supply to customers with special requirements for water quality, and the purging of the system is fed by water systems with lower quality.
The main source of industrial water supply should be treated industrial and urban waste water and runoff from the territory of the enterprise. Fresh water from water sources should be used only for special purposes and to fill water losses in the systems. Wastewater treatment and regeneration of technological solutions used methods to ensure the simultaneous extraction of valuable components to produce marketable products or recycled for further use. In the design of the main production ¬ nology should be conducted at the same time the design of water supply systems in the light of evidence-based claims to water quality and strict regulation of water use and sanitation. Development of new processes should thus be characterized by a significant reduction in consumption of raw water and the formation of polluted runoff, or total exclusion of water from the manufacturing operations.
For indirect systems working capital items of equipment used in the steel industry, as well as in other industries, ¬ gih, creating besproduvochnogo mode, and use to recharge treated wastewater is primarily due to a solution of the problem of corrosion of pipelines and equipment and deposition salts, air-conditioned water.
For the basic iron and steel industries - aglodomennogo, steelmaking and rolling - the most serious problem in creating a closed system drainage water is desalination of highly wastewater produced in the boiler water desalination, power plant blowdown, neutralization of rinsing water etching and degreasing solutions, as well as the rascally local waters water recycling systems.
Are effective methods to use waste water production as a make-up water supply systems of other manufactures. This is especially important for these waste waters, as phenolic waste water and neutralized
acid-containing waste water, disposal and reuse of which presents considerable difficulties. The use of phenolic wastewater in the form of supplements to the make-up water systems, water recycling can significantly reduce the rate of corrosion of metal heat exchangers. This is due to a sharp decrease in the circulating water of dissolved oxygen, which reacts with organic and inorganic substances easily oxidized (hydrogen sulfide, thiosulfate, cyanide, etc.) contained in the phenolic water.
Despite the importance of these principles create a closed drainage systems, water management, the most radical and promising is the introduction of low water, and anhydrous tehnoogii. By this means these processes, the use of which can significantly reduce water consumption, the amount of sewage and the degree of contamination, or completely eliminate the use of water and waste water. It should be divided into two main areas - improving cooling technology and implementation of appropriate manufacturing processes.
In the steel industry to production processes, completely eliminates the use of water in the first place should be carried ¬ ty dry gas cleaning. For modern EAF furnaces in the foreign and domestic practice, usually include only dry gas cleaning for oxygen converters used primarily drainage system as the process gases without post-combustion and post-combustion, and with the subsequent purification of wet-type apparatus. However, when using konverterngo gas as a fuel application of dry cleaning facilities is much more economical.
Having examined each of metallurgical and proanalizirovov their need for water consumption, we can conclude that the major trends in the reduction of water-intensive production may be the following measures:
- Replacement of evaporative water-cooled furnace;
- In the blast furnace gas cleaning scrubbers, electrostatic injector replacement;
- The work of the non-afterburning converter gas;
- The introduction of dry-cooling and cleaning of flue gases;
- Replacement of open hearth furnaces converters or DSP, and others;
However, at present in connection with the general increase in the volume of water consumed and the scarcity of fresh water is particularly characteristic of the conditions of the Donbass, neobohodimo strive to create a closed water-supply systems, or to move to the inland production.
1. Андоньев С.М., Жильцов В.М., Левин Г.М. Особенности промышленного водоснабжения – Киев: Стоитель, 1981.– 248 с.
2. Аксенов В.И. Замкнутые системы водного хозяйства металлургических предприятий – М.: Металлургия, 1991. – 126 с.
3. Рациональное использование и защита водных ресурсов в черной металлургии / Г.Н.Красавцев, Ю.И. Ильичев, А.И.Кашуба –М.: Металлургия, 1989. – 285 с.
4. Буторина И.В. Возможные пути решения проблем водопотребления на металлургических предприятиях Украины // Сталь-2005 – № 2 – с. 91-95.
5. Белевцев А.Н., Белевцев М.А., Мирошкина Л.А. Процессы и аппараты очистки воды в металлургии [электронный ресурс]. – Режим доступа: http://www.knigafund.ru/books/42847




