Abstract
Сontent
- Introduction
- 1. The relevance, purpose and tasks, research hypothesis
- 2. General characteristics of the concept of "phytontcides"
- 3. Review of existing methods for determining the activity of substances phytoncides
- 3.1 The method of "dripping"
- 3.2 The method of "quantitative assessment phytoncides activity"
- 3.3 "Contact method"
- Experimental technique
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Donetsk is one of the most industrial developed centers of Ukraine. In the Donetsk region centered about 800 large and medium-sized industrial enterprises in the mining, metallurgy, chemical industry, power generation, construction materials, in operation for about 300 mineral deposits. Anthropogenic impact on the environment in many regions of Donetsk has reached a level that is threatening the environment and public health.
Emissions from the city, in cooperation with enterprises of Donetsk agglomeration form stable in ambient air concentrations of pollutants. The sources of pollutants in the atmosphere are not only industry, but also transport, human and animal. Biological pollution – this is a big danger for us.Biological pollution – is bringing in ecosystems uncharacteristic for them species of living organisms that are harmful to human health and economic activity.
The question arises as to reduce the level of microbial contamination of the air environment stselyu minimize the risk of morbidity. Excellent natural weapon against biological pollution is phytoncides activity of plants. Plants play a leading role in a person's life, so the study of their properties phytoncide is very important. Elucidation of the quantitative and qualitative aspects of the action of volatile production by microorganisms is of great theoretical and practical significance.
1. The relevance, purpose and tasks, research hypothesis
The purpose of this paper is to study the seasonal phytoncides activity of some woody deciduous and coniferous trees of the city of Donetsk, which grow in areas with different anthropogenic impact in relation to the test culture – bacterium of the genus Bacillus subtilis. Bacillus subtilis is moving gram-positive rod, not pathogenic to humans [1].
The hypothesis of the study is that if a property of phytoncides plant will have a bacteriostatic or bactericidal effect on this kind of bacteria are not pathogenic, and then to pathogens will be exerted influence, too. It is known that the intensity of phytoncides activity depends on the time of year, the type of plant and the size of its growth, so the study highlight phytoncides real plants requires consideration of these factors.
The main objectives of the study were:
1. Theoretical analysis of the literature on the research topic;
2. Selection of appropriate research methods;
3.Opredelenie phytoncyds the ability of plants to show activity against bacteria of the genus Bacillus in different seasonal periods;
4. Identification of emission rate phytoncyds substances by plants that grow in areas with different anthropogenic impact;
5. Implementation of a comparative analysis of manifestation phytoncyds activity on the species diversity of plants.
6. Development of recommendations and a plan of landscaping plants with the greatest phytoncyds activity.
2. General characteristics of the concept of "phytoncides"
Since ancient times, people surrounded the rich and diverse world of plants and herbs. Primitive man was trying to find a close-growing plants from the home remedy against many diseases. For information about using the healing properties of plants and herbs can be found in the monuments of ancient culture – Sanskrit, European, Chinese, Greek, Latin.
Phytoncides – there are a substance produced by plants and having antibacterial, antifungal properties.
Phytoncides were discovered by Professor B. Tokin in 1928. Since the discovery of Phytoncides production has accumulated a great amount of material on the antimicrobial and antiviral substances of higher plants.
In the B.P Tokin’s book – 'Medicinal plants Poisons, "the author holds a small historical review of research phytoncyds production [2].
Phytoncides properties are particularly valuable in a city where the air contains 10 times more harmful bacteria than the air in the fields and forests. Of trees and shrubs that have antibacterial properties that have a positive impact on the state of urban air pollution, should be called: white acacia, barberry, birch, pear, oak, spruce, honeysuckle, willow, viburnum, chestnut, maple, larch, lime, juniper, fir, sycamore, lilac, pine, poplar, cherry, apple tree. Phytoncidic activity exhibit and herbaceous plants - lawns, flowers and vines.
On the release rate of volatile production plants affected by seasonality, the stage of vegetation, soil and climatic conditions, time of day.
The maximum antibacterial activity of most of the plants are showing in the summer. Therefore, some of them can be used as a therapeutic material [3].
3. Review of existing methods for determining the activity of substances phytoncides
3.1 The method of "dripping"
Nutrient agar inoculated with an 18 hour culture of the test microbe. For planting at the edge of the cup pipetted 1-2 drops of the test plant filtrate or juice. Gently tilt the cup and drop slowly flows over the surface of an agar plate. Plates inverted and put into a thermostat at night at a temperature optimal for growth of the test microbe. On bactericidal juice judged based on the amount of sterile zone formed on both sides of "falling drop" ("tracks") [8].
3.2 The method of "quantitative assessment phytoncides activity"
To study the effect of volatile fractions of volatile production by bacteria can be used the following method to quantify phytoncides activity.
Nutrient agar inoculated with an 18 hour culture. After seeding with the culture plates subjected phytoncides volatile fractions (excluding cup serving control). The treatment is carried out at different exposures and conditions of the thermostat. Initially, it is best to use long-term treatment – 12-18 hours. If this exposure is observed bactericidal effect, it is necessary to reduce the exposure (10, 30 minutes, 1.2 hours, etc.).
1 g plant slurry partitioned thin layer on the inner surface of the cover plates with the sowing. To avoid influence from the volatile fractions to control phytoncides crops and crops cultivated fitontsidami other plants, during the experiments in the same incubator each dish carefully wrapped in a thick paper. This cup was placed in a thermostat at a temperature optimal for the test object.
After a certain period of time the crop is removed together with the cover, replaced with a new last. After one day produce the first view and in the minutes record the number and nature of colonies. Observations of the cups are within 5 days. If the test plant has antibacterial properties with respect to the test strain and cups remain sterile during the entire period of observation, that in order to control the subsequent seeding should be done should be done after seeding the surface with a sterile nutrient medium [8].
3.3 "Contact method"
To determine the activity of tissue phytoncides juice or water extraction from plants can also use the "contact" method. For juice test plant tissue ground first in vegetable grater (if possible) and then in a porcelain mortar until a slurry state. Mush squeezed through two layers of cheesecloth. The resulting juice is passed through a bacterial filter at vacuo. In this way, juice "succulent" plants. Of plants for which this method is not acceptable, prepared water extraction.
Water extraction can be obtained in various ways. Vegetable pulp is poured in distilled water 1:1 and allowed to stand overnight at room temperature. The next day the slurry was squeezed through cheesecloth and the resulting liquid was passed through a bacterial filter in vacuo. In some cases, a greater effect is achieved by autoclaving. This plant material is filled with distilled water and autoclaved for 30 minutes at a pressure of 0.5 atm. Upon cooling squeezed through cheesecloth and filtered through a bacterial filter.
Initially, it is recommended to test the action of the native juice or concentrated aqueous extracts without their preliminary dilutions.
Poured into a sterile vial under aseptic conditions 5m test juice or aqueous extract and inoculated with one drop of bacterial emulsion containing 1 m 2 billion microbial bodies (the optical standard). As a test object is a sensitive test strain the juices. The latter may be selected by a preliminary study "fitontsidnym capacity" juice experiments with many kinds of bacteria.
The control tube is from 5 m3 saline seeded same amount of microbial suspension. Tubes throughout the experiment incubated at optimal for growth of the test organism temperature. At certain intervals (immediately, after 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 24 hours) of the tubes to make a 0.05 m3 seeding culture on nutrient agar. After 24 hours of incubation the results of a determination (counting of colonies on agar colony morphology and Discover). After establishing antibacterial tissue juice or aqueous extract of its activity can be determined by diluting the test fluid by a so-called dilution method. Stud juice or aqueous extract is carried out in sterile test tubes in a specific volume. Possible dilution: 1:10, 1:20, 1:40, 1:80, 1:160, 1:320, etc.
The tubes were inoculated with various dilutions of a standard drop of 18-hour culture of the test object. The test fluid is diluted in the broth. Serves as a control tube containing the native juice or water and removing the initial concentration of the test tube with the broth. The volume of fluid in the experimental and control must be identical.
The tubes were placed for 5 hours in a thermostat at the optimum temperature for growth of the microbe, and the incubation period after seeding cultures produce - 0.05 m3 - in agar.Cups with sowing was placed in a thermostat. The next day results determined. Most juice dilution at which no growth of microbes, indicates the degree of the activity of tissue extracts juice or water. All of the above methods of studying the antibacterial properties of higher plants can be used to detect new fitontsidonositeley.
In the application of these methods, of course, control is required [4]. Definition phytoncides activity of woody plants during late fall, winter and spring. The experimental procedure and the obtained results at the moment
4. Experimental technique
In this work, we used the method of determining the biological activity of phytoncides woody plants. The method consists in the following: poured into Petri dishes prepared culture media for the cultivation of microorganisms. A sample of the microorganism Bacillussubtilis subjected to breeding with distilled water to a suspension of 1:100 million.
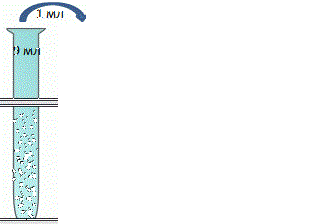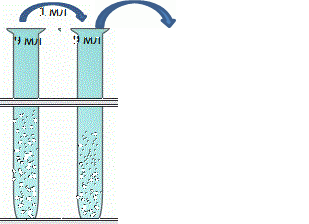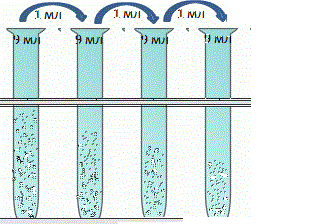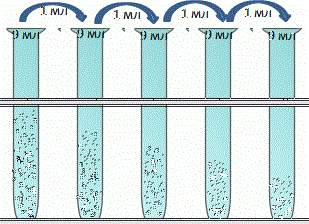
Figure 1 – Bacillus subtilis 1:10 bln. (animation, 70,1 Kb)
Then, the suspension was prepared in a volume of 0.5 m3 poured onto the culture medium in Petri dishes. Next to each Petri dish pawned sample plants linkage to 2 grams, and each sample was control - a cup with a suspension of microorganisms. After preparation, all samples were sent to the cup thermostat in which the temperature was 35 degrees C for 48 hours.
Figure 2 – Control Petri's dish
Figure 3 – Petri's dish with leaves of trees Betula verrucosa
Figure 4 – Petri's dish with leaves of trees Robinia pseudo-acacia
After germination, bacteria Bacillussubtilis, reporting the number of colonies of microorganisms in cups with different types of plants, with varying terrain of their growth, compared with each other and control. Thus, it was revealed that phytoncidic activity of the studied species of woody deciduous plants in late autumn period is minimal. Talking about the intensity discharge phytoncides substances according to the locus of the plant is also at this stage it is impossible, because in this seasonal period, leaves almost no isolated phytoncide substances.
5. Conclusion
At the moment, the experiment continues research phytoncide properties of plants in the spring and summer. Final results will be available by the end of the summer season, then we can make specific findings on the emission rate of volatile production different kinds of trees, compare the release rate of volatile production plant grows in areas with different anthropogenic impact and offer advice on gardening of plants that have the greatest phytoncidic activity.
References
