Abstract
Сontents
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Frequency measurement by rational approximations
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
There is the change of frequency of the carrier signal often present in modern telecommunication systems, the causes of which are features of both algorithms for their operation (periodic jumps in frequency, in connection with which there is a transition from one frequency range of operation to another - frequency hopping, WiMAX), and the influence external factors (the Doppler effect during the moving of a transmitter and/or receiver, the effect of ambient noise and noise of equipment). All this leads to the fact that theoretical calculations and models in many respects do not correspond to the actual processes, which exist in telecommunications systems and networks. Therefore, both during construction of the system and its operation (to diagnostic equipment) ones of the most important parts are the measurement of the paremeters of a signal, transmitted at the different parts, holding the collection and analysis of the received information and identification the existing problems. However, the identification of gaps and problem areas can not be realised without the reliable and timely information.
Theme of the research is dedicated towards the gathering information about the parameters of the signal in the channel with a certain accuracy in the limited time and the problem of estimating the frequency on the basis of these data.
1 Theme urgency
Relevance of the work is to find methods for solving the fundamental problem of limitations "error-measurement time" in terms of the problem of increasing the accuracy of frequency measurement during a limited time, which can then be used to further diagnose the state of the telecommunications link.
The goal is to improve the accuracy of frequency measurements during a limited time measurement.
It is necessary to solve the following problem to achieve this goal :
- The formation a conception of diagnosing the state of the telecommunications link using the frequency measurement.
- The substantiation of the requirements for frequency measurement process.
- The overview of existing methods of measuring frequency in the aspect of limitation "error-measurement time".
- The performance of structural and algorithmic synthesis circuits of the frequency meter.
Method of research: mathematical methods, structural and algorithmic synthesis.
2 Frequency measurement by rational approximations
For most practical purposes the exact estimate of the frequency over a short period may be achieved by using a special mathematical processing. In particular, this approach characterizes this method (fig. 1).
Unknown frequency is measured by comparing it with a standard frequency. There are two sinusoidal signals at the input to the system with a reference (or standard), and unknown (or study) frequency. Zero crossings are detected at both frequencies, creating two independent regular sequence of narrow pulses. Unknown and reference sequences obtained pulses are compared in matches. This comparison is performed using gate AND. Pulse sequence matches generated. Coincidence pulses can be used as a feature for starting and stopping a pair of digital counters.
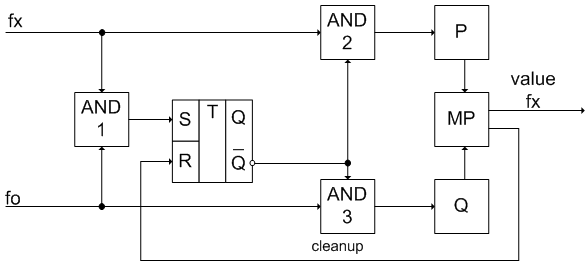
Figure 1 – Functional diagram of the frequency measurement by rational approximations
The reference sequence and the test sequence of narrow pulses received at counters and the measuring of unknown frequency is realised by multiplying the reference frequency by a certain ratio of the target sequence of pulses to the number of pulses of the standard sequence derived from two digital counter [8].
A pulse sequence with unknown frequency fx enters to the input of frequency meter. There is a reference source with a frequency f0, and it can be either built-in or external. It is recommended the use of high-frequency source of the atomic frequency standard (error 10^-9-10^-10). In addition, the value of the reference frequency must be a multiple of ten. It should be noted that the pulses generally have no common edge (i.e. has a slope) and unstable position in time (jitter). This identification of the front and rear edges generally occurs after reaching half of the amplitude value. However, in this case, to simplify the presentation of the method's operation, there is no jitter. Also take into account there is non-ideal fronts in the model.
The pulse sequence of the unknown and the reference frequencies input to a gate I. After the first full match starts counting pulses. After reaching the counter pulses of unknown frequency value equal to the specified powers of ten, there is a calculation of unknown frequency.
Form the requirements for elements of the scheme:
- reference frequency generator: error 10^-9-10^-10;
- RS-trigger: the absence of an undefined state, fmax=max(f0,fx);
- gates
AND
: fmax=max(f0,fx); - counters: fmax=max(f0,fx), the selected digit capacity affects the option to select r. For 16 bits, we have 65,536 states, i.e. r=1…4 (Σm(Pn)=10…10000). For 32 bits, we have 4,294,967,296 possible states, i.e. r=1…9 (Σm(Pn)=10…1000000000).
- microprocessor: fmax=max(f0,fx )/10^r;
- digital display unit: no special requirements.
Conclusion
Measuring the frequency with sufficient accuracy for a certain, pre-specified time interval - one of the fundamental problems of the telecommunications industry. There are many different methods of measurement. However, the practical application requires a specific, most appropriate solutions for each of the tasks.
The existing methods of frequency measuring in the conditions of limitation "error-measurement time" for the device diagnosing the state of the communication channel by measuring the frequency of the signal were analysed. As a result of the conceptual validation of these methods for accurate measurements for diagnostic purposes, such as jitter, as well as their advantages and limitations, has been chosen as the most suitable the innovative modernizated method of discrete accounts - a method of frequency measuring based on rational approximations. During the investigation it was found that the error of methods depends not only on the ideas underlying the methods themselves, but also on the ratio of the measured and reference values. The selected method works with the optimal ratio, and it is not accidental, but the standard mode of the measurement process.
Also looked for controversial issues (the effect of jitter pulses, determining the degree of overlapping pulses and the corresponding pulse width for the run of the method), and ways to solve them in terms of practical implementation of the method.
Further investigation will be concluded in the modeling process, the operation of this method in MatLab and minimize the impact of its weaknesses on the obtained results.
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Козловский Е.А. Искусство позиционирования / Е.А. Козловский — М.: Вокруг света, 2006. - № 12 (2795). — 204-280 с.
- GPS-навигаторы для путешественников, автомобилистов, яхтсменов/ В.С. Найман — Санкт-Петербург: НТ Пресс, 2008.— 400 с.
- Бакланов И.Г. Технологии измерений в современной телекоммуникации. / И.Г.Бакланов – М.: Эко-Трендз, 1998. – 264 с.
- Скляр Б. Цифровая связь. Теоретические основы и практическое применение. Изд. 2-е, испр. :Пер. с англ. – М. : Издательский дом «Вильямс», 2003. – 1104 с.
- Аппаратура для частотных и временных измерений/ Под ред. А.П.Горшкова. Изд-во «Советское радио», 1971, 336 с.
- Ратхор Т.С. Цифровые измерения. Методы и схемотехника/ Т.С. Ратхор — М.: Техносфера, 2004. — 376 с.
- J.C. Fletcher, Frequency measurement by coincidence detection with standard frequency/ US Patent 3, 924,183, 1975.
- Daniel Hernаndez Balbuena, Oleg Sergiyenko, Vera Tyrsa, Larysa Burtseva, Moisеs Rivas Lоpez, Signal frequency measurement by rational approximations, Measurement, vol. 42, no. 1, Elsevier, 2009, pp. 136–144.
- Полапа А.А. Анализ и обоснование методов измерения частоты колебаний в условиях ограничения «время – погрешность измерений» / А.А. Полапа // Мат. 9-й Междунар. молодежной научно-технической конф. «Современные проблемы радиотехники и телекоммуникаций» (РТ-2013). — Севастополь: Изд-во СевНТУ, 2013. — С. 158 — 159.
