Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Layout of the work rolls in wheel-rolling machine for rolling the workpiece in the horizontal wheels
- 2. Analysis of power and speed conditions rolling wheels of "Vyksa Metallurgical Plant" VMP
- 3. Calculation of the conditions of contact interaction wheels rolls in rolling it on the existing technology of VMP
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Urgent problem facing today's leading manufacturers were punched-rolled wheels Ukraine (JSC "Interpipe NTRP") and Russia (JSC "Vyksa Steel Works" (VSW)), is a decrease of metal production, including by reducing the scrap rate on Forging line. The solution to this problem is connected with the need to carry out research in two directions. The first area - an analysis of temperature-speed, power and deformation modes of punching and rolling wheel blanks on the basis of experimental data obtained in industrial production wheels. The second direction - this theoretical research and development aimed ultimately at creating new methods of analysis and design of metal-saving technologies punching and rolling wheels.
The actual problem of domestic wheel-rolling production is the lack of methods for calculating the technology billet rolling wheels provide high prediction accuracy and power metal forming process parameters. The solution to this problem is connected with the necessity of further development of the theory of wheel-rolling production and tasks that previously had no relevance.
Master's thesis is devoted to the study and solution of the following tasks: evaluation of the current state of production of wheel blanks for Forging line, theoretical studies of metal deformation processes in the manufacture of wheels, improving the rolling wheel blanks and the method of their calculation.
1. Technology Analysis rolling billet on railway wheel mill
Technology of production of wheels includes a number of basic operations. Directly related to the master's work belongs to Deformation of the billet wheels in the wheel-modern machines is a continuous rolling of a vicious circle - the wheel rim blank - between the work rolls of different configurations, at different locations around the circumference of the rim.
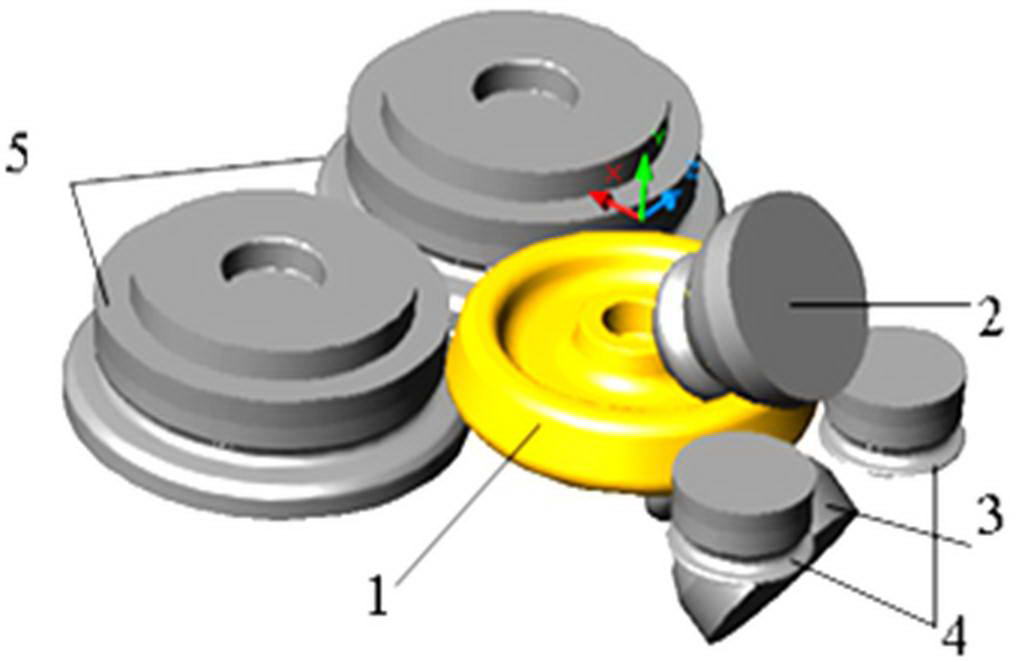
1 — billet wheel; 2 — sloping top roll ; 3 — sloping bottom roll; 4 pressure rollers; 5 — the root rolls.
The value of rolling wheels on the inner rim diameter of 146-147 mm, and the total amount of axial compression was 28 mm rim.After rolling, the temperature of the rough wheel rim increased as a result of deformation heating on ~ 50°С.
2. Analysis of power and speed conditions rolling wheels of "Vyksa Metallurgical Plant" VMP
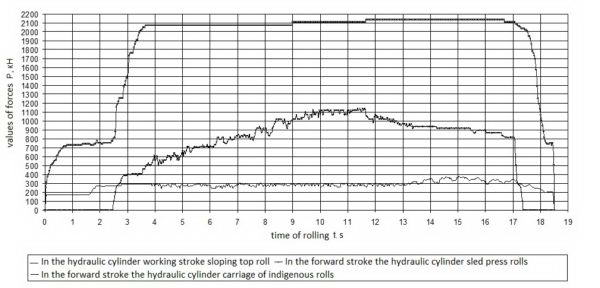
Fixing the gauge readings performed by a digital video camera Canon Power Shot A 570IS and then send the information to a computer. Processing of the video recordings construction of arrays comprising pressure data versus time, was carried out on a computer with a time step Δt=0,033 с.
The resulting values of the forces (averaged over 3 m parallel measurements of pressure) when rolling roughing wheels are presented as plots of the time and strain are shown in Fig. 2.1
The calculation of the increment of the internal diameter of the wheel rolling steps are carried out on the basis of data on the movement of the carriage of indigenous rolls and pressure rolls move the sled. These data rolling wheels each fixed by specially provided sensors and automatically displayed in the form of plots in real time. In addition, this display also automatically increments plotted inner diameter rolling wheel. Setting the automatic system is conducted on the increment of the inner diameter of the rolling wheel. The system counts from zero to the desired value by rolling the wheel opening. These graphs built using any third-averaged values of the parallel measurements of the relevant parameters, are shown in Fig. 2.2.
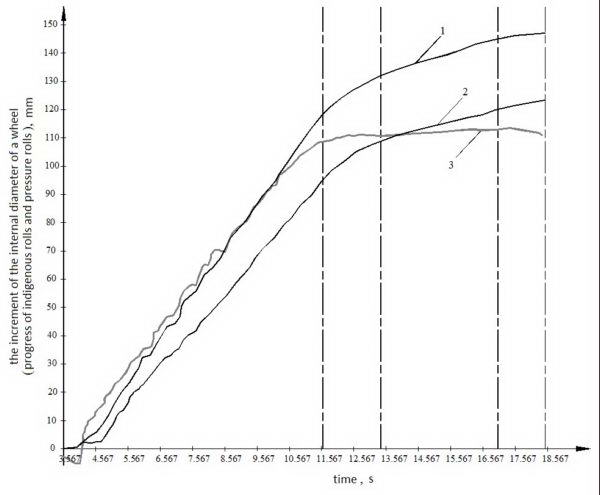
1 – the increment of the internal diameter of the wheel; 2 – carriage stroke indigenous rollers; 3 – move the slide pinch rolls.
3. Calculation of the conditions of contact interaction wheels rolls in rolling it on the existing technology of VMP
In the current method of calculating the parameters of rolling billet wheel contact friction conditions are specified as conditions Amantonaand this time with no valid data on the amount of contact friction coefficient of 0.3 - 0.35. However, the simpleextension of the results of experimental studies on the determination of the coefficient of friction during hot rolling of longitudinalThe rolling steel billets wheel is at least unreasonable. Moreover, setting conditions such frictionand a use of such values of the coefficient of friction with respect to the pin rolling blanks wheels leads to incorrectvalues ??of shear stress greater than the yield stress of the deformed metal shear.
Currently, the analysis of the deformation processes workpieces wheels are widely used mathematical modeling techniques,based on the finite element method. However, in the literature there is no scientifically sound method of calculating the conditions of contactinteraction with the wheel rolls workpiece. At its creation and directed part of master's work.
In the proposed method shows a diagram of finding the thickness of the metal layer with a uniform stress-strain state Fig. 3.1
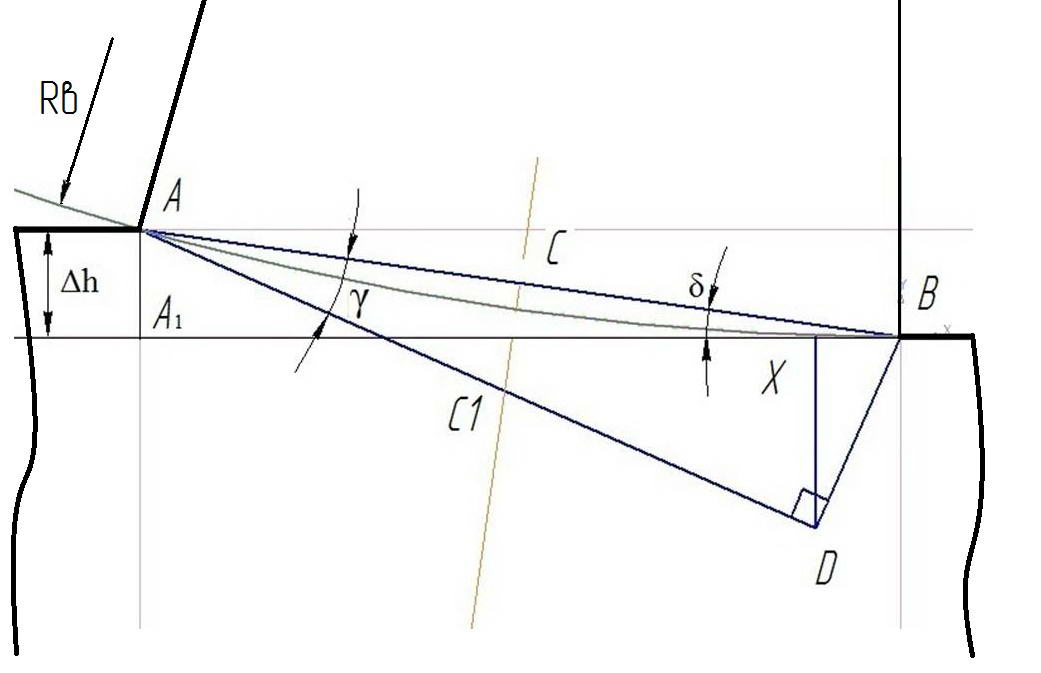
On the basis of this scheme has been obtained experimentally and theoretical formula for calculating the index of contact friction forces
Found that the range of the technological factors, existing in practice, used in the calculationas input parameter for friction contact with an upper sloping roller varies from 0.27 to 0.44,and on contact with the lower inclined roller varies from 0.21 to 0.32.
Conclusion
The study of such issues as the changing of speed and power parameters of rolling wheels on the gaugescurrently available, and the modes of breakdown studies of the conditions of contact friction with rolling wheelsmake it possible to simulate the process to further his study and improvement that will providedecrease of metal production.
Master's thesis devoted to the important task of improving the scientific technology of railway wheels.As part of the research carried out:
- Technology Analysis of deformation in the production of railway wheels.
- analysis methods for developing technologies punching and rolling wheels.
- Mathematical modeling of deformation processes on different technological transitions Forging line.
- Development of a method of calculation conditions of contact interaction wheel blanks with rolling rolls.
Further research is focused on the following aspects:
- Improvement modes punching and rolling wheels.
- flowsheet and calibration for punching and rolling wheel blanks on Forging line of "Interpipe NTRP".
In writing this essay master's work is not yet complete. Final completion: December 2013.Full text rabotyi materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his manager after that date.
References
- Шифрин М.Ю. Резервы производительности и выхода годного при прокатке колес / Михаил Юльевич Шифрин. – М.: Металлургия, 1989. – 144 с
- Производство железнодорожных колес / [Г.А. Бибик, А.М. Иоффе, А.В. Праздников и др.]. – М.: Металлургия, 1982. – 232 с.
- Яковченко А.В. Проектирование профилей и калибровок железнодорожных колес А.В. Яковченко, Н.И. Ивлева, Р.А. Голышков. - Донецк: Донецкий национальный технический университет, 2008. - 491с.
- Чекмарев А.П., Николаев В.А. Исследование коэффициента трения при горячей прокатке // Изв. вузов Черная металлургия. – 1958. – № 12. – С. 57–67.
- Трение и смазки при обработке металлов давлением: справочник / [А.П. Грудев, Ю.В. Зильберг, В.Т. Тилик]. – М.: Металлургия, 1982. – 312 с.
- Контактное трение в процессах обработки металлов давлением / [А.Н. Леванов, В.Л. Колмогоров, С.П. Буркин и др.]. – М.: Металлургия, 1976. –416 с.
- Хайкин Б.Е. Инженерные формулировки закона трения в условиях обработки металлов давлением / Б.Е. Хайкин // Изв. вузов Черная металлургия. – 1990. – № 1. – С. 38–41.
- Зильберг Ю.В. Закон и модели пластического трения / Ю.В. Зильберг // Изв. вузов Черная металлургия. – 2000. – № 11. – С. 22 – 24.
- Зильберг Ю.В. Некоторые физические особенности пластического трения / Ю.В. Зильберг // Кузнечно-штамповочное производство. – 2002. – № 6. – С. 22–26.
- Евстратов В.А. Теория обработки металлов давлением / Виталий Алексеевич Евстратов. – Харьков:Вища школа. Изд-во при Харьк. Ун-те, 1981. – 248 с.
- Снитко С.А. Анализ силовых и скоростных параметров прокатки колес / С.А. Снитко // Наукові праці ДонНТУ. Металургія: Зб. наук. пр. – Донецьк, 2008. – Вип. 10 (141). – С. 163–172.
- Целиков А.И. Теория продольной прокатки [учебник для студентов машиностроительных и металлургических вузов] / А.И. Целиков, Г.С. Никитин, С.Е. Рокотян – М.: Металлургия, 1980. – 320 с.
- Губкин С.И. Пластическая деформация металлов / Сергей Иванович Губкин. – М.: Металлургиздат, 1960. – Т.2. – 416 с.
- Томленов А.Д. Теория пластического деформирования металлов / Александр Дмитриевич Томленов. – М.: Металлургия, 1972. – 408 с.
- Солод В.С. Математическое моделирование сопротивления деформации при горячей прокатке углеродистых сталей / В.С. Солод Я.Е. Бейгельзимер, Р.Ю. Кулагин // Металл и литье Украины. 2006. – № 7–8. – С. 52 – 56.
- Целиков А.И. Теория прокатки. / А.И. Целиков, А.И. Гришков. – М.: Металлургия, 1970. – 358 с.