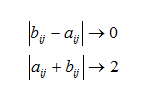Abstract
Сontent
Introduction
For decades, human resource management policies in the Soviet Union guided not by the interests of the person, and on the requirements defined by the general thrust of the economy to a predominantly extensive growth. It was subordinated to the task of overcoming the lack of personnel, the search for additional sources of manpower to staff the growing number of jobs. This has resulted in an almost complete depletion of human resources and excessive involvement of women in the economy and the elderly with disabilities.
The transition to a market economy will inevitably lead to big changes in the use of labor resources.
In modern society, the labor force – a kind of commodity, for the operation of which, like any other resource, you must have the appropriate conditions, above all, a certain relationship with those who need this resource to those who can provide this resource. For effective and quality operation of this relationship and create employment agencies.
1. Relevance of the topic
Currently recruiting agencies to become more and more important issue of effective interaction with the companies - customers.
Process of recruiting is becoming more difficult. This can be explained by the fact that companies are more demanding for candidates and applicants, in turn, selectively apply a potential place of employment and conditions of the offering of the Company. There are many different ways to find the employee meets the requirements of the employer and requirements of the job by the applicant. Development of analytical support and ordering information flow ensures the effective functioning of the employment agency and increase its competitiveness in the recruitment services market in Ukraine.
Master's thesis is devoted to the information-analytical support of the employment agency and the approach for the selection of applicants with the requirements of the employer's position methodology of fuzzy logic. Fuzzy logic is a convenient tool for the analysis, as the majority of the phenomena is impossible to describe the precise quantitative values.
2. The purpose and objectives of the research, the expected results
Purpose – perform a comprehensive analysis of the employment agency, to develop the concept of information-analytical system of governance and to put into practice some of its elements.
Subject of the master's work are the methods of improvement tasks of information-analytical department of recruitment agencies.
Object master's work – this model talent management agency.
To achieve the goal to achieve the following objectives:
- analyze and study the market recruitment services;
- determine by what method is a realization of information and analytical support personnel agency;
- introduce the concept of information-analytical systems automate the management of recruitment agencies;
- provide a detailed description of staffing agency LLC "Majordom";
- build a model of formation of profit Recruitment Ltd "Majordom";
- create a fuzzy knowledge base to determine the extent to which the applicant requirements of the employer.
Methods that have been used: :
- methods of analysis and synthesis;
- construction of mental maps;
- creation of automated systems;
- analysis of hierarchies;
- analytical methods of data;
- methods of fuzzy logic;
- methods for creating business processes;
- methods of simulation.
3. The analysis of recruitment services market
The modern market infrastructure constantly transforming and evolving. This process is associated with the reorganization of society, the active development of the economy, the succession of technologies, organization of labor relations. This all implies significant changes in the employment relationship. Market infrastructure includes a set of institutions to promote employment, career counseling, professional training and retraining, the network assets, employment centers. She was mediated link between the employer on behalf of the executive director of the company and social groups of applicants. The main elements of the infrastructure of the labor market can be called a state employment service, which includes the bodies of three levels of government: national, regional and local.
Public and private employment services, as a kind of mediator, can be very useful in identifying applicants for the job, because they can hold a voir dire and thorough examination of the individual applicants. Staffing Services is unable to due to changes in some benchmarks, priorities and innovations in socio-economic and political spheres of public life fully meet the requirements change. For the proper functioning of a modern market economy requires specialized business services, including in the field of HR. At present, we can say that, along with other sectors of business services in Ukraine has formed industry recruitment services [26 - 29].
Characteristic features of modern Ukrainian market of recruitment services:
- Geographical distribution market recruitment services are very stretched, indicating that demand for this type of service;
- Steady upward trend in regional contracts for recruitment;
- Increasing quality requirements for recruitment services, due to the intensification of contacts and developing relationships with clients, the increasing number of orders from local customers, as well as regular training programs for personnel recruitment companies in the field;
- Development and promotion of recruiting companies to market other types of services, which is caused by the desire to diversify its business and reduce risk. Additional services are available in the field of management consulting, training, and human resource management;
- Lack of common pricing. Service price is set independently by each individual company;
- Competition in some sectors of the market, especially when working with large Ukrainian and Western companies.
Conditionally whole recruitment business can be represented as a pyramid.
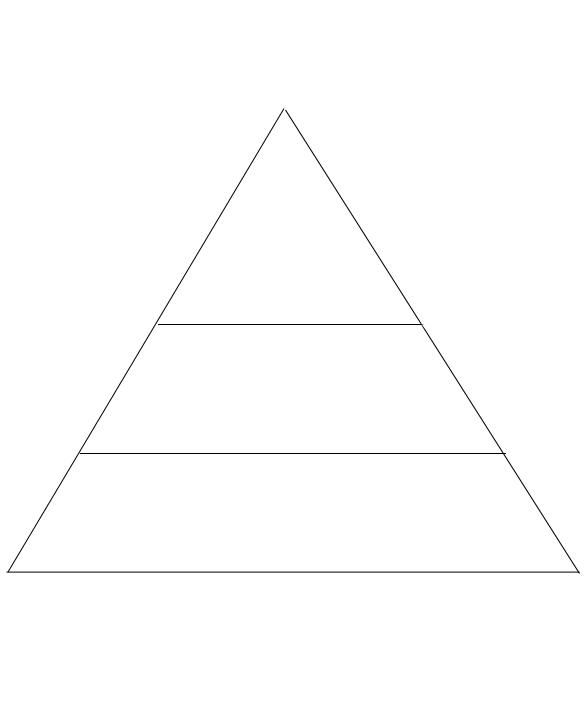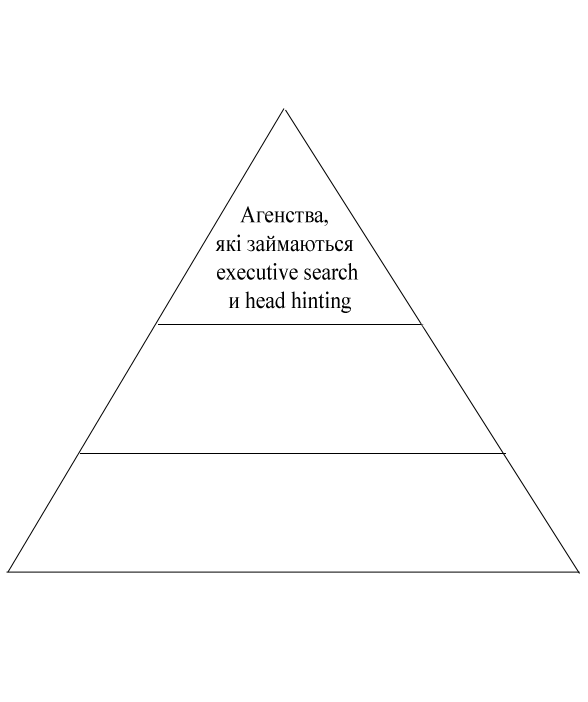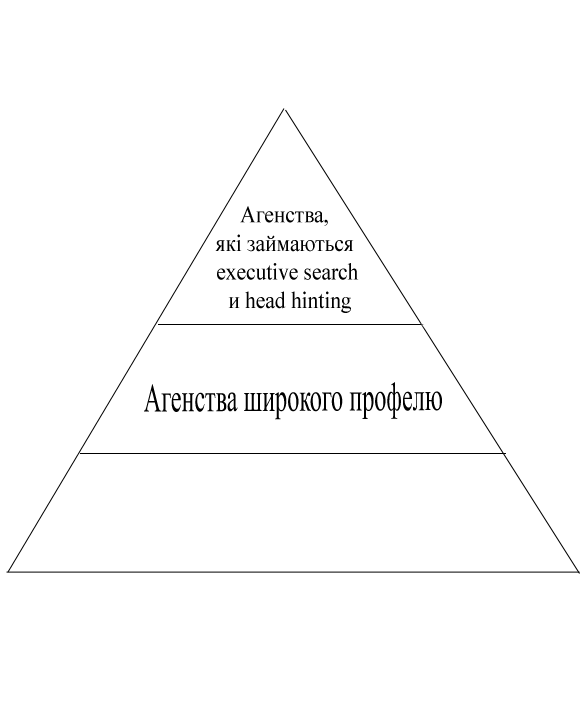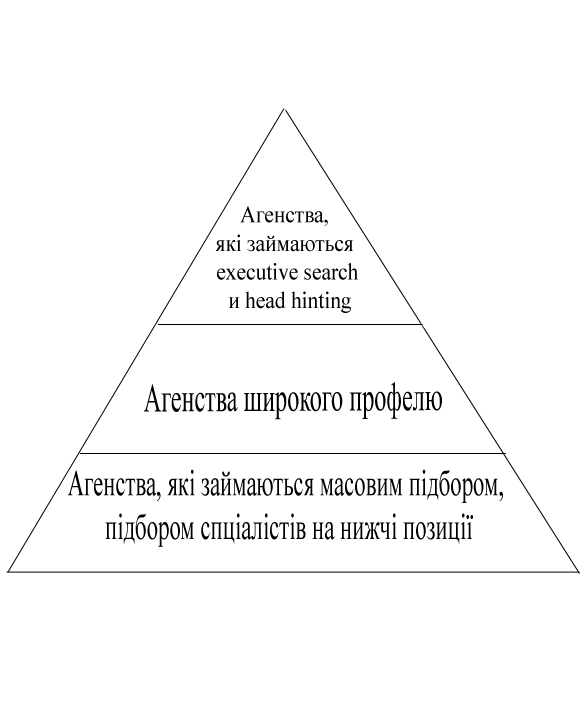
Figure 3.1 - Representation of the recruiting business
(animation: 4 frames, 5 cycles of repetition, size 14,7 KB)
Employment agencies – organizations that provide services in recruitment – not engaged in employment. The main task of recruiting agencies qualitative and fastest filling of vacancies offered by their customers [41].
Characteristic feature of recruitment agencies – they do not take money from candidates. This is natural, because they do not make them any services. Ethics personnel officer confirms this fact.
Today recruitment agency for the applicant – is not the way to find a job, but a way to make a career. The agency is closely monitoring his "protege" as they work at the new location as quickly delve into the problems of course, take responsibility. And when an employer treats them, they pick up information about those with whom you've already dealt with.
Customers recruitment agencies - are organizations that require a particular specialist [36].
The main functions of the employment agency as a subject of social relations is the organizational, regulatory and informative. Organizational includes personnel diagnosis, planning strategies and recruiting staff.
Informative function recruitment agencies manifested in the successful interaction and communication entities and relationships is realized through adaptation programs of candidates for the new job, training of existing staff and corporate culture. Seminars and workshops - basic forms of influence aimed at the acquisition of knowledge and skills of effective communication, psychology, negotiation and sales, and help to reveal the professional and personal reserves of participants.
The regulatory function of recruitment agencies as mediators of social relations in the labor market is to provide guarantees for the recruitment, monitoring of employment candidates and track prospects, as further mutually beneficial cooperation and the strategic objectives of the customer enterprise [56].
Employment Agencies – a professional company specializing in the delivery of effective staffing solutions. The current labor market recruitment agencies are becoming increasingly important: visionary leaders who understand the importance of investing in human resources, seek solutions that can actually recoup the investments made.
Not surprisingly, today the subject of interest of all players in the market of labor, is a top recruitment agencies: in order to find a reliable performer task of recruitment, it is necessary, first of all, choose a decent recruitment agency. As in any market, in personnel matters only criterion for this choice is the reputation of the proposed service, and established her base of successful projects [ 22 ].
As the long-standing practice, and from the point of view of professionals the most reliable are just job recruitment agencies, for example, major Ukrainian experts with great possibilities prefer to host your resume the best recruitment agencies in Ukraine. Given the specificity of Ukrainian labor market, it is necessary to recognize that recruitment agencies are working in special conditions that require maximum professionalism and efficiency.
Regularly interact with a large number of companies and a huge number of candidates, recruitment agency is constantly in the flow of relevant information about the labor market. In a business environment that is rapidly changing, an opportunity to obtain relevant information quickly and fully analyze the current trends and as a result, make the right decision.
4. Information and analytical support personnel agency
Automation recruitment agencies require knowledge of the subject area. The accumulation of experience comes in communication with specialists staffing agencies, from the director to the ordinary recruiter.
The software created for recruitment agencies should be resolved in the complex task of preserving the professional and efficient processing of information they work with recruitment agencies.
Employment agencies are looking for staff who need their customers. Program for employment agencies to help them do this as easily as possible. And the better, faster, and more accurate recruitment agency finds a job candidate for the customer, the more the agency earns money.
Staffing business is growing more and more intense, because the benefits of the business are not in machines and equipment that have and those of competitors, and competent personnel, a team of specialists, system management, system of selection of personnel, reserve personnel, the ability to increase profitability [15].
The work of the agency can use the advanced development of information systems and HR-art technology effective recruitment (eg, working in a software product 1C: Enterprise).
Configuration "1C: Recruitment Agency" is intended for the following tasks:
- Business Process Automation personnel (recruitment) agencies and personnel departments of companies engaged in the selection and monitoring of personnel staffing agency relationships with clients and candidates.
- Automating the process of assessment of knowledge, skills and personal characteristics of candidates who applied to the agency (company) to find work.
- Creating a common information base of clients and candidates for vacant positions that automatically match the requirements of the employer to the particular post (application clients) with disabilities (CV) of candidates who applied to the recruitment agency.
- Improving productivity of managers on recruitment due to a significant reduction in time to process the information.
- Operational management of the agency, receiving reports on the work of managers for recruitment.
- Program is focused on staffing agencies, as well as service personnel in medium to large organizations and institutions.
Schematically stages of work with the candidate staffing agency presented in Figure 4.1.
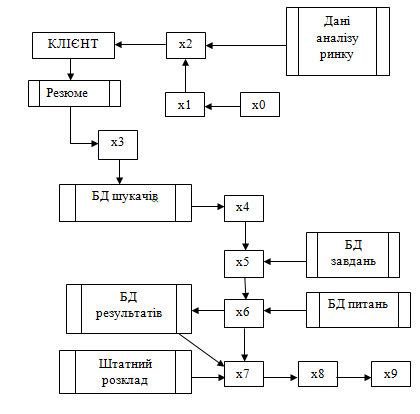
Figure 4.1 – Information flows Recruitment
where x0 – Definition of salary and benefits; x1 – Planning staff; x2 – Recruitment of staff; x3 – The selection of personnel; x4 – Professional adaptation, x5 – Education staff; x6 – Certification of personnel; x7 – Shuffle personnel; x8 – Leadership training; x9 – Social security personnel.
Development and systematization of analytical support information flow ensures the effective functioning of the employment agency and increase its competitiveness in the recruitment services market in Ukraine.
5. The concept of information-analytical systems automate the management of recruitment agencies
Labor market acts as a mechanism for the relationship between an employer in need of labor, and the applicant, that is, a potential employee. As the level of relations between the subjects most effectively operates a specialized social institution - recruitment agency.
Employment agencies are a professional company specializing in the delivery of effective staffing solutions. The current labor market recruitment agencies are becoming increasingly important: visionary leaders who understand the importance of investing in human resources, seek solutions that can actually recoup the investments made.
Success of the recruitment agency determined by the availability of qualified personnel in state agencies, sustainable relationships with employers, the database for candidates using advanced technology works [19].
Job Recruitment requires automation of the bank's customer data as the demand for jobs and the demand for workers is always there. With a huge volatile stream of information about employment agency is very difficult to quickly and accurately provide the necessary data, operating without the use of an information system. It is therefore very important question about the automation of the agency, in particular specialist on the staff, which communicates directly with clients and selects the most appropriate alternative for job seekers and job vacancies. Clients or customers Recruitment act as potential candidates who are looking for suitable jobs and employers that require a skilled worker.
According Roshchina AV, recruitment agency – an organization that provides recruitment services for companies customers.
As the Roschin, recruitment agency – is an intermediary between the employer and the job seeker, a kind of buffer, which is a guarantor that the company will get just such a specialist that she needed, and expert-decent working conditions and wages promised by [7].
As the Allin ON, namely recruitment agencies contribute to the creation of a civilized labor market, and this applies not only to the person who is looking for a job, but the employer [68] .
Main objectives of any employment agency (according Odegova YG):
- Provide relevant information on the level of wages the most sought-after experts of the most dynamic industries.
- Demonstrate the trends in changes in wages [72].
According Muzychenko VV task of recruitment agencies can be divided into two groups.
The first group – are tasks that relate to the client:
- search and selection of personnel in accordance with the requirements of the employer;
- reliability of selection;
- selection in strictly approved the contract term.
Second group of problems related to the agency itself:
- profitability of the agency;
- finding and training their own staff [43].
According Utkin VB automation of all human activities in the solution of practical problems should have methodological support. Interesting and important for management professionals are especially automation of management of the company as a process of development, implementation and use of technology, software tools and mathematical methods designed to automate the collection, storage, retrieval, processing and transmission of information used for the management of ergatic systems during implementation of new information technology management [61].
Automation recruitment agencies require knowledge of the subject area. The accumulation of experience comes in communication with specialists staffing agencies, from the director to the ordinary recruiter. The software created for recruitment agencies should be resolved in the complex task of preserving the professional and efficient processing of information they work with recruitment agencies. Since staffing agencies engaged in selection of personnel who need their customers, the development of information and analytical support for recruitment agencies to help serve most effectively and carry out selection to best match the requirements of the customer in the shortest possible time to analyze the data received from the customer to compare the requirements of the employer and Applicant wishes to find the option that best match criterion: for the employer - a skilled worker with all the necessary qualities for the job seeker - an appropriate workplace corresponding to its requirements. That is necessary to find the most appropriate alternative for job seekers and vacancies.
To achieve sustainable development of human agency and enhance its market competitiveness, in the work of the agency must use the advanced development of information systems and HR-art technology effective recruitment (eg, working in a software product "1C: Recruitment Agency" or specially designed and adapted to the needs and specifics of a particular recruitment agency software environment). principal agency staff are experts on the selection of vacancies, personnel managers who directly interact with the client and take advantage of the offer or other types of services. Orientation-based management of business processes provides a competitive advantage for the organization in a highly competitive environment, and the management based on business processes can not be effectively implemented without the use of information technologies and systems.
Represent the process of recruitment agency in successive stages, as depicted in Figure 5.1.
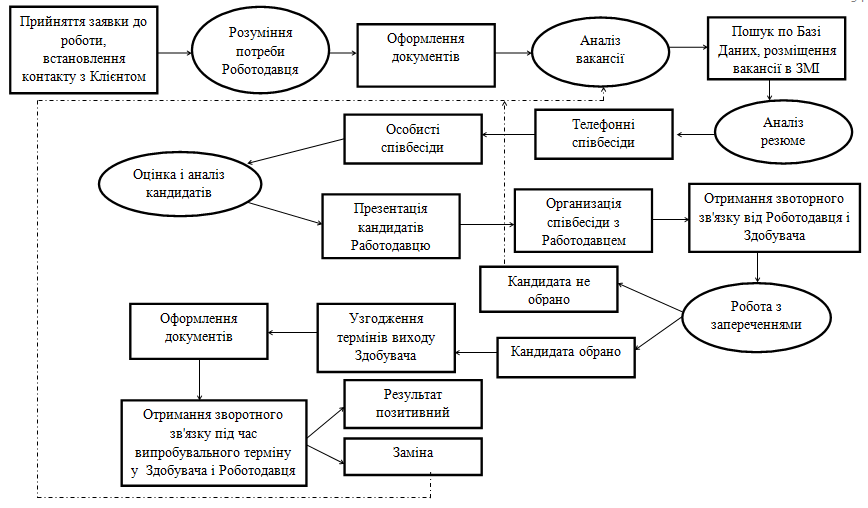
Figure 5.1 - Process of Recruitment
Automating the process of recruiting a staffing agency is an important aspect, since the introduction and processing of questionnaires and maps employers significantly reduces maintenance time per customer, and the search results and issue the necessary information is accurately and promptly. Greatly simplifies tracking the implementation of treaty obligations.
Automation of information flow and document management is achieved through the use of technical means for collecting, recording, processing, creation of primary and effective documents and data communications over any distance [55].
Requirements listed above and the methods have their own idea in the concept that the mechanism of interaction between job seekers and employers with information and analytical support (Figure 5.2), based on the methods and models of fuzzy logic.
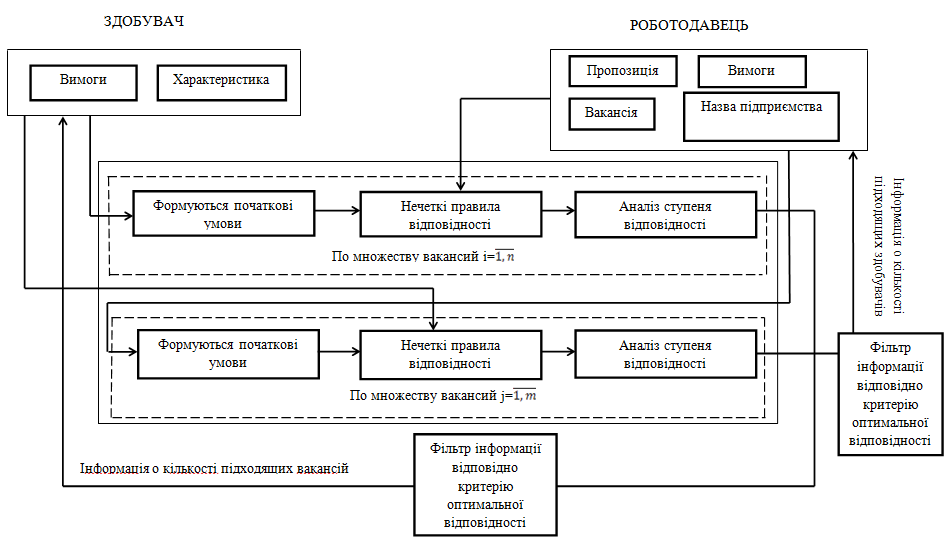
Figure 5.2 – The concept of interaction between the applicant - recruitment agency - the employer
Thus, the concept of information and analytical support for recruitment agencies in its implementation should help to serve most effectively and carry out selection to best match the requirements of the customer as soon as possible to analyze the data received from the customer to compare the requirements of the employer and the applicant wishes to find an option that meets the criterion of optimal match: for the employer – a skilled worker with all the necessary qualities for the job seeker – an appropriate workplace corresponding to its requirements. That is necessary to find the most appropriate alternative for job seekers and job vacancies.
6. The system of fuzzy evaluation of the extent to which "applicant-vacancy»
About fuzzy sets world learned 40 years ago from an article by Zadeh "Fuzzy Sets" in the journal "Information and Control". The theory of fuzzy sets, perceived at first very skeptical, now has become an effective method of modeling under uncertainty.
Popularity of fuzzy set theory in the design due to the fact that fuzzy systems are developed quickly, they come easier and cheaper to clear analogues.
Since staffing agencies engaged in selection of personnel who need their customers, the development of information and analytical support for recruitment agencies to help serve most effectively and carry out selection to best match the requirements of the customer in the shortest possible time to analyze the data received from the customer, to compare requirements of the employer and the applicant wishes to find the option that best match criterion: for the employer - a skilled worker with all the necessary qualities for the job seeker - an appropriate workplace corresponding to its requirements. That is necessary to find the most appropriate alternative for job seekers and vacancies.
When an employer becomes a recruitment agency on his part is a proposal to competitors, and also formed a number of requirements for a potential candidate. This can be called the application of the employer.
Employer may offer some position in a certain area, social benefits, career prospects, a certain mode of operation, working conditions and wages. But to the applicant there are certain requirements, while meeting where it will be hired. It may be some personal and professional qualities. Every employer his vision of the ideal worker.
Criteria by which the employer chooses the employee may be represented in the form of mind maps.
Mind maps, map views, or associative card – the way the image of the overall systems thinking with the help of diagrams.
Mind map is implemented as a tree diagram, which shows the words, ideas, tasks or other concepts related branches that extend from the central concept or idea.
Implement this ideology, you can use the software Mindjet MindManager Pro 7. The result is shown in Figure 6.1.
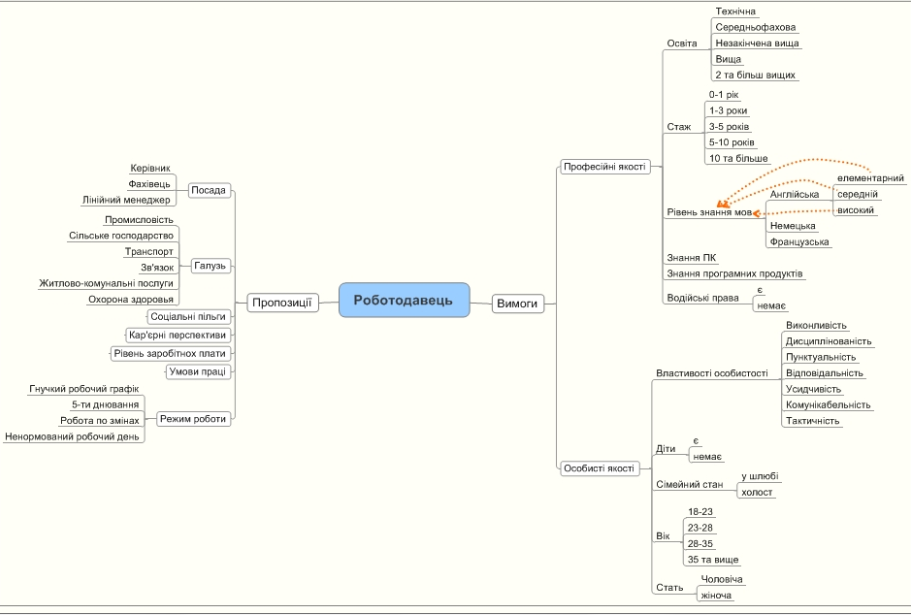
Figure 6.1 – Mind map "The Employer"
Similarly looks intelligence card to the applicant. But those factors, which are for the employer offer to act as the requirements of the applicant, and the factors which the employer is a requirement for the applicant are characteristic.
The employer, by contacting the recruitment agency, is their condition and wishes for the future employee. All information is entered into a database, which lists all of the requirements for the applicant required position and the level of s/n Example base in Figure 6.2.:
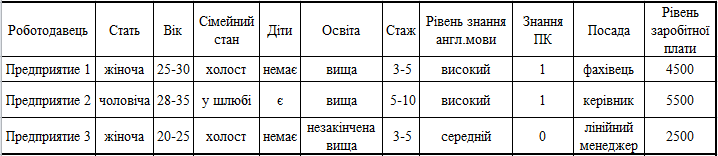
Figure 6.2 – The data on the requirements of the employer
These Jobseekers also entered into the database, which shall include: gender, age, marital status, children, education, experience, knowledge of English, knowledge of the PC, the desired position, the level of s/n In Figure 6.3 database shows the characteristics of job seekers:
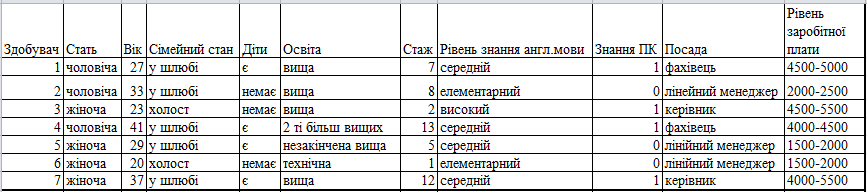
Figure 6.3 – Characteristics of the applicant
A database of employers and job seekers are made up of criteria by which to determine compliance with the requirements of the employer of the applicant.
Before you perform the fuzzy-logic analysis of the sample can be filtered by a clear sign, as follows: sex, age, marital status, education, position.
Filtration clear signs eliminated. Those signs that are left, have formed a fuzzy knowledge base, fuzzy microcontroller.
Consider the knowledge base, which is responsible for the result of the "degree of compliance". It consists of three input variables and one output variable.
Input linguistic variables are such indicators: input linguistic variables are such indicators:
X1: Experience {"low", "sufficient", "large"};
X2: The level of knowledge of English. the language {"bad", "satisfactory", "good", "excellent"};
X3: The level of knowledge of PC {"bad", "good", "excellent"}.
Starting linguistic variable is:
Y1: Degree of compliance {0-1}
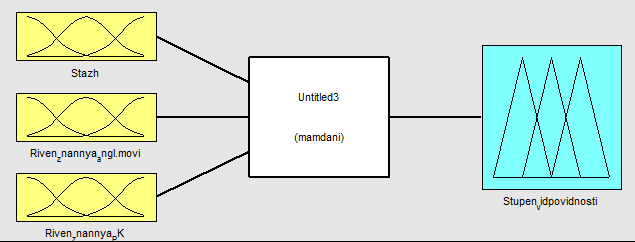
Figure 6.4 – A general view of the knowledge base "The degree of compliance"
Each of the linguistic variables of the form of fuzzy numbers are given in the form of a trapezoid. For example, the variable "experience" consists of three terms, which are the domain of 0 to 20, and are divided into parts corresponding to the value of time (Figure 6.5).
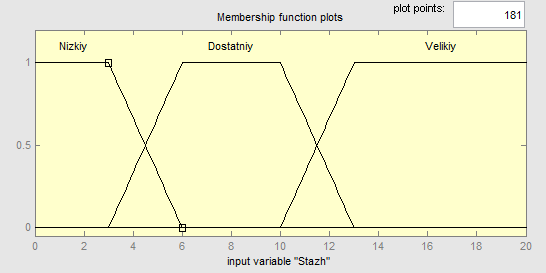
Figure 6.5 – The linguistic variable "Experience"
The variable "level of knowledge of English. first "consists of four terms which have the domain from 0 to 100. The numbers determine the score for the exam. They are divided into sections that correspond to a specific evaluation on a scale Balonskoy system (Figure 6.6):
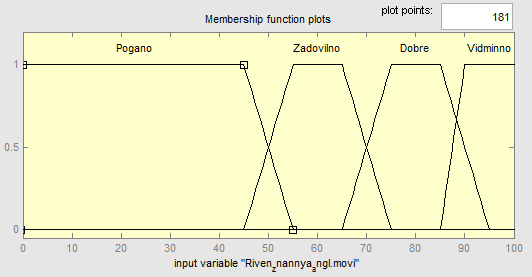
Figure 6.6 – The linguistic variable "Level of knowledge of English language "
The variable "Level of computer knowledge" consists of three terms, which are the domain of 0 to 1 (Figure 6.7):
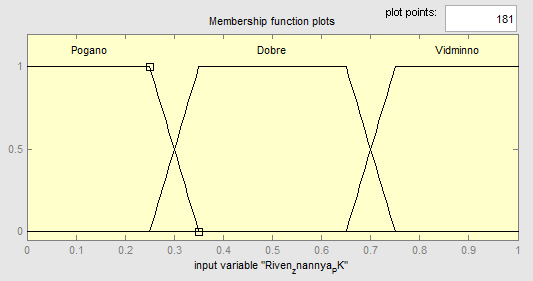
Figure 6.7 – The linguistic variable "Level of knowledge of the PC"
The output linguistic variable "Degree of compliance" is composed of three terms, which are the domain of 0 to 1. Baths are divided into parts, which determine the extent to which the applicant, the requirements of the employer (Figure 6.8).
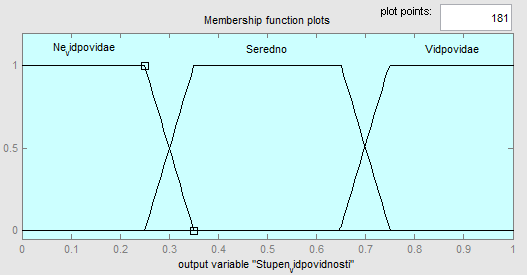
Figure 6.8 – Linguistic variable output "Degree of compliance"
After identifying all the linguistic variables are production rules for the knowledge base. Some of them are shown in Figure 6.9.
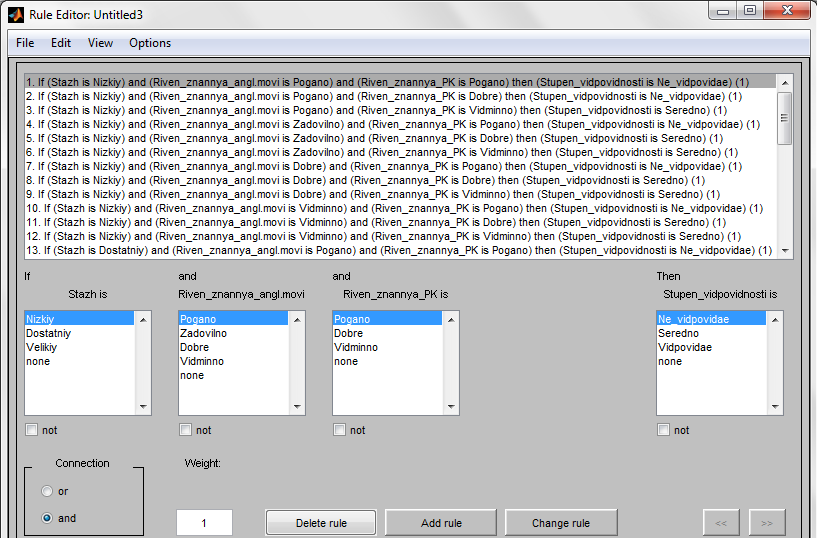
Figure 6.9 – Production rules
Consider some of them:
- If (Stazh is Velikiy) and (Riven_znannya_angl.movi is Vidminno) and (Riven_znannya_PK is Dobre) then (Stupen_vidpovidnosti is Vidpovidae) (1)
This means that if the user entered the system seniority of the applicant will belong to the term "big", the level of knowledge of English. language would be "excellent", the level of knowledge of the PC will be responsible, "Well", the applicant will be "responsible" employer's requirements.
- If (Stazh is Nizkiy) and (Riven_znannya_angl.movi is Pogano) and (Riven_znannya_PK is Dobre) then (Stupen_vidpovidnosti is Ne_vidpovidae) (1)
This means that if the user entered the system seniority of the applicant will belong to the term "low" level of proficiency in English. language is "Bad", the level of knowledge of the PC will be responsible, "Well", the applicant is "not responding" requirements of the employer.
Using a software package Simulink, create a model to determine the individual level of compliance. This requires the following components: three input variables, one knowledge base, one screen of output. The result is that the system has the form (Figure 6.10).
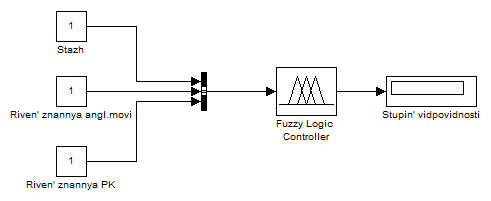
Figure 6.10 – Model for determining the degree of compliance
Test this model. Imagine that the company is looking for an employee. This place is tested several candidates. As input features will be performing candidates. The output will be the extent to which each individual applicant requirements of the employer.
Table 6.1 shows the characteristics of job seekers:
For Jobseekers Ivanov model to calculate the degree of compliance with the requirements of the applicant is as follows (see Figure 6.11):
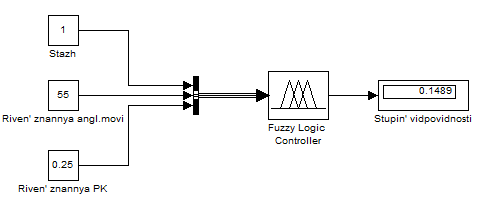
Figure 6.11 – The degree of conformity of the applicant Ivanova
For Jobseekers Petrova model to calculate the degree of compliance with the requirements of the applicant is as follows (Figure 6.12):
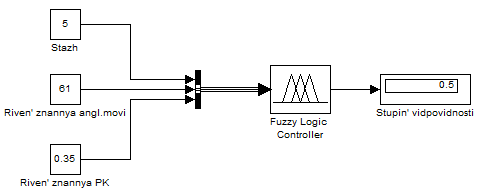
Figure 6.12 – The degree of conformity of the applicant Petrova
For Jobseekers Sidorova model to calculate the degree of compliance with the requirements of the applicant is as follows (Figure 6.13):
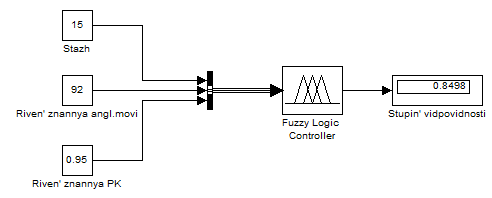
Figure 6.13 – The degree of conformity of the applicant Sidorova
Thus, the model is used to determine compliance with the requirements of the employer of the applicant. From these calculations it can be concluded that the most suitable candidate for the requirements of the employer's competitor Sidorov, because it corresponds to the highest degree.
Similarly knowledge base determine the extent to which the applicant requirements of the employer based knowledge base is the extent to which the employer wishes of the applicant.
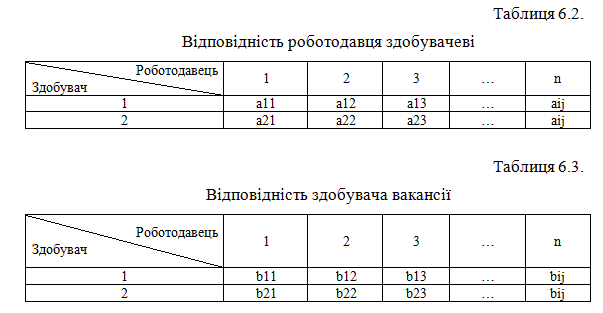
On the basis of calculations based on fuzzy knowledge generated arrays Employer Compliance (tabl.6.2) and job seekers (tabl.6.3), where rates range from 0 to 1. What is closer to 1, the greater the degree of compliance.
Once identified the extent to which all need to find options that will at the same time the most maximum and meet the following criteria:
This means that the most suitable to each other will be those applicants and employers, the extent to which the subtraction will tend to zero, and the sum is close to two.
This expert system is based on the input information, which can not be represented as a well-defined values in order to assess the degree of compliance with the requirements of the employer and job seeker on the contrary, job seeker needs.
Findings
Services of recruitment agencies in the field of HR in demand for the modern world. The slogan of "cadres decide everything" to this day is still relevant. From effectively chosen depends on the work of all employees of the organization or enterprise, especially for highly skilled, experienced managers.
Despite these difficulties, there has been steady growth in sales recruitment services. Regional companies are gradually coming to the realization that even the full content of the HR department is not always able to solve the problem of enterprise staff and is often uneconomical. Drawing for solutions to this problem recruitment agency, the firm is able to significantly extend the range of specialist search: in fact most of the major agencies involved in the selection of personnel in several Ukrainian regions. In addition, the recruitment agency helps companies formulate requirements for the candidate with the overall situation in the sector and the market as a whole. The development of the Ukrainian economy and the analysis of the global staffing industry can make a prediction: the amount of recruiting in Ukraine will grow, this business has growth potential.
Development and systematization of analytical support information flow ensures the effective functioning of the employment agency and increase its competitiveness in the recruitment services market in Ukraine.
Job Recruitment is based on the principle of industry specialization: each consultant involved in the selection of staff in a specific industry segment, which makes it possible to provide a qualitative assessment of the labor market.
Was a model of formation of profit employment agency, which aims to determine at what amount of variable costs and at what period of profit staffing agency will be maximum.
The concept of information and analytical support for recruitment agencies in its implementation should help to serve most effectively and carry out selection to best match the requirements of the customer as soon as possible to analyze the data received from the customer to compare the requirements of the employer and the applicant wishes to find an option that meets the criterion of optimal match: for the employer – a skilled worker with all the necessary qualities for the job seeker – an appropriate workplace corresponding to its requirements. In this paper the approach for the selection of applicants with the requirements of the employer's position methodology of fuzzy logic, the proposed expert system for determining the degree of compliance with the requirements of the employer of the applicant.
Proposed expert system based on the input information, which can not be represented as a well-defined size, to evaluate the degree of compliance with the requirements of the employer and job seeker on the contrary, job requirements of the applicant.
List of sources
- Андрєєв А.Ф. Основи кадрового менеджменту / А.Ф. Андрєєв, Н.В. Гришина, С.Г. Лопатіна.- М.: «Юрайт», 2008. – 354 с.
- Андрушків Б.М., Кузьмин О.Е. «Основи менеджменту»:- Львів: «Світ», 2007.- 296 с.
- Базаров Т. Ю., Маліновський П. В. Управління персоналом в умовах кризи. – К.: «Либідь», 2010.-345 с.
- Бовтрук А.П., Управління персоналом: практикум: – К:КНЕУ, 2009. – 106 с.
- Бортников П.К. Идейно-теоретические и методологические основы организационно-управленческих игр. - Г. Пресса, 2007.-560 с.
- Блейк Р. Р Наукові методи управління: Навч. Посібник - К: МАУП, 2009. – 689 с.
- Блейк Р. Р., Мутон Дж. С. Наукові методи управління: - К., Пер. з англ., 2011.- 371 с.
- Бранченко Г.Н. Менеджмент організації: посібник., Ж.: ЖІТІ, 2006.-265 с.
- Братченко В.Ф Управління персоналом організації в сучасних умовах // Персонал. -2011. -№ 3. –С.4.
- Горелов М.А. Економіка трудових ресурсів. – К:КНЕУ, 2007. – 206 с.
- Грачев М.В. Суперкадри. Управління персоналом в міжнародній корпорації: – М., 2008.-345 с.
- Данілюк В.М., Петюк В.М., Цинбалюк С.О. Менеджмент персоналу: Навч.-метод. посіб. — К.: КНЕД, 2007. - 398 с.
- Дорофієнко В.В. Управління персоналом навч. вид. у 2-х кн./ В.В.Дорофієнко, Ю.М.Комар, Н.Л.Сапельнікова; за заг. ред. С.Ф.Поважного; ДонДУУ. - Донецьк: СПД Купріянова В.С., 2010. – 425 с.
- Економіка підприємства: Підручник / За заг. ред. д.е.н., проф. Л.Г.Мельника. – Суми: ВТД «Університетська книга», 2010. – 648 с.
- Журавель П.В Сучасна парадигма в управлінні персоналом // Персонал. - 2007. -№5.- С.39-42.
- Жуковський М.О. Трудові ресурси як складова конкурентоспроможності підприємства // Актуальні проблеми економіки. – 2007.-№2 – С.68-69.
- Журавльов П.В. Персонал. Словник понять і визначень / П.В. Журавльов, С.А. Карташов, М.К. Маусов. - М.: Іспит, 2009. – 318 с.
- Журавльов В.В., Савруков Н.Т. Аналіз господарсько – фінансової діяльності підприємства: Санкт – Петербург: 2007. - 81 с.
- Іващенко В.І., Болюх М.А. Економічний аналіз господарської діяльності. – К: ЗАТ «НІЧЛАВА», 2009. – 256 с.
- Кібанов А.Я., Шушпанов Д.Г. Управління трудовими ресурсами: Навч. посібник. – К.: Видавничий Дім «Юридична книга», 2005. – 358 с.
- Ковпаків В. М. Теорія і практика ухвалення управлінських рішень: Навчань. посібник. — 22е видавництво, перераб. і доп. — До.: МАУП, 2011. — 504 с.: мул. — Библиогр.: с. 247-251.
- Колот А.М. Мотивація персоналу: Підручник. – К:КНЕУ, 2009. – 337 с.
- Колот А. Інноаційна праця та інтелектуальний капітал у системі факторів формування економіки знань // Україна: аспекти праці. – 2007. - №4 –С.4
- Коробов М.Я. Фінансово-економічний аналіз діяльності підприємств. Навчальний посібник. – К: Тов. «Знання», 2012 – 275 с.
- Коростильов В. А. Управлінське консультування: Навч.-метод. посіб. — К.: МАУП, 2007. - 104 с.
- Кравчено Т.С. Аналіз концепцій кадрового менеджменту // Персонал, -2009. - №5. - С.36-40
- Кравченко К.А. Пошук і відбір персоналу: Історія і сучасність. / / Управління персоналом. -2010. - № 12. - С.39-42.
- Кузнєцова Н.В. Оцінка потреби персоналі / / Довідник з управління персоналом. - 2008. - № 6. - С.15-36.Лук’янхін В.О., Менеджмент персоналу. – Суми: Університетська книга, 2008. – 592 с.
- Магура М.И. Пошук і відбір персоналу / М.І.Магура. - М.: ЗАТ «Бізнес-школа« Інтел-Синтез », 2007. – 316 с.
- Магура М.И. Сучасні персонал-технології, М.І.Магура,М.Б.Курбатова. - М.: ЗАТ «Бізнес-школа« Інтел-Синтез »», 2010. -376 с.
- Мескон М. Х., Альберт М., Хедоури Ф. Основи менеджменту.- М.:ДЕЛО, 2009. – 702 с.
- Моргунов Є. Управління персоналом: дослідження, оцінка, навчання / Е.Моргунов. - М.: ИНФРА-М, 2007. – 339 с.
- Одегов Ю. Г., Журавльов П. В. Керування персоналом. - М.: ИНФА, 2008. – 319 с.
- Олександрова Т. Г. Управління персоналом: Методичні вказівки до практичних занять: Оренбург: ГОУ ОГУ, 2012. – 63 с.
- Осовська Г.В., Крушельницька О.В. Управління трудовими ресурсами: Навч. посібник. – К: Кондор, 2007. – 224 с.
- Орлов О.О. Планування діяльності промислового підприємства. – К: Скарби, 2012. – 336 с.
- Осовська Г.В. Основи менеджменту: Навч. посібник, для студентів вищих навчальних закладів. — К.: «Кондор», 2009– 365 с.
- Павленко Н.А. Трудові відносини: запитання та відповіді. – Х: Фактор, 2009.-456 с.
- Патора Р., Андел І.В. Управління працевлаштування випускників навчальних закладів/ Соціально-економічні дослідження в перехідний період. Щорічник наукових праць. Інститут регіональних досліджень. – Львів, 2007.№3. – С. 257-268.
- Поршнєв А. Г. Керування організацією. -М.: ИНФА, 2008. – 212 с.
- Пушкарьов М.М Кадровий менеджмент: конспект лекцій., К.: Либідь, 2011.-300 с.
- Реверчук С.К., Реверчук Н.Й, Скоморович І.Г., Інвестування: наука про інвестування, Львівський національний університет ім. І. Франка. – К.: Атіка, 2009. – 264 с.
- Румянцева З.П. Менеджмент організації . - М.: ИНФА, 2008. - 202с.
- Роррінг В.Г. Мистецтво управління: М. БЭК 1997г. Ростов-на-Дону «Фенікс» 2008. – 82 с.
- Савицька Г.В. Економічний аналіз діяльності підприємства. - Київ: Знання,2008.- 662 с.
- Семикіна М.В., Економічна мотивація інвестування в розвиток людського капіталу підприємства // М.В. Семикіна, Актуальні проблеми економіки. – 2004. - № 5. - С. 178-185.
- Соломанідіна Т. О., Соломанідін В. Г. Мотивація трудової діяльності персоналу: М.: «Журнал »Управління персоналом, 2005. 278 с.
- Татарников К.Р. Управління кадрами: Учебн. Пособ.- До: МАУП, 2009- 582 с.
- Татарников А. А. Управління кадрами в корпораціях США, Японії, Німеччини: — М., 2009.-150 с.
- Тимошенко І.І., Соснін А. С. Менеджер організації: Навчальний посібник для менеджерів – К.: Видавництво Європейського університету, 2009. – 350 с.
- Травін В.В., Дятлов В.А. Основи кадрового менеджменту: М.- «Справа», 2009. – 543 с.
- Уткін Е. Управління фірмою: - М. «Акаліс», 2010. – 35 с.
- Фаткутдінов Р.А. Система менеджменту: Підручник для вузів. – К.: Банки і біржі, ЮНІТІ, 2008. – 447 с.
- Хміль Ф. Управління персоналом: Підручник/ Федір Хміль . - К.: Академвидав 2009. – 487 с.
- Храмів В. О., Бовтрук А.П. Основи управління персоналом: Учебн.-метод. Пособ. - До. МАУП, 2001. - 112 с.
- Цимбалюк С. О. Технології управління персоналом. навч. посіб. / С. О. Цим¬балюк. — К. : КНЕУ, 2009. – 399 с.
- Чижов Н.А. Персонал предприятия: технология управления и развития / Н.А.Чижов. - М.: Издательский центр «Анкил», 2009. – 275 с.
- Шаховой В. А. Кадровий потенціал системи управління: -М., 2005.-100 с.
- Шкатулла В.І. Теорія і практика управління персоналом: Учебн. Пособ. -К: МАУП, 2008.-125 с.
- Щокін Г.В. Соціальна теорія і кадрова політика: Учебн.-метод. Пособ. - К., МАУП, 2008 – 432 с.
- Щічкін Г. В. Основи кадрового менеджменту: — К., 2009.-260 с.
- Шічкін С. В. Управління персоналом в сучасній організації. Учбово-практичний посібник: Видання 4-те, пер. і доп.; Бізнес-школа «Інтел-синтез», 2009 – 320 с.
- Аллин О.Н., Сальникова Н.И. Кадры для эффективного бизнеса. Подбор и мотивация персонала / О.Н. Аллин. – М.: Генезис, 2005. – 248 с.
- Аристов С.А. Имитационное моделирование экономических систем: Учеб. Пособие. – Екатеринбург: Изд-во Урал.гос.экон.ун-та. 2004. – 123 с.
- Евенко Л.И. Системы, стандарты, практика подготовки профессиональных менеджеров в зарубежных странах (программа МВА) / Л.И. Евенко. – М.: ЗАО «Книжный мир», 1998. – 200 с.
- Имаева А. Будни рекрутера: от заявки до Job-offer / А. Имаева. – М.: Проспект, 2007. – 150 с.
- Кафидов В.В. Управление персоналом / В.В. Кадифов. – М.: Академический Проект, 2003. – 144 с.
- Лысенко Ю.Г., Егоров П.В., Овечко Г.С., Тимохин В.Н. Экономическая кибернетика: Учебное пособие; изд. 2-е / Под ред. Ю.Г. Лысенко, ДНУ. – Донецк: ООО «Юго-Восток, Лтд», 2008. – 516с.
- Малыкин В.И. Математическое моделирование экономики / Учебно-практическое пособие. – М.: Издательство УРАО, 2008. – 160с.
- Музыченко В.В. Управление персоналом / В.В. Музыченко. – М.: Академия, 2003. – 528 с.
- Штовба С.Д. Проектирование нечеких систем средствами MATLAB. – M.: Горячая линия – Телеком, 2007 – 288с.
- Уткин В.Б. Информационные системы в экономике: Учебник для студ. высш. учеб. заведений / В.Б. Уткин, К.В. Балдин. – М.: Издательский центр «Академия», 2004.-288 с.