Abstract
Contents
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. Cadastre its definition and classification
- 4. Foreign experience of water cadastre
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
For the efficient operation of leading natural resource inventories, should be the primary measure to bring the legislation into conformity with the requirements of today. In this case, the important point is not so much to improve the organizational structure of the existing management of this area, how to improve the quality and efficiency of administrative work, reduced mainly to better define new targets and methods of their solutions. This approach can be explained by the fact that society has an interest in the high quality of its inventories. Quality control ensure clearly defined, science-based goals and objectives, the objective of determining the functional-structural construction management agencies, modern forms and methods of operation, democracy, technical equipment and personal characteristics such employees of the management as a sense of duty, competence, respect for the rule of law, discipline, principles.
1. Theme urgency
The research activities of the state bodies in the sphere of environmental protection have dedicated their works: A. Getman, V. Zuev, L. Kovalenko, V. Kolpakov, V. Kostitsky, N. Malyshev, M. Malishko, V. Muntean, B. Rozovsky, Y. Shemshuchenko. However, a comprehensive study of the legal and administrative framework for the activities of public authorities in the sphere of conducting natural resource inventories have been conducted. Necessary to determine the system of state bodies, is maintaining natural resource inventories. Management of the State Water Cadastre (PEC) - is the systematic collection, updating, analysis, synthesis of information on water resources, their condition, the dynamics of water bodies, identification of patterns of change in quantity and quality of surface and groundwater in time with variable water conditions and the variety of the impact of human activity. The end result in this case is the data on the state of water resources, reserves and pollution of surface and groundwater. One of the priorities of the PEC is the comparison of the accumulated information contained therein as the territorial aspect, and in time. For now clear, the current system is not doing the PEC. All information about the bodies of water stored in paper form, which causes some discomfort in finding some characteristics of water bodies, graphic material to them. In this master's work the problem of determining the parameters and structure of input data, the development of information processing algorithm in the system, the connection water inventory inventory of land management, the creation of a database model of water bodies by the example of the city of Donetsk.
2. Goal and tasks of the research
In the master's work solved the following problems:
- Analysis of doing water cadastre in Ukraine and abroad;
- Characterization input processing algorithm development information system, Communications Water Cadastre of Land management inventory;
- Create a database model water bodies.
3. Cadastre its definition and classification
Inventories (French Cadastre) - a systematic fund information, which periodically replenish and refine through an appropriate system of supervision over one or another natural object [ 2 ]. At present, inventory engaged in all countries. It is closely intertwined with the concepts of accounting, evaluation and use of various natural resources, engineering, their ecological condition and marked distinguishing intra-uniform in terms of its territorial units of different ranks, mapping and a description of the quantitative and qualitative characteristics of r 'objects [ 2 ]. Depending on the classification of different inventory becomes essentially answering one purpose for which it was created. Thus, we can classify inventory on several criteria. The classification scheme is shown in scheme 1.

Schemeа 1 – Classification of inventory
By appointment inventory can be classified into three broad categories:
- tax and fiscal - to describe the real property to determine the order and size of its tax;
- legal or law - to protect the rights owner of the property;
- Multi - for a wide range of legal, economic, environmental, urban problems, and to address the management and planning of development areas.
Multipurpose Cadastre contains information about objects of different types: natural resources, infrastructure, socio-economic phenomenon.
There is the concept of single-species inventory that contains information about a single object (building, plumbing, etc.) and bahatovydovoho that contains information about multiple objects of the same type (infrastructure inventory, inventory of natural resources, social events, etc.).
According to the principle of territorial cadastre divided into national and regional. In the first case, the inventory covers the country in the second - the branch spread of inventory limited territorial regions (regions, cities, towns, etc.). When updating inventory carried out by the same requirements for the country, based on a qualitative methodological support, then the inventory regardless of the territorial principle, called the state [ 2 ].
The issue of rational use and protection of water resources is regulated by the Water Code of Ukraine. Rational use of water resources is impossible without systematic hydrological data. At the present time, the cadastral system for many kinds of natural resources in the active process of creation. Unified state system of accounting treatment and their use provides systematic monitoring of groundwater regime and record of all waters unified state fund justifies their areas management.
Keeping the State Water Cadastre (PSC) - a systematic collection, updating, analysis,compile information on water resources, their condition, the dynamics of water, identify patterns of change in quantitative and qualitative indicators of surface and groundwater in time based on variable conditions of water management and the whole diversity of human exposure activity. The end result in this case is the data on the state of water resources, stocks and levels of contamination of surface and groundwater [ 2 ].
In Ukraine inventory designation, its structure is changed according to the political and economic situation. Centuries consecutive Ukraine experienced land reforms that significantly changed the content and form of inventory. The first reforms were carried out, when Ukraine was part of the Russian and Austro-Hungarian empires. Then she was part of the empire, which was called the USSR. The latest reform is now - in years when Ukraine became an independent state. During the primitive density of settlement in the immediate Ukraine was not high, so the land had great value. While the primary value was economic tools, live poultry and livestock, and mastered land, solutions to common economic needs and protect Courtyard able to unite the community and the community - in some localities (towns, villages). This principle of association Courtyard and communities contributed to the fund land areas, which jointly managed Courtyard residents, communities, villages and cities.
Importantly, 40% of all information relating to water cadastre can be obtained from topographic maps. Only in 1926, Ukraine initiated forest inventory, the purpose of which is about the quantitative and qualitative composition of forests, forest groups and categories of security information on forest users and other data needed for efficient forest management. In forestry use such planning and cartographic materials like plates forestry, afforestation plans, schemes of forest enterprises. The plates are in M ??1:5000, 1:10 000, afforestation plans - M 1:25 000 - 1:100,000. Since 1927 is the registry (cadastre) minerals. The essence of this inventory is that each mineral deposits are special passport and registration card. The passport note a deposit of stocks and so on. Registration cards are based on topographical limits with a population of field.
Analysis of the current state of cadastral works in Ukraine indicates the need for radical change as the structure and content of the work. In fact, inventory is not a coherent system of accounting, assessment and effective use of natural resources and the whole social and industrial infrastructure.
Particularly noteworthy are the organizational and economic issues creating and maintaining inventory. Decide on interconnection providing inventory information of all concerned departments and organizations. Typically, fragments inventory are various departmental services and organizations. For example, the Bureau of Technical Inventory have information about the individual and state building, architectural surveying services departments have partially topographic and geotechnical information; separate management, departments and units of local government - issues of quantity and quality of the entire production and social infrastructure that nahodytsya in their jurisdiction. This disorder and departmental decentralization often leads to duplication of the same work several organizations that require significant material and economic costs. This points to the need for a single integrated inventory management system, especially during the formation and development of various forms of ownership. Each potential owner should know where to find information about a particular object that interests him. The law provides for the establishment of an independent Ukraine and conduct a number of state inventories are shown in scheme 2.
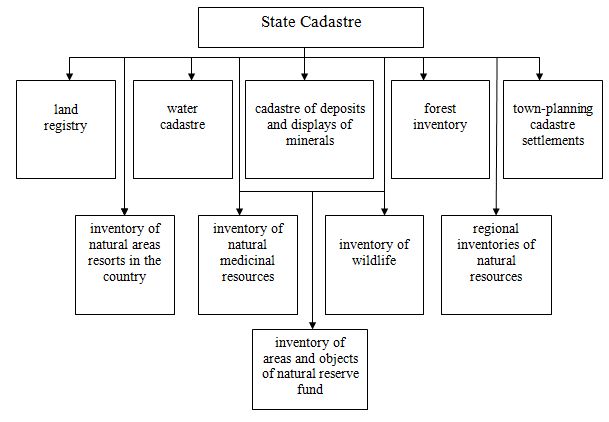
Scheme 2 - State Cadastre of Ukraine
Another important problem is the lack of regulatory and technical framework for creating and maintaining inventory orhanizaniyno and technological unprepared individual industries to register.
4. Foreign experience of water cadastre
European Water Framework Directive - European Directive on Water (Derektyva) was the result of years of discussions with the European Union's policy of integrated water resources management and gathered in itself all the modern approaches to water management. The fundamental principles of the Directive are:
- ensuring the protection, improvement and restoration of all surface water bodies with a view to achieving by 2015 their satisfactory ecological condition;
- water management within the water basin with the creation of a special government agency management;
- the study and use of water bodies of each water basin, assess the extent and sources of anthropogenic impacts on water bodies, the economic analysis of water use;
- developing long-term program of action for each water basin, which should be reviewed and refined every 6 years, with the obligatory post them for discussion;
- active involvement in the development, updating and implementation of programs of all basin stakeholders, including water users, local authorities and the public;
- the practical application of the principle of full cost recovery for the study, protection and restoration of water resources, restoration of water bodies by means of payments for water use and water pollution (the so-called principle of "water pays for water" and "polluter pays");
- the licensing of water use based on norms of acceptable impacts on water bodies and water quality objectives;
- monitoring of water bodies and protected areas;
- coordination in transboundary water with neighboring countries and the desirability of creating inter-state governing body.
Directive on Water is most relevant existing water legislation in France. In 1921, France passed a law to create a program of the Rhone River Basin, which includes three priorities - electric power, navigation, irrigation and agricultural water supply. In 1933, established the National Company of the Rhone River with the function of the contracting authority of this program, primarily at the expense of output power. The State has provided all the rights to develop water management system of the river Rhone and operation of all facilities. Adopted in 1964, the Water Act made fundamental changes in the system of state management of water resources in France. The entire country was divided into six hydrographic basins, all of which were created by basin committees (water parliaments) and the basin of the Agency. Pools committees that include representatives of all stakeholders were empowered to determine the policies of the basin and the establishment fees for water use (which, in principle, contrary to the French Constitution, which involves issues of general taxation only elected legislative assembly). Ponds Agency is an executive state financial and technical bodies to ensure implementation of basin-wide policy under the self-financing using the levers of economic incentives (payments and subsidies). Adopted in 1992, the Law on Water addition:
1) introduced a number of priorities for water management basin solving environmental problems based targets;
2) identified the need for joint management of surface and groundwater;
3) established the need for basin committees master plan for development and management of water services pools, as well as development plans at the pools.
In Spain, Water Act 1985, which replaced the act of 1879 law declared all water resources are state property and brought national integrated water resources management from planning, river basin management and payment for water use. The master plan of water management developed by the Federal Government with all the regional plans. In a country with 1926 water management exercise 14 Basin Confederations, whose functions include: development of water resources, water pricing, issuing permits for water use (intake and discharge), monitoring of water bodies and enforcement of the standards (of and quality). Confederation manages the President and Committee of Directors, which includes representatives of ministries, representatives of water users and autonomy. Within the Confederations under commission from various areas of water management. Act 1985 established payment: by public water, the water intake for water pollution. However, these payments currently cover only a small part of the cost Confederations, the rest is covered by subsidies from the government. Subject of legal regulation in the CIS only relations associated with the water that is in the water bodies (surface and underground). In the UK, the main issue of legal regulation is to ensure drinking water supply, treatment and disposal of wastewater. In Germany the basis of legal regulation is the problem of purification and sewage, including storm. Basis of Water U.S. law is the law of individual states, which mainly regulates relations in the sphere of snowmelt and storm water. In some countries in the arid zone of the right to own water, which increases the value of land, property rights and is regarded as belonging to the land. So in some U.S. states, the principle of seniority (in time) water rights, and therefore, even with state ownership of water, growing cities and industries are forced to buy "water rights" in their traditional rulers - the farmers. Furthermore, it is assumed legislative regulation of "rationality" in terms of melt water and groundwater. In river basins are usually water users associations that monitor so that each water users did not exceed their rights and not abuse it, and most importantly, protect their interests and rights in its relations with neighboring associations. In the Eastern U.S. states apply the principle of so-called "right shore" (which existed in Russia until 1917), in which the right to use water with only the owners of coastal land. Selection of water permitted to the extent not infringe located downstream users. Issues reasonable (rational) use of water resources and compliance with other "water rights" in the United States tested in court. Currently, almost all countries is the role of the state in regulating water relations. Growing importance authorization procedure of groundwater for use based on priority water users. In advanced economies statutory need for long-term programs of integrated use and protection of water bodies to reduce their pollution and prevent the depletion of water resources. Water legislation of most foreign countries involves government regulation of use and protection of water bodies. In almost all countries established state water management agencies entrusted with the function of regulating relations in the sphere of water management in the interests of society.
U.S. law surface water and groundwater are regulated by different laws. The emphasis in the regulation of the use of surface water is a system of permits for water use. By law potential user of water applies, which has publicly notified the public (for possible objections). An official of the State, under the law, considers the application and makes a decision about accepting or refusing. After obtaining water users shall in due time (usually 5 years) actually start to water, then it is not right to water use restrictions on the term. Permitting water management, applicable to state law, supplemented by measures of control exercised by the federal government and aimed primarily at providing irrigation and flood protection. If the rule states in regulating water relations in the U.S. for a long time are two river basin water management. Since 1933 the Department has successfully Tennessee Valley, a zone of which covers seven states. Management is mainly engaged in power generation (1 in the U.S.), he owns 29 hydroelectric plants, 511 power plants and 3 nuclear power plants. However, from the outset included in the functions of the integrated water resources management and development of the basin, including the navigation, flood control measures, protection of water and natural resources, reforestation and erosion control, support and recreational activities to combat water-related diseases. Since 1961, operates the Delaware River Basin Commission, which consists of four state governors, located in the basin, and a representative of the President of the United States. The Commission is responsible for issues of water supply, pollution reduction, conservation and restoration of water resources, regional planning. The Commission has licensing functions and sets targets for water quality. UK legislation, in England and Wales has a centralized system of water management. From 1945 to allocate scarce water resources as advisory bodies were established Tips River, formed mainly on elective basis. In 1963, River tips have been converted to Android (with a permanent staff of employees), whose task was part of monitoring the quality and quantity of river water. In 1973 he established 10 regional departments The river that received broad powers regarding management of the drinking water supply, purification and sewage, maintenance of navigation and flood control, setting standards and issuing permits (licenses) for sampling of water and wastewater, and water monitoring. In the departments were between 60 and 40 percent of elected local representatives. In 1989, Parliament adopted a decision on the privatization of the regional offices and the creation of The river at their base the Water Service Companies in charge of drinking water supply, purification and sewage. The functions of the state of water resources were transferred to the Office of National River, which is responsible for the anti-flood measures governing the use of water, fishing and some shipping issues. In 1999 - another radical change in the management structure of the transfer of planning the use of water and land resources in the regional (territorial) Assembly. German law, despite the fact that Germany is a federal republic is authorized to manage water resources shared between the federal government and state governments. In 1976, legislation introduced by the national tax system for pollutant discharge. The recipients of these funds is the Earth, but they are required to send the money for the quality management of water resources. At the national level unified system of integrated management of water resources do not exist, but in some Lands in the early twentieth century were created River Association. This Rurverband (Ruhr Valley), which deals with construction and operation of reservoirs and facilities to clean drinking water stations for wastewater and storm water. This is a self-governing organization, but the law is controlled by the government of North Rhine-Westphalia and the German Federal Ministry of Environment. Activities of the Association at the expense payments for water intake and effluent discharge. The governing bodies of the Association are partners Assembly (150 members), the Supervisory Board and the Executive Committee.
If we return to the disintegration of the USSR in the years 1992-1995 in all CIS countries adopted new water legislation - Water Codes and Laws of water. Most of these codes and laws define the entire system of water legislation, reveal the content and structure of the legislation regulating water relations. Subject of legal regulation of water legislation of CIS countries are water relations that define social relations on the natural water bodies. All of the Water Code and the law found its decision on the ratio (division) of water legislation in other sectors prirodnoresursnyy legislation. Full-reflected sphere of public administration in the use and protection of waters, open types and forms of control (public, institutional, industrial, public). In all countries of the CIS in the sphere of management in the use and protection of water bodies included in the economic regulation of water use. Attached legal mechanism for enforcing water legislation by all participants water relations, dispute resolution and liability for violation of water legislation. Currently accumulated a significant number of international legal sources in the field of water management. First, regional agreements on the treatment of transboundary watercourses.
Information cadastral registration in most countries are making a big impact on the overall land use policy of the country, so most precise information on the size and condition of land resources are extremely important, and hence increased attention to cadastral records [ 9 ]. Historically, that:
- land registry data used in section processing, combining land during land transactions, based on these published documents certifying the right of land ownership (use);
- Cadastral information used by the authorities at various levels for decision-making related to land use (land use planning, control and improvement of land, etc.);
- from land registry records and conducted evaluation not only of land, which were considered property, but also other real estate related to land (buildings, engineering structures, etc.), which provided information basis for taxation;
- Materials cadastre were landowners tool that enabled them to maintain land ownership in the complex: coordinating construction of various objects (buildings, roads, water supply and sanitation, recreation and shopping centers), to land operations coordinated use of their land to the public interest.
Therefore, as rightly observed SN Volkov, land cadastre abroad involves not only technical actions, but also a land inventory process associated with the registration of land and other immovable property and transactions with it [ 10 ]. Ultimately, the information obtained as a result of land cadastre is inextricably linked to the concepts of accounting, valuation of land resources assessment and possible use of a particular purpose. First, land registry function played fiscal cadastre, and only in the late XIX century increased its legal role related to the registration and protection of land rights. It should be noted that the foreign practice of "inventory" is most often associated with the term "real estate". But when real estate is understood and provides the following definition: a social description that contains information on the number, value, ownership plots of land and other property, tightly bound (connected) to the ground. In 1985, the International Panel on cadastre and land information gave more generalized definition of inventory. Currently, the accepted practice in a foreign land cadastre concept, approved by the UN in conjunction with the International Federation of Surveyors (FIG) in Bogor (Bogor, Indonesia, 18-22 March 1996) and then in Bafertskoy (Bathurst, Australia, October 22, 1999 c) a declaration according to which "inventory - is usually based on land (parcels) modern land information system containing a record of property rights (such as rights, restrictions and responsibilities). It usually includes a geometric description of land, linked to other records describing the nature of rights, ownership or management with respect to these rights and often the cost of land and its improvements. Inventory may be appointed for fiscal purposes (eg, evaluation and equitable taxation), legal purposes (for example, register the transfer of ownership of the property) to assist in the management and use of land (eg, planning and other administrative purposes), and creates an opportunity for sustainable development and environmental protection. "
Conclusion
This master's work is not completed yet. Final completion: December 2013. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Енциклопедичний словник України
- Курганевич Л.П. Водний кадастр: Навч. посібник. - Львів: Видавничий центр ЛНУ імені Івана Франка, 2007. - 116 с.
- Б. Вишневсъкий В. І. Річки і водойми України. Стан і використання. - К.: Віпол, 2000. - 376 с.
- Земельний кодекс України чинний, поточна редакція від 05.01.2013
- Геренчук К. И. Некоторые итоги и задачи географических исследований для оценки земли // Вопросы географии. Сб. 67. География и земельный кадастр. - М.: Мысль, 1965. - С. 24-31
- Водний кодекс України -13 червня 1995 року - згідно з Постановою Верховної Ради України від 6 червня 1995 року N 214/95-ВР.
- Порядок ведення державного водного кадастру: Постанова Кабміну України від 8.04.1996(21.06.04), № 413.
- Розпорядження Кабінету Міністрів України від 3 вересня 2010 року за №1029 «Про схвалення Концепції Загальнодержавної цільової програми розвитку водного господарства на період до 2020 року»
- Лук’янчиков Д. Государственный кадастровый учет земельных участков.
- Волков С.Н.. Землеустройство. Том 7. Землеустройство за рубежом. – М. КОЛОСС - 2005.
- Сидоренко В.Н. Правовое регулирование ведения государственного земельного кадастра. Автореферат диссертации на соискание ученой степени кандидата юридических наук. – М., 2003.
- Коротеева Л.И. Земельно-кадастровые работы. Технология и организация. – Ростов н/Д: Феникс, 2006. – с.23.
- Рассказова А. Опыт управления земельными ресурсами в зарубежных странах // Электронный журнал Investzem.Ru
- Филиппова А.П. Зарубежный опыт функционирования кадастровых информационных систем // Земельный вестник России, № 1 –2, 2005 – с.63-68.
- Иофин З.К. Мировой водный баланс, водные ресурсы Земли, водный кадастр и мониторинг: учебное пособие /З.К.Иофин - Вологда: ВоГТУ, 2009.- 141 с.
- Мартин А. докторант Національного університету біоресурсів і природокористування України, кандидат економічних наук: стаття «Проблеми державного земельного кадастру в Україні», УДК 322.2.
- Маценко О.М. Науково-методичні засади удосконалення організаційно-економічного механізму водокористування: дисертація на здобуття наукового степеня доктора економічних наук. – Суми: Сумський державний університет, 2009. - 202 с.
- Джуган В.О. Правове регулювання використання та охорона вод в Україні: дисертація на здобуття наукового степеня доктора юридичних наук. – Івано-Франківськ: Прикарпатський національний університет імені Василя Стефаника, 2009. - 91 с.
- Водна стратегія України на період 2011-2020 років (проект). - Київ: Національна академія аграрних наук України Державний комітет України по водному господарству Інститут водних проблем і меліорації НААН, 2010. - 31с.
- Перович Л. Сучасний стан та перспектива розвитку кадастрової системи України: стаття «Львівська політехніка», національного університету, розділ сучасні досягнення геодезичної науки та виробництва, випуск II (22) до ІІ з’їзду УТГК, офіційна хроніка, освіта, наукове, виробниче та громадське життя, 2011. - ст. 40- 42.
