Abstract
Сontent
- Introduction
- 1. Theme urgency
- 2. Goal and tasks of the research
- 3. An approach to the unification of synthesis of Moore FSM on FPGA
- Conclusion
- References
Introduction
Ukraine’s transition to a market economy has identified the need to implement a new, modern conditions of adequate state urban policy. The main instrument for the implementation of this policy is the system of the urban cadastre – state, regional and basic (local) levels. Urban planning reform in the state, which began with the entry into force March 12, 2011 the Law of Ukraine "About Regulation of urban development" has created legal basis for the formation and functioning of the urban cadastre and led to the activation of these processes in Ukraine.
Creating appropriate automated system must be integrated enterprise solution, which is based on modern geoinformation technologies with the creation of a central data repository (with the inclusion of a single system of information resources industry inventories, inventories urban district and municipal level, and another due to information legislation) and the definition unity of organizational, technical and technological principles of construction of geoinformation subsystems of different levels [1].
1. Theme urgency
2. Goal and tasks of the research
Purpose of the work is structured input data for the urban cadastre of local level and develop an algorithm to automate the process of filling the inventory data.
Main objectives of the study:
- Research the experience of developed countries in the conduct of the urban cadastre and automation.
- Design the algorithms to automate the process of filling the urban cadastre data.
- Design the program of automation with followed approbation.
Research object: town‑planning cadastre.
Research subject: database of urban cadastre.
Within the master’s work is planned to obtain program module of data filling the urban cadastre from documentation of urban planning, land management and other project for followed use during exploitation. The program module will be developed for ArcGIS 10.1.
For experimental evaluation the module will be used project, that was created in the ArcGIS program with a topographical survey of Kurakhovo and a corresponding set of attribute data.
3. Overview of Research and Design
With purpose to identify ways of effectively manage of data of urban cadastre, it was analysis the legislation of following countries:
- Republic Belarus;
- Russian Federation;
- United Kingdom.
3.1 The Urban cadastre of the Republic of Belarus
The Urban cadastre is one of the most important elements of information and legal support of the central and local authorities in the spatial planning and management of urban development activities. In Belarus, it is a unified tier system,that is appropriate of levels of government, and includes inventories: republican, regional (regions and Minsk) and local (cities, administrative districts and other territorial units) [2].
Unity of urban cadastre system of all territorial levels provided the same type of legal, regulatory and methodological base creation and maintenance of inventories. The Urban cadastre of each level contains a mandatory level, which inherent in this data set.
The Urban cadastre includes a digital map of the area, a database, that describing objects of cadastral registration, including database of registers and rolls (fig. 1).
With the help of digital topographic maps (terrain models) carried the territorial binding of attribute data for specific information items inventory.
Object composition of the inventory is determined in accordance with the Classification and composition data from the State Urban Cadastre
(KM 02250.01–98).
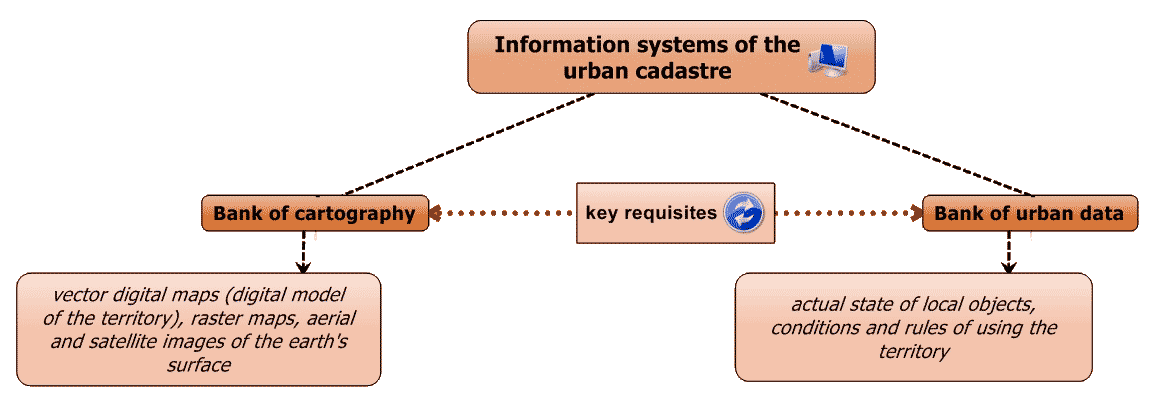
Figure 1 – Information systems of the urban cadastre territorial level
3.2 The Urban cadastre of the Russian Federation
State town–planning cadastre of the Russian Federation (RF) is a unified system of accounting, recording, storing and provide information about following territorial levels objects:
- Russian Federation;
- subject of the Russian Federation (republic, territory, region, city of federal importance, autonomous region and autonomous area);
- municipality (district or assimilated thereto unit, urban settlement, urban area or assimilated thereto unit group of rural settlements – rural district or assimilated thereto unit, rural settlement) [4].
Conducting the urban cadastre is based on the use of information and computer technologies. The information of urban cadastre whith computer organization consists of three main parts: a database (DB), cartographic information and information retrieval system (IRS) (fig. 2).

Figure 2 – Data of the urban cadastre of RF
(animation: 7 shot, 6 cycles of reiteration, 55 KB)
3.3 UK Planning System
In the UK such thing as a town‑planning cadastre not exist, instead there land–use planning system. This planning system is most clearly began to develop in 1947. It has several levels: state (national), regional and local levels (fig. 3).
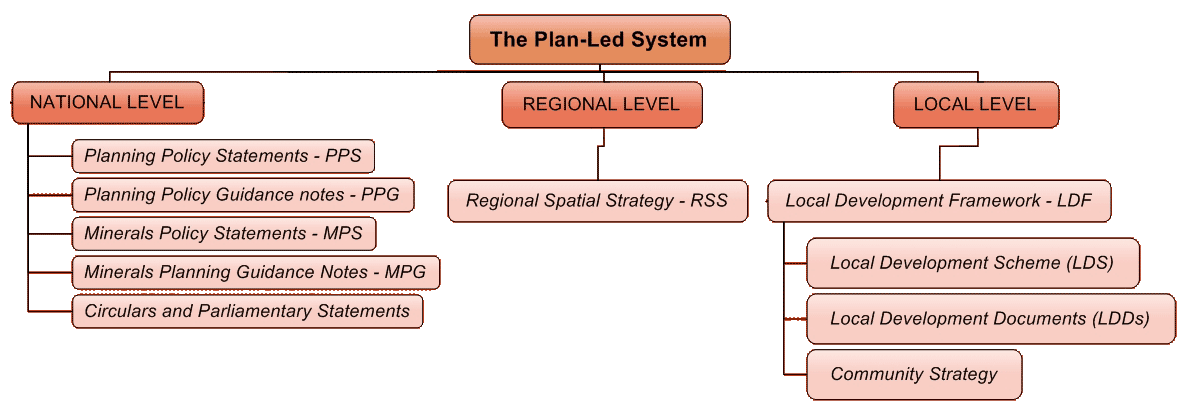
Figure 3 – The planning system in the UK
According to British experts, information base of land management in the UK is different from other European countries. Thus, they believe that if in Europe use planning, land evaluation, land management is based on the Land Registry, the UK Land Registry is no formal. Information about the nature of ownership of real estate, real estate and land use is managed by different organizations, respectively, at the Royal state land registration office, Management of real estate valuation and the Department of Environmental Protection [11].
Conclusion
Analysis experience creating inventory abroad shows that in the UK there is no analogue of the urban cadastre in our understanding. However, widespread system of solving problems recording and storing information on real estate, as well as planning restrictions and easements.
In the former Soviet Union (Russia, Belarus) town‑planning cadastre developed in forms close to the Ukrainian model. Further development of the urban cadastre in Ukraine should occur by ensuring flow of information about objects and Urban Development to ensure linkages with other information systems, which are both at the local and regional levels.
Implementing proper information policy for the needs of urban development activities, its technological support in accordance with the latest technology, the introduction of modern information systems processing and information display provides a wide range of automation tasks of managing the development of the territories at the local, regional and national levels through the implementation of computational problems and modeling systems in various areas of urban development activities.
Addressing these issues will enable significantly increase efficiency and quality issues related to urban development activities, to ensure sustainable development of the territories of Ukraine.
This master’s work is not completed yet. Final completion: January 2015. The full text of the work and materials on the topic can be obtained from the author or his head after this date.
References
- Ю. Палеха, Т. Нечаєва, В. Смілка. Містобудівний кадастр – інформаційна основа оновлення містобудівної документації у місті Києві. – 2012. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://irbis–nbuv.gov.ua... .
- Положение о порядке создания и ведения государственного градостроительного кадастра Республики Беларусь, мониторинга объектов архитектурной, градостроительной и строительной деятельности – утверждено Постановлением Совета Министров Республики Беларусь от 1 июня 2011 г. № 687. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://www.unece.org/... .
- Строительные нормы Республики Беларусь CНБ 3.01.02–98
Состав, содержание, порядок создания и ведения государственного градостроительного кадастра
, Приказ Министерства архитектуры и строительства РБ от 31.12.1998 № 437. - Постановление Правительства Российской Федерации от 29.07.1998 № 856
О ведении государственного градостроительного кадастра и мониторинга объектов градостроительной деятельности в Российской Федерации
. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://pravo.gov.ru... . - Строительные нормы и правила Российской Федерации 14‑01‑96
Основные положения создания и ведения градостроительного кадастра Российской Федерации
от 01.12.1996. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://www.stroybm.ru... . - Градостроительный Кодекс Российской Федерации от 29.12.2004 № 190–ФЗ. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://pravo.gov.ru... .
- Постановление Правительства Российской Федерации от 09.06.2006 № 363
Об информационном обеспечении градостроительной деятельности
. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://pravo.gov.ru... . - Информационные системы обеспечения градостроительной деятельности для муниципальных образований /Служба градостроительного кадастра города Москвы, ГУП
ИТЦ Москомархитектуры
– г. Москва, 2009 г. - А. А. Зенков (ИТП
Град
, Омск). Система требований как обязательное условие обеспечения качества документации. – 2009 – [Электронный ресурс] – http://www.gisa.ru/59933.html. - The Planning System: General Principles/Published by the Office of the Deputy Prime Minister. Printed in the UK, January 2005.
- Особенности планирования и организации использования земель в Великобритании. Нижневартовск, 2011. – [Электронный ресурс] – http://bibliofond.ru.
